
What is UX design and why it is important: UX short for User Experience design, has become a widely recognized term in the tech world. However, its meaning can sometimes get lost amidst the buzzwords commonly tossed around in startup environments. In essence, UX design encompasses all aspects of a product that users interact with, including websites, landing pages, the product itself, services, and community interactions.
Knowing what UX stands for is one thing, but truly understanding its intricacies is crucial for mastering the discipline. If you’re keen to dive deeper into what UX designers do, best practices, and how to start your journey in UX, read on.
Table of Content
What is User Experience (UX)?

User Experience (UX) design is the process of creating products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users. It involves a deep understanding of user needs, behaviors, and pain points, and aims to enhance the overall interaction between the user and the product. UX design isn’t just about making a product look good; it’s about ensuring that every touchpoint in the user’s journey is intuitive, accessible, and enjoyable.
For instance, consider a website with a seamless checkout process—this is a direct result of effective UX design.
User Experience (UX) is simply the interaction a user has with a product or service. This includes the product’s appearance, the user’s feelings and interactions with it, and how its elements affect the user. UX design is the process UX designers employ to ensure the product experience is smooth, intuitive, and enjoyable.
The primary goal of UX design is to create an experience that is intuitive, efficient, and relevant to the user. This involves understanding users’ needs, values, abilities, and limitations, along with the company’s business goals.
While aesthetics are important, the main focus of UX designers is to build user-friendly experiences, emphasizing empathy with users and creating products that guide them seamlessly from start to finish.
The Importance of UX
The importance of UX design cannot be overstated in today’s digital landscape. A well-designed user experience can significantly impact a business’s success by increasing user engagement, improving conversion rates, and reducing bounce rates. For example, an e-commerce site with easy navigation and a streamlined purchase process will likely see higher sales than one with a confusing interface. Moreover, good UX design helps build trust with users, making them more likely to return and recommend the product to others. In contrast, poor UX can lead to frustration, driving users away to competitors.
The prevalence of UX vacancies and its credit for substantial business successes underscore its importance. Companies like Airbnb and Land Rover attribute their significant growth to good UX. Elon Musk famously stated, “Any product that needs a manual is broken,” highlighting the necessity of intuitive design.
Donald Norman, who coined the term in the early 90s while at Apple, emphasized the importance of user empathy. Today, many tech companies prioritize UX investments, recognizing that placing the user first is essential for success.
What Does a UX Designer Do?
A UX designer’s role is multifaceted. It involves research, design, testing, and iteration. A UX designer start by conducting user research to understand the target audience’s needs and preferences. This research forms the foundation for designing user personas, wireframes, and prototypes. UX designers then work closely with UI designers and developers to bring the designs to life, ensuring that the final product aligns with user expectations. For instance, a UX designer working on a mobile app might conduct usability tests to identify issues and refine the app’s interface based on user feedback. This iterative process ensures that the product is both functional and user-friendly. Explore our in-depth article on the UX design process for more insights.
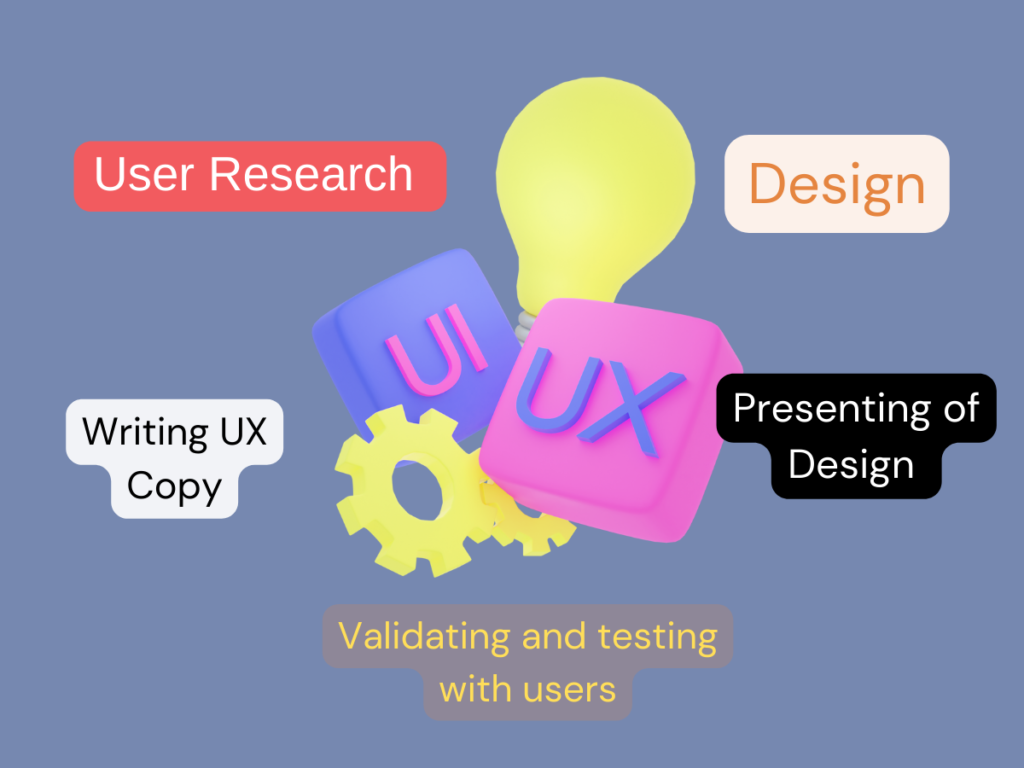
A UX designer’s role can vary widely, encompassing several fields such as interaction design, information architecture, visual design, usability, and human-computer interaction. UX designers conduct research, craft and design interfaces, generate UX copy, tests and validates with sample users, and introduce their designs to businesses. Here’s a closer look of what they do:
- User Research: To design a strong product, UX designers must understand the user’s needs, pain points, behaviours, and goals. They study the industry and competitors to identify opportunities and technical challenges.
- Design: Design in UX focuses on solving problems and connecting with users to enhance usability and accessibility. UX designers prioritize user needs over aesthetics, aiming for designs that offer the best user experience.
- Writing UX Copy: Clear and direct UX copy helps users navigate a product seamlessly. The content should match the actions users can take, to ensure they understand the functionality at every step.
- Validating and Testing with Users: User testing, often conducted in person, allows designers to observe user interactions and identify issues. Feedback and natural user reactions guide necessary adjustments.
- Presenting the Design to the Business: UX designers must present their ideas effectively to get them approved. They provide wireframes, prototypes, site maps, and other UX artefacts to move designs forward.
Principles of UX Design
Several key principles guide effective UX design. Firstly, usability is paramount—users should be able to accomplish their goals with ease and efficiency. Secondly, consistency is crucial in creating a cohesive experience across different platforms and devices. Thirdly, accessibility ensures that the product is usable by people with diverse abilities, such as those with visual impairments. Additionally, empathy is essential, as designers must understand and anticipate user needs and frustrations. For example, incorporating clear calls-to-action and minimizing loading times are practical applications of these principles.
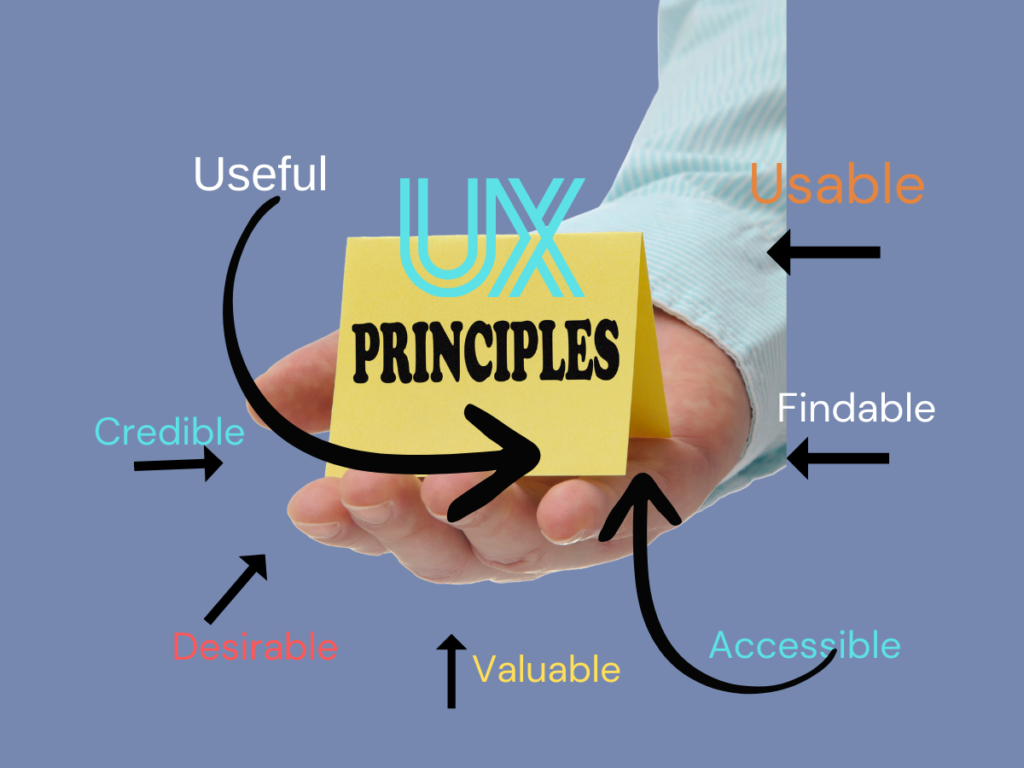
Peter Morville’s Honeycomb model outlines seven facets of UX: Useful, Usable, Findable, Credible, Desirable, Accessible, and Valuable. These principles ensure a comprehensive approach to UX design:
Useful: The product must fulfil a purpose, whether practical or entertainment-based.
Usable: The product should be efficient and intuitive to use, enhancing safety and comfort.
Findable: Easy navigation is crucial, especially for web-based products.
Credible: Trustworthiness is vital; users must believe in the product’s promises.
Desirable: Emotional design and branding create a strong user following.
Accessible: Products should cater to a wide range of abilities, making them easier for everyone to use.
Valuable: The product must offer value to both the business and the customer, balancing all other principles.
UX vs. Graphic Design vs. UI
Understanding the distinctions between UX design, graphic design, and UI design is crucial for anyone involved in the creation of digital products. Though they are often used interchangeably, each plays a unique role in the development process.
UX Design (User Experience Design) focuses on the overall feel of the product. It involves research, testing, and the development of wireframes and prototypes to ensure that the user’s journey is smooth, intuitive, and satisfying. UX designers prioritize functionality and usability, aiming to make the user’s interaction with the product as effortless as possible.
Graphic Design, on the other hand, is more concerned with the visual elements of the product. Graphic designers work on creating the product’s aesthetic, including logos, icons, typography, and color schemes. While UX designers focus on how a product works, graphic designers focus on how it looks. Their work is essential for creating a visually appealing interface that aligns with the brand’s identity.
UI Design (User Interface Design) bridges the gap between UX design and graphic design. UI designers are responsible for translating the UX designer’s wireframes into visually appealing interfaces that are easy to navigate. They focus on the layout of each page, button, and icon, ensuring the design is both functional and attractive. UI design is a point where visual design meets interaction design, bringing the product to life.
For example, when designing a mobile app, the UX designer would map out the user flow and ensure navigation is logical. The graphic designer would create the app’s visual identity, such as its colour palette and icons. The UI designer would then integrate these elements into the app, creating a cohesive and user-friendly interface. Understanding the differences between these roles is key to successful product development.
While these design roles are interconnected, they focus on different aspects of a product:
UX Designer: Focuses on the logic, structure, and functionality of a product. They build wireframes, prototypes, and site maps to ensure an optimal user experience.
Graphic Designer: Concentrates on the aesthetic elements, creating assets like logos, brochures, and icons using programs like Photoshop and Illustrator.
UI Designer: Works on the touchpoints of the product, including buttons and screen transitions, ensuring a pleasurable user interface.
Some Examples of Bad and Good UX
The impact of UX design on a product’s success can be illustrated through examples of bad and good UX design.
Bad UX Design: A common example of poor UX design is a website with a cluttered interface and confusing navigation. Imagine a website where the search bar is hidden, the links are not clearly labelled, and the checkout process requires multiple unnecessary steps. Users are likely to become frustrated and abandon the site, leading to a high bounce rate and lost sales. Another example is a mobile app with small, hard-to-tap buttons and inconsistent navigation, which can leave users confused and dissatisfied.
Good UX Design: On the flip side, a well-designed website or app prioritizes ease of use and intuitive navigation. A good UX design example is an e-commerce site with a clean layout, a visible and easy-to-use search bar, and a streamlined checkout process that allows users to complete purchases in just a few clicks. Another example is a mobile banking app that offers clear instructions, a simple interface, and fast, reliable transactions, leading to high user satisfaction and repeat usage.
One well-known example of excellent UX design is Apple’s product ecosystem. Apple products are known for their intuitive design, consistent user experience across devices, and attention to detail. Whether you’re using an iPhone, iPad, or MacBook, the experience feels seamless and familiar, which is a testament to the power of good UX design.
These examples highlight the importance of UX design in creating products that attract users and keep them engaged and satisfied. Investing in good UX design can make the difference between a product that fails and one that thrives in a competitive market.
Bad UX Example 1: A visually appealing product with unclear functionality.
Bad UX Example 2: Drop-down menus that are excessively long.
Good UX Example 1: Duolingo’s onboarding process.
Good UX Example 2: Amazon Prime’s 1-click purchase tool.
Why Is UX Design Important
Here are seven arguments for why UX design is important:
1. Improves User Satisfaction
A well-designed user experience (UX) significantly boosts user satisfaction by making interactions with a product or service more intuitive and enjoyable. For example, Airbnb invested heavily in UX research to better understand their users’ needs. They simplify their booking process and enhance search filters, and ultimately improve user satisfaction, resulting in higher booking rates and customer retention.
2. Increases Conversion Rates
Effective UX design can lead to higher conversion rates, as users are more likely to complete desired actions when the process is smooth and straightforward. Amazon is a prime example of this. By optimizing their checkout process, including the introduction of the one-click purchase button, Amazon reduced cart abandonment rates and increased conversions, which significantly contributed to their success.
3. Reduces Development Costs
Investing in UX design early in the development process can save time and money by reducing the need for costly redesigns and fixes later on. For instance, IBM found that every dollar invested in UX design brought a return of $100, largely due to reduced development costs and increased sales. This demonstrates that good UX design is not just beneficial for users but also for a company’s bottom line.
4. Enhances Brand Loyalty
A positive user experience can foster brand loyalty, as users are more likely to return to a product or service they find easy and enjoyable to use. Apple has consistently demonstrated this with its products. The seamless and user-friendly design across all Apple devices has created a strong, loyal customer base that often chooses Apple products over competitors, even when they are more expensive.
5. Boosts Accessibility
UX design plays a crucial role in making products accessible to a wider audience, including people with disabilities. For example, Microsoft has focused on inclusive design by incorporating accessibility features into their products, such as voice recognition and screen readers. This approach has not only made their products more usable for people with disabilities but has also opened up new markets and increased customer satisfaction.
6. Improves User Retention
Good UX design can help retain users by ensuring they have a positive and engaging experience. Duolingo, the popular language learning app, excels in user retention through its gamified UX design. By making the learning process fun and rewarding, Duolingo keeps users coming back, which has helped it maintain a strong user base and grow steadily over time.
7. Provides a Competitive Advantage
In a crowded market, excellent UX design can be a key differentiator that sets a product or service apart from the competition. Slack, the team collaboration tool, gained a competitive edge by prioritizing UX design. Its clean interface, intuitive navigation, and seamless integration with other tools made it the go-to choice for teams, helping Slack dominate the market despite the presence of larger, more established competitors.
Here Is How You Can Start Learning UX Design
To begin your UX journey, focus on understanding user needs, learning design principles, and practising usability testing. Explore various tools and methods, and continually seek feedback to refine your skills.
Embracing these concepts and practices can help you to start creating user experiences that are functional, delightful and valuable.
LEARN MORE ABOUT UX DESIGN
Here are my recommended links for more articles on UX design:
- This comprehensive guide covers everything from the basics of UX design to advanced topics, offering a deep dive into the field.
This article by the Nielsen Norman Group provides a thorough understanding of UX design principles and best practices, with practical insights for beginners and experienced designers.
You may also want to read Top 12 Freelancer Web Design Tips
FAQS About UX Design

1. What is UX Design?
Answer: UX design, or User Experience design, is the process of creating products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users. This involves the design of the entire process of acquiring and integrating the product, including aspects of branding, design, usability, and function. A well-crafted UX design ensures that users find value in what you’re providing, making their interaction with the product seamless and enjoyable.
2. How Does UX Design Differ from UI Design?
Answer: UX design focuses on the overall experience a user has with a product or service, including ease of use, efficiency, and satisfaction. UI (User Interface) design, on the other hand, is concerned with the look and feel, presentation, and interactivity of a product’s interface. While UI design deals with the surface-level details like colors, typography, and buttons, UX design encompasses the entire journey from start to finish, ensuring the user’s needs are met.
3. Why is UX Design Important for My Business?
Answer: UX design is crucial for your business because it directly impacts customer satisfaction, retention, and conversion rates. A well-designed user experience can lead to higher customer loyalty, lower bounce rates, and better overall performance of your website or app. By investing in UX design, you can create a product that meets user needs effectively, ultimately driving business growth.
4. What Does a UX Designer Do?
Answer: A UX designer is responsible for researching, designing, and implementing user experiences that are functional, intuitive, and enjoyable. This includes conducting user research, creating user personas, wireframing, prototyping, and testing designs. They work closely with developers, product managers, and other stakeholders to ensure that the end product aligns with both user expectations and business goals.
5. Can Good UX Design Improve My Website’s SEO?
Answer: Yes, good UX design can significantly improve your website’s SEO. Search engines like Google consider user experience signals, such as page load time, mobile responsiveness, and ease of navigation, when ranking websites. By providing a positive user experience, you increase the likelihood of higher engagement, longer dwell time, and lower bounce rates—all of which can positively influence your SEO rankings.
6. How Do I Measure the Success of UX Design?
Answer: The success of UX design can be measured through various metrics, including user satisfaction surveys, usability testing, task completion rates, and user engagement statistics like time on site and conversion rates. Tools like Google Analytics, Hotjar, and user feedback platforms can provide valuable insights into how users interact with your product, allowing you to refine and improve the user experience.
7. What Are the Key Principles of UX Design?
Answer: The key principles of UX design include usability, accessibility, simplicity, consistency, and user-centricity. These principles guide designers in creating experiences that are easy to use, accessible to all users, and aligned with the users’ needs and expectations. By adhering to these principles, designers can create products that are not only functional but also delightful to use.
8. How Long Does It Take to Develop a Good UX Design?
Answer: The time it takes to develop a good UX design depends on the complexity of the project, the amount of user research needed, and the level of detail required in the design process. For a simple website, it might take a few weeks, while more complex applications or systems could take several months. It’s important to allocate sufficient time for research, testing, and iterations to ensure the final design meets user needs effectively.
9. Do I Need a UX Designer for My Small Business Website?
Answer: Yes, even small businesses can benefit from having a UX designer involved in the development of their website. A UX designer can help ensure that your website is user-friendly, accessible, and designed to convert visitors into customers. This can lead to better customer satisfaction, higher engagement, and ultimately, more sales or leads for your business.
10. What Are Some Common UX Design Mistakes to Avoid?
Answer: Common UX design mistakes include ignoring user feedback, overcomplicating the design, neglecting mobile users, and failing to test the design with real users. Another frequent mistake is prioritizing aesthetics over functionality, which can lead to a beautiful design that’s difficult to use. Avoiding these pitfalls can help ensure your product provides a positive user experience.


3 Comments
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
проверить провайдеров по адресу самара
domashij-internet-samara006.ru
провайдер по адресу самара
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://x-vavada.ru Vavada – эксклюзивный обзор казино: честные отзывы о выплатах, секретные бонус-коды. Только проверенная информация о лицензии Кюрасао и слотах с высокой отдачей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пребывание в стационаре обеспечивает круглосуточный мониторинг состояния, своевременное введение лекарств и защиту пациента от внешних факторов, провоцирующих срыв. Все палаты оснащены необходимым оборудованием, соблюдаются санитарные нормы, а условия размещения соответствуют медицинским стандартам.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]наркологическая клиника ярославль.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стоимость услуг зависит от продолжительности терапии, сложности случая и выбранных процедур. Однако клиника предоставляет гибкую систему оплаты, включая рассрочку и страховое покрытие.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены рязань[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного вмешательства. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что позволяет оперативно снизить концентрацию токсинов в крови и восстановить нормальные обменные процессы. Этот этап критически важен для стабилизации работы внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод рязань[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
мистические места Лучшие мистические произведения – это те, которые не только пугают, но и заставляют задуматься о смысле жизни, о природе добра и зла, о границах человеческого познания. Они оставляют после себя долгое послевкусие и заставляют переосмыслить свое отношение к миру.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При остром алкогольном отравлении появляются головокружение, рвота, сильная слабость, скачки давления, нарушение дыхания, обмороки и судороги. Это сигнал о том, что организм не справляется с интоксикацией, и без срочного медицинского вмешательства возможны опасные осложнения, вплоть до комы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk00.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom novokuznetsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Метод лечения
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/lechenie-narkomanii-czena-vladimir/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
grunge Metalcore: Металкор – это сплав агрессии метала и мелодичности хардкора. Тяжелые риффы, гроулинг и скриминг сочетаются с чистым вокалом и запоминающимися припевами. Это музыкальная ярость, которая выражает протест и энергию.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1win app download apk 1win3025.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://пф-яндекс.рф/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Электросчетчик с пультом Счетчики с пультом: Как экономить, не нарушая закон?
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://creditka.org.ua/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает заведующая отделением клинической психологии ФГБУН «НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии» Минздрава России, наличие в команде специалистов с опытом работы в области зависимости — это основа качественной помощи.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/platnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-nizhnem-tagile
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for the good writeup. It in truth was once a leisure account it. Glance complex to more delivered agreeable from you! By the way, how could we keep in touch?
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов нарколога на дом недорого – это комфортное и целесообразное решение для людей, столкнувшихся с проблемами зависимости. Часто такие люди стесняются обращаться в клиники и предпочитают анонимное лечение. На сайте vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk002.ru можно найти информацию о доступных услугах выездного нарколога, который предложит консультацию нарколога и экспертную поддержку. Недорогие услуги нарколога, такие как помощь в борьбе с наркоманией и алкоголизмом, обеспечивают возможность получения медицинской помощи на дому. Психологическая поддержка и реабилитационные программы проводятся квалифицированными специалистами, что гарантирует безопасность и конфиденциальность. Обратитесь к дешёвому наркологу для избавления от зависимости и начните путь к выздоровлению вместе с поддержкой специалистов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar001.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой – это опасная стадия! В Волгоградской области нарколог поможет круглосуточно! Мы всегда на связи, чтобы помочь вам справиться с запоем. Мы предлагаем быстрое, безопасное и индивидуальное лечение. Наша служба вывода из запоя работает четко и без сбоев. Мы предлагаем детоксикацию и стабилизацию состояния в любом месте. Мы начинаем с диагностики, чтобы понять, как лучше вам помочь.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя дешево волгоград[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает заведующий отделением наркологии Владимирского областного клинического диспансера, «только комплексная модель, включающая медикаментозную поддержку и психотерапию, даёт устойчивый эффект». Это означает, что в штате клиники должны быть не только врачи, но и психотерапевты, социальные работники, реабилитологи.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/]наркологическое лечение наркомания[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
провайдеры интернета по адресу самара
domashij-internet-samara005.ru
проверить интернет по адресу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой может быть не только физически тяжёлым, но и психологически разрушительным. Поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за помощью. Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — это необходимая медицинская процедура, которая помогает победить алкогольную зависимость и восстановить здоровье. Мы в клинике «АнтиЗависимость» предлагаем круглосуточную помощь в комфортных условиях — на дому или в стационаре.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Игнорирование этих симптомов или попытки самолечения могут привести к серьезным осложнениям. Своевременная установка капельницы на дому позволяет быстро улучшить состояние пациента и минимизировать последствия запоя.
Разобраться лучше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-nizhniy-novgorod0.ru/vyzvat-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya-nizhnij-novgorod/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В клинике применяются доказательные методы лечения, соответствующие международным и российским рекомендациям. Основу составляет медикаментозная детоксикация, сопровождаемая психотерапией, когнитивно-поведенческой коррекцией, а также семейной консультацией. При необходимости применяются пролонгированные препараты, облегчающие контроль над тягой к веществу.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-klinika-pomoshh-v-yaroslavle/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
запчасти для гидромассажных ванн Колесики для душевой кабины: восстановление функциональности
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного вмешательства. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что позволяет оперативно снизить концентрацию токсинов в крови и восстановить нормальные обменные процессы. Этот этап критически важен для стабилизации работы внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в рязани[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Одним из ключевых направлений является проведение капельниц, призванных вывести токсины из организма и нормализовать водно-электролитный баланс. Используемые препараты и состав растворов подбираются индивидуально, исходя из клинической картины и истории болезни пациента.
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-yaroslavle/https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой – это состояние, когда организм требует постоянного поступления алкоголя для нормальной работы. Запой вызывает накопление вредных веществ, что негативно влияет на органы и иммунную систему. Не пытайтесь самостоятельно избавиться от запоя, это может навредить. Получите квалифицированную помощь на дому от клиники «Семья и Здоровье». Мы быстро приедем и окажем круглосуточную поддержку при запое. Длительное употребление алкоголя опасно для здоровья и жизни. Не ждите, пока станет слишком поздно, обратитесь за помощью при запое!
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]вывод из запоя цены на дому красноярск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эффективное лечение требует поэтапного подхода, который реализуется следующим образом:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда запой становится угрозой для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится ключевым для спасения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных осложнений. В Рязани вызов нарколога на дом позволяет начать лечение в самые критические моменты, обеспечивая детоксикацию организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования в условиях, где пациент чувствует себя комфортно и сохраняет свою конфиденциальность. Этот формат оказания медицинской помощи особенно актуален для тех, кто хочет избежать длительного ожидания в стационаре и предпочитает лечение в привычной домашней обстановке.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно рязань[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это не просто многодневное пьянство, а проявление зависимости, при котором каждое утро начинается с новой дозы спиртного. Организм человека уже не способен самостоятельно справляться с последствиями переработки этанола, и любое промедление ведёт к нарастанию тяжёлой интоксикации. Даже при резком прекращении употребления алкоголя последствия могут быть непредсказуемыми: от судорожных припадков до алкогольного психоза.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Рефрижераторные перевозки https://agrohimija.ru/novosti/51496-pochemu-temperaturnyy-rezhim-kritichen-dlya-refrizheratornyh-perevozok.html по России и СНГ. Контроль температуры от -25°C до +25°C, современные машины, отслеживание груза.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
макросы варфейс Устали от отдачи в Warface? Попробуйте макросы на варфейс блади! Это простой способ улучшить свою стрельбу и стать настоящим профи. Получите преимущество в игре прямо сейчас!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
завьялов илья поинт пей Как Илья Завьялов Построил Успешный Бизнес в Point Pay
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для оценки уровня учреждения важно понимать, какие конкретно методики в нём используются. Ниже приведён обобщённый обзор подходов в современных наркологических клиниках региона:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/]лечение наркомании владимирская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш агрегатор – beautyplaces.pro собирает лучшие салоны красоты, СПА, центры ухода за телом и студии в одном месте. Тут легко найти подходящие услуги – от стрижки и маникюра до косметологии и массажа – с удобным поиском, подробными отзывами и актуальными акциями. Забронируйте визит за пару кликов https://beautyplaces.pro/irkutsk/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная зависимость – это значительная трудность, с которой имеют дело большое количество людей в Красноярске . Психологическая поддержка имеет огромное значение в лечении алкоголизма . Медицинские учреждения предлагают программы детоксикации и реабилитацию зависимых , что включает в себя не только медицинское, но и психологическое сопровождение . вывод из запоя цена Поддержка семьи также важна , поскольку она способствует созданию доверительной атмосферы. Признаки зависимости могут проявляться по-разному , и раннее обращение за помощью в случае запоя способно изменить жизнь к лучшему. Советы по отказу от алкоголя включают в себя поиске новых увлечений и замене вредных привычек на более здоровые. Необходимо помнить, что обращение за помощью – это первый шаг к выздоровлению .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш агрегатор – beautyplaces.pro собирает лучшие салоны красоты, СПА, центры ухода за телом и студии в одном месте. Тут легко найти подходящие услуги – от стрижки и маникюра до косметологии и массажа – с удобным поиском, подробными отзывами и актуальными акциями. Забронируйте визит за пару кликов https://beautyplaces.pro/category/salon-brovej-i-resnicz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интернет по адресу самара
domashij-internet-samara004.ru
узнать интернет по адресу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Москве приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga006.ru
лечение запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного вмешательства. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что позволяет оперативно снизить концентрацию токсинов в крови и восстановить нормальные обменные процессы. Этот этап критически важен для стабилизации работы внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Разобраться лучше – https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-ryazan/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Своевременное вмешательство позволяет снизить концентрацию токсинов, нормализовать обмен веществ и предотвратить необратимые повреждения, что делает срочный вызов нарколога на дому жизненно необходимым.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno rjazan'[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь на дому становится всё более востребованной благодаря своей доступности, конфиденциальности и эффективности. Клиника «МедТрезвость» предлагает пациентам целый ряд важных преимуществ:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в санкт-петербурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Метод лечения
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/]центр лечения наркомании[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
See more here https://Malut-United-FC.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вся процедура проходит под полным контролем врача и занимает от 40 минут до 2 часов. Пациенту и его родственникам даются рекомендации по дальнейшему лечению и профилактике повторных запоев.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-anonimno-msk/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — опасное состояние, которое стремительно приводит к тяжелым последствиям для организма. Обычные домашние методы восстановления при алкогольной интоксикации не только малоэффективны, но и небезопасны. Для быстрого и безопасного выведения токсинов требуется профессиональная помощь нарколога с применением капельницы от запоя.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva000.ru/]капельница от запоя наркология москва[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
завьялов илья поинт пей Point Pay: Безопасность и Надежность под Руководством Ильи Завьялова
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проблемы, связанные с употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ, могут застать человека врасплох и требовать немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В Туле предоставляется наркологическая помощь, направленная на купирование острых состояний и оказание поддержки пациентам в кризисной ситуации. В клинике «Здоровье+» используются современные методы лечения, основанные на отечественных клинических рекомендациях, с акцентом на безопасность и индивидуальный подход.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]наркологическая помощь тула[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
рулонные шторы блэкаут пятигорск Шторы Пятигорск: Изысканность и уют в вашем доме Пятигорск – город, славящийся своей красотой и гостеприимством. И, конечно же, каждый житель стремится создать в своем доме атмосферу комфорта и уюта. Шторы играют в этом важную роль, добавляя изысканности и завершенности интерьеру.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Первый и самый важный момент — какие методики применяются в клинике. Качественное лечение наркозависимости включает несколько этапов: детоксикация, стабилизация состояния, психотерапия, ресоциализация. Одного лишь выведения токсинов из организма недостаточно — без проработки психологических причин употребления высокий риск рецидива.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/]наркологическое лечение наркомания владимир[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге начинается с детального осмотра и оценки состояния пациента. Врач измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и определяет степень интоксикации.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar005.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь «ТюменьМед» не ограничивается только физической детоксикацией. В состав команды входят психологи и социальные работники, которые проводят мотивационные беседы, обучают навыкам самоконтроля и оказывают помощь в планировании досуга и социальных активностей после детоксикации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/]наркологическая клиника тюмень.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
смеситель для душевой кабины купить в екатеринбурге Душевая кабина запчасти ролики: замена и установка
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед началом терапии врач собирает анамнез, оценивает состояние органов-мишеней (печень, почки, сердце), проводит лабораторные тесты на уровень электролитов и маркёры цирроза. Результаты обследования играют ключевую роль при выборе схемы инфузий и психотерапевтических методик.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На этом этапе врач детально выясняет, как долго продолжается запой, какие симптомы наблюдаются, и имеются ли сопутствующие заболевания. Точный анализ информации помогает оперативно определить степень интоксикации и подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации, что является ключом к предотвращению дальнейших осложнений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в рязани[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости требуют незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства. Длительные запои или острое отравление могут привести к тяжелым осложнениям и серьезным проблемам со здоровьем. Клиника «МедТрезвость» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает квалифицированную наркологическую помощь прямо на дому, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность пациента. Наши специалисты оперативно выезжают по адресу, проводят все необходимые процедуры и помогают максимально быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента в комфортных домашних условиях.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/psikhiatr-narkolog-na-dom-spb
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Специалист уточняет, сколько времени продолжается запой, какой тип алкоголя употребляется, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Тщательный анализ этих данных помогает определить оптимальные методы детоксикации и скорректировать терапевтическую стратегию для минимизации риска осложнений.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод рязань[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
подключить проводной интернет ростов
domashij-internet-rostov006.ru
подключить домашний интернет в ростове
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После вызова врач клиники «ЗдравЦентр» прибывает к пациенту в течение 30–60 минут. Он проводит первичный осмотр, оценивает степень тяжести алкогольной интоксикации, измеряет пульс, давление, уровень кислорода и другие показатели здоровья. На основании этих данных составляется индивидуальный план лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva00.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому в москве[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Москве — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru/]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya moskva[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga005.ru
лечение запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Метод лечения
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова врач наркологической клиники «МедАльянс» прибывает на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Сначала специалист оценивает общее состояние пациента, измеряет давление, уровень кислорода в крови и уточняет детали анамнеза.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva000.ru/]после капельницы от запоя в москве[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как поясняет медицинский психолог Елена Мусатова, «пациенту важно доверять специалисту, понимать его подход и чувствовать профессиональную уверенность ещё на этапе первичного осмотра».
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в первоуральске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Removing eraser clothes from images is an advanced tool for creative tasks. Neural networks, accurate generation, confidentiality. For legal and professional use only.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Профессиональная https://narkologicheskaya-klinika43.ru. Лечение зависимостей, капельницы, вывод из запоя, реабилитация. Анонимно, круглосуточно, с поддержкой врачей и психологов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Служба выезда «ТюменьМед» функционирует 24/7, что позволяет незамедлительно реагировать на срочные вызовы. В распоряжении клиники — собственный автопарк с санитарными машинами, оснащёнными всем необходимым для проведения инфузионной терапии на дому. При экстренном вызове врач прибывает к пациенту в пределах города в течение 30–60 минут.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сразу после поступления вызова специалист прибывает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра. На данном этапе нарколог:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]нарколог на дом рязань.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости требуют незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства. Длительные запои или острое отравление могут привести к тяжелым осложнениям и серьезным проблемам со здоровьем. Клиника «МедТрезвость» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает квалифицированную наркологическую помощь прямо на дому, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность пациента. Наши специалисты оперативно выезжают по адресу, проводят все необходимые процедуры и помогают максимально быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента в комфортных домашних условиях.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]narkolog-na-dom sankt-peterburg[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar004.ru
вывод из запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
макросы для мышки x7 варфейс бесплатно скачать Сделайте свою игру в Warface незабываемой с помощью макросы варфейс! Забудьте о сложных настройках и наслаждайтесь точной стрельбой. Доминируйте на поле боя и покажите всем, кто здесь лучший!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
завьялов илья поинт пей Завьялов Илья: Путь к Успеху и Роль в Point Pay
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Борьба с наркотической зависимостью требует системного подхода и участия опытных специалистов. Важно понимать, что лечение наркомании — это не только снятие ломки, но и длительная психотерапия, обучение новым моделям поведения, работа с семьёй. Согласно рекомендациям Минздрава РФ, наиболее стабильные результаты достигаются при прохождении курса реабилитации под наблюдением профессиональной команды в специализированном центре.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма в владимире[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в круглосуточном наблюдении, могут пройти курс терапии в стационаре. Обстановка клиники рассчитана на комфортное пребывание: палаты с индивидуальным санитарным блоком, охрана, контроль приёма препаратов, поддержка психологов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь тула[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
где в пятигорске можно купить жалюзи шторы Рулонные шторы Пятигорск купить: Просто и удобно Купить рулонные шторы в Пятигорске стало еще проще! Многие магазины предлагают онлайн-заказ с доставкой на дом, что экономит ваше время и силы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После вызова врач клиники «ЗдравЦентр» прибывает к пациенту в течение 30–60 минут. Он проводит первичный осмотр, оценивает степень тяжести алкогольной интоксикации, измеряет пульс, давление, уровень кислорода и другие показатели здоровья. На основании этих данных составляется индивидуальный план лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva00.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге начинается с детального осмотра и оценки состояния пациента. Врач измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и определяет степень интоксикации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В условиях стационара или на дневном стационаре применяются сбалансированные инфузионные растворы, витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для поддержки печени. Цель — минимизировать интоксикацию и предотвратить осложнения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-tyumen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
домашний интернет в ростове
domashij-internet-rostov005.ru
домашний интернет ростов
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного вмешательства. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что позволяет оперативно снизить концентрацию токсинов в крови и восстановить нормальные обменные процессы. Этот этап критически важен для стабилизации работы внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом рязань[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
go to the site https://petitedanse.com.br
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
visit the site https://lmc896.org
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
экстренный вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Установка и ремонт москитных сеток в Алматы Компания “Okna Service” в Алматы предлагает комплексные услуги по ремонту пластиковых окон, применяя исключительно материалы премиум-класса. В спектр услуг входит установка высококачественных уплотнителей, обеспечивающих идеальную герметичность и защиту от сквозняков, а также замена специализированной фурнитуры, такой как ручки и петли для различных систем открывания. Также осуществляется ремонт и замена москитных сеток, подверженных повреждениям и деформациям. Для повышения удобства эксплуатации окон специалисты “Okna Service” предлагают установку дополнительных устройств: доводчиков для дверей, ограничителей открывания (особенно актуально для семей с детьми) и монтаж пластиковых откосов внутри и снаружи помещения, улучшающих внешний вид окон. В сервисном центре в Алматы можно заказать и приобрести все необходимые комплектующие для ремонта окон, с их последующей доставкой и квалифицированной установкой. Подбор материалов осуществляется с учетом особенностей каждой оконной конструкции, что гарантирует надежность и долговечность ремонта. Замена изношенных элементов способствует восстановлению первоначальных характеристик окна, обеспечивая теплосбережение и комфорт в доме.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Метод лечения
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/]центр лечения наркомании[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для каждого пациента используется индивидуальный монитор жизненно важных функций, передающий данные врачу в клинике через защищённый канал связи. Это обеспечивает безопасность при лечении как лёгких, так и тяжёлых форм интоксикации, снижая вероятность осложнений.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог тюмень[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сразу после поступления вызова специалист прибывает на дом для проведения первичного осмотра. На данном этапе нарколог:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/]запой нарколог на дом рязань[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости требуют незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства. Длительные запои или острое отравление могут привести к тяжелым осложнениям и серьезным проблемам со здоровьем. Клиника «МедТрезвость» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает квалифицированную наркологическую помощь прямо на дому, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность пациента. Наши специалисты оперативно выезжают по адресу, проводят все необходимые процедуры и помогают максимально быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента в комфортных домашних условиях.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение запоя краснодар
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar003.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Москве приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому в Москве[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
завьялов илья поинт пей PointPay с Ильей Завьяловым: Развитие партнерской сети и расширение глобального присутствия
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — опасное состояние, которое стремительно приводит к тяжелым последствиям для организма. Обычные домашние методы восстановления при алкогольной интоксикации не только малоэффективны, но и небезопасны. Для быстрого и безопасного выведения токсинов требуется профессиональная помощь нарколога с применением капельницы от запоя.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva000.ru/]капельница от запоя вызов в москве[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стандартная процедура включает внутривенное введение растворов, которые эффективно выводят токсины, восстанавливают электролитный баланс и устраняют обезвоживание. Дополнительно врач назначает медикаменты для защиты сердца, печени и нервной системы, а также, при необходимости, седативные препараты для стабилизации психического состояния.
Углубиться в тему – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь может понадобиться в разных ситуациях — от тяжёлой алкогольной интоксикации до абстинентного синдрома при отказе от наркотиков. Своевременное обращение за помощью снижает риски для жизни и здоровья, а также упрощает последующую терапию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Метод лечения
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/]лечение наркомании владимир.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Давно слежу за этой темой, хочу поделиться находкой:
Между прочим, если вас интересует raregreen.ru, посмотрите сюда.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://raregreen.ru]https://raregreen.ru[/url]
Пишите, что у вас получилось.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
как установить макрос на варфейс Надоело проигрывать в Warface? Пора использовать макросы варфейс! Они увеличат вашу точность, упростят контроль отдачи и дадут вам преимущество над соперниками. Начните побеждать уже сегодня!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интернет провайдеры ростов
domashij-internet-rostov004.ru
домашний интернет в ростове
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk003.ru
лечение запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов врача-нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге начинается с детального осмотра и оценки состояния пациента. Врач измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови и определяет степень интоксикации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь может понадобиться в разных ситуациях — от тяжёлой алкогольной интоксикации до абстинентного синдрома при отказе от наркотиков. Своевременное обращение за помощью снижает риски для жизни и здоровья, а также упрощает последующую терапию.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь тула[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Возможные признаки
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tula10.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врач индивидуально подбирает:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает заведующий отделением наркологии Владимирского областного клинического диспансера, «только комплексная модель, включающая медикаментозную поддержку и психотерапию, даёт устойчивый эффект». Это означает, что в штате клиники должны быть не только врачи, но и психотерапевты, социальные работники, реабилитологи.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/]анонимное лечение наркомании[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждая выездная бригада укомплектована портативным лабораторным оборудованием для экспресс-анализов крови и мочи, современными инфузионными насосами и средствами телеметрии. Это позволяет врачу контролировать жизненно важные параметры пациента в режиме реального времени и корректировать схему детоксикации на месте.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в тюмени[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Специалист уточняет, сколько времени продолжается запой, какой тип алкоголя употребляется, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Тщательный анализ этих данных помогает определить оптимальные методы детоксикации и скорректировать терапевтическую стратегию для минимизации риска осложнений.
Подробнее тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-ryazan/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда запой становится угрозой для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится ключевым для спасения здоровья и предотвращения серьезных осложнений. В Рязани вызов нарколога на дом позволяет начать лечение в самые критические моменты, обеспечивая детоксикацию организма и восстановление его нормального функционирования в условиях, где пациент чувствует себя комфортно и сохраняет свою конфиденциальность. Этот формат оказания медицинской помощи особенно актуален для тех, кто хочет избежать длительного ожидания в стационаре и предпочитает лечение в привычной домашней обстановке.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-ryazan/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости требуют незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства. Длительные запои или острое отравление могут привести к тяжелым осложнениям и серьезным проблемам со здоровьем. Клиника «МедТрезвость» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает квалифицированную наркологическую помощь прямо на дому, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность пациента. Наши специалисты оперативно выезжают по адресу, проводят все необходимые процедуры и помогают максимально быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента в комфортных домашних условиях.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar002.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Профессиональная клиника никогда не скрывает информацию о своих сотрудниках. На официальных сайтах нередко размещены сканы дипломов, сведения о специализации и стаже, участие в отраслевых конференциях и проектах Минздрава.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-pervouralske/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
visit the site online https://justicelanow.org
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
best site online https://penzo.cz
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Разобраться лучше – https://bloc.xarxa-omnia.org/rierabonet/2014/05/21/que-es-per-a-mi-internet/internet6
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
подключить интернет
domashij-internet-perm006.ru
тарифы интернет и телевидение пермь
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
гайнулин эмиль нилович Эмиль Гайнулин: личный бренд в Telegram. История успеха, принципы работы и вдохновляющие советы для тех, кто хочет создать свой прибыльный канал.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
interesting and new https://fgvjr.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
the best and interesting https://edicionesdelau.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Выяснить больше – https://yadunewsnation.in/nation/10536
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Выяснить больше – https://www.certificadogas.com/hola-mundo
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы сосредоточимся на интересных аспектах одной из самых актуальных тем современности. Совмещая факты и мнения экспертов, мы создадим полное представление о предмете, которое будет полезно как новичкам, так и тем, кто глубоко изучает вопрос.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://umis.fr/produit/stethoscopes
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vistoweekly.com/nasdaq-fintechzoom
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот обзорный материал предоставляет информационно насыщенные данные, касающиеся актуальных тем. Мы стремимся сделать информацию доступной и структурированной, чтобы читатели могли легко ориентироваться в наших выводах. Познайте новое с нашим обзором!
Углубиться в тему – https://fisioterapia-alcala126.com/20-anos-centro-fisioterapia-alcala
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья сочетает познавательный и занимательный контент, что делает ее идеальной для любителей глубоких исследований. Мы рассмотрим увлекательные аспекты различных тем и предоставим вам новые знания, которые могут оказаться полезными в будущем.
Подробнее – http://www.gliaaesthetics.co.uk/podcasts-for-everyday-english-2
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья для ознакомления предлагает читателям общее представление об актуальной теме. Мы стремимся представить ключевые факты и идеи, которые помогут читателям получить представление о предмете и решить, стоит ли углубляться в изучение.
Разобраться лучше – https://optionfootball.net/other-spread-gun-formations/spread-gun-trips
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Грузоперевозки Луганск Грузоперевозки Луганск: Страхование грузов. Защита вашего груза от любых рисков. Спокойствие и уверенность.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar001.ru
вывод из запоя краснодар
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить iphone спб купить iphone спб .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk002.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Узнать больше – https://iartfivas.it/5-amazing-glitter-artists-to-find-at-a-festival
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://socalais-athletisme.fr/how-i-made-200-new-friends-in-one-year
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Углубиться в тему – https://help.myshopkit.app/en/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интернет провайдеры пермь
domashij-internet-perm005.ru
подключение интернета пермь
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После вызова врач клиники «ЗдравЦентр» прибывает к пациенту в течение 30–60 минут. Он проводит первичный осмотр, оценивает степень тяжести алкогольной интоксикации, измеряет пульс, давление, уровень кислорода и другие показатели здоровья. На основании этих данных составляется индивидуальный план лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva00.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя москва[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «МедАльянс» оказывает профессиональную медицинскую помощь на дому в Москве и Московской области круглосуточно. Опытные врачи-наркологи приедут в течение часа после вызова, проведут полную диагностику, поставят капельницу и быстро вернут пациента в стабильное состояние.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva000.ru/]после капельницы от запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Критерий
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Грузоперевозки Луганск Перевозка мебели Луганск: Аккуратная и бережная перевозка мебели любой конфигурации.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga006.ru
вывод из запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сессия с психологом Женская энергия – источник силы, творчества и интуиции, который необходимо раскрывать и поддерживать.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как эфирные масла помогают в проработке страхов Применение эфирных масел в повседневной жизни. Ароматизация воздуха, массаж, добавление в косметику – множество способов использования.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk001.ru
лечение запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова врач наркологической клиники «МедАльянс» прибывает на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Сначала специалист оценивает общее состояние пациента, измеряет давление, уровень кислорода в крови и уточняет детали анамнеза.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva000.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «МедАльянс» оказывает профессиональную медицинскую помощь на дому в Москве и Московской области круглосуточно. Опытные врачи-наркологи приедут в течение часа после вызова, проведут полную диагностику, поставят капельницу и быстро вернут пациента в стабильное состояние.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva000.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому цена москва[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выбор наркологической клиники — ключевой шаг на пути к выздоровлению, от которого зависит не только физическое и психическое состояние пациента, но и устойчивость достигнутых результатов. Современные учреждения предлагают широкий спектр услуг, однако уровень подготовки персонала, методики лечения и условия пребывания могут существенно отличаться.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Первое, что необходимо уточнить перед вызовом — наличие у врача лицензии и профильного медицинского образования. Только сертифицированный нарколог может назначить препараты, поставить капельницу и провести детоксикацию без ущерба для здоровья пациента.
Получить больше информации – https://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-v-nizhnem-tagile
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает руководитель направления клинической токсикологии НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии, «оказание помощи на дому требует не меньшего профессионализма, чем лечение в стационаре, ведь врач действует в ограниченных условиях».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в нижнем тагиле[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интернет провайдер пермь
domashij-internet-perm004.ru
подключить домашний интернет пермь
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Take a spin through bright visuals and multiplier wins in the bonanza sweet demo, offering an exciting preview of the full game experience.
Sweet Bonanza is a popular online slot game that has captured the attention of players worldwide. With its bright graphics and engaging mechanics, it stands out as a top choice.
The unique characteristics of Sweet Bonanza are what truly set it apart. The game employs a cascading reel system, enabling players to achieve several wins with one spin.
On top of that, Sweet Bonanza provides a free spins option that enhances the overall fun. The potential for large payouts during free spins makes this aspect incredibly exciting.
To sum up, Sweet Bonanza is a captivating slot game that offers much to players. The combination of its eye-catching graphics and generous rewards makes it a top choice for many.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выбор наркологической клиники — ключевой шаг на пути к выздоровлению, от которого зависит не только физическое и психическое состояние пациента, но и устойчивость достигнутых результатов. Современные учреждения предлагают широкий спектр услуг, однако уровень подготовки персонала, методики лечения и условия пребывания могут существенно отличаться.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выбор наркологической клиники — ключевой шаг на пути к выздоровлению, от которого зависит не только физическое и психическое состояние пациента, но и устойчивость достигнутых результатов. Современные учреждения предлагают широкий спектр услуг, однако уровень подготовки персонала, методики лечения и условия пребывания могут существенно отличаться.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в первоуральске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает главный врач клинического отделения, «в условиях стационара мы можем оперативно реагировать на малейшие изменения в состоянии пациента, что критически важно при тяжёлых формах запоя».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова врач наркологической клиники «МедАльянс» прибывает на дом в течение 30–60 минут. Сначала специалист оценивает общее состояние пациента, измеряет давление, уровень кислорода в крови и уточняет детали анамнеза.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva000.ru/]капельница от запоя цена москва[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает руководитель направления клинической токсикологии НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии, «оказание помощи на дому требует не меньшего профессионализма, чем лечение в стационаре, ведь врач действует в ограниченных условиях».
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkolog-na-dom-nizhnij-tagil11.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-v-nizhnem-tagile
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Одним из ключевых направлений является проведение капельниц, призванных вывести токсины из организма и нормализовать водно-электролитный баланс. Используемые препараты и состав растворов подбираются индивидуально, исходя из клинической картины и истории болезни пациента.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec006.ru
вывод из запоя череповец
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Грузоперевозки Луганск Грузоперевозки Луганск: Страхование грузов. Защита вашего груза от любых рисков. Спокойствие и уверенность.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Черная полоса в жизни Гадалка: предсказание будущего по линиям судьбы. Гадалка – это человек, обладающий даром предвидения, способный предсказывать будущее с помощью различных инструментов, таких как карты Таро, кофейная гуща или линии на ладони.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выбор наркологической клиники — ключевой шаг на пути к выздоровлению, от которого зависит не только физическое и психическое состояние пациента, но и устойчивость достигнутых результатов. Современные учреждения предлагают широкий спектр услуг, однако уровень подготовки персонала, методики лечения и условия пребывания могут существенно отличаться.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-pervouralsk11.ru/]наркологическая клиника свердловская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Одним из главных преимуществ стационарного лечения в нашей клинике является полная анонимность. Мы понимаем, что многие пациенты боятся раскрытия своей зависимости и осуждения со стороны окружающих. В “Восстановление души” мы гарантируем конфиденциальность всех процедур и защиту личных данных пациента. Это создает безопасную и доверительную атмосферу, необходимую для успешного лечения и психологического восстановления.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk2.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena-v-irkutske/]kapelnica ot zapoya kruglosutochno narkologiya irkutsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В статье рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые помогут сориентироваться при выборе капельницы от запоя, понять механизм действия и особенности процедуры, а также избежать типичных ошибок при обращении за медицинской помощью.
Выяснить больше – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
подключить интернет в омске в квартире
domashij-internet-omsk006.ru
подключить интернет омск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-1.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов нарколога на дом в Каменске-Уральском обеспечивает безопасность пациента, исключая необходимость посещения медицинского учреждения, что особенно актуально при тяжелом состоянии или психологическом сопротивлении. Такая помощь включает в себя детоксикацию, купирование абстинентного синдрома и консультации по дальнейшему лечению.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Близкий человек в запое? Не ждите ухудшения. Обратитесь в клинику — здесь проведут профессиональный вывод из запоя с последующим восстановлением организма.
Углубиться в тему – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy11.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя калуга
vivod-iz-zapoya-kaluga004.ru
вывод из запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Грузоперевозки Луганск Грузоперевозки Луганск: Транспортировка негабаритных грузов. Специализированный транспорт, опытные такелажники, оформление необходимых разрешений. Безопасная и надежная доставка.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника «ЗдравЦентр» оказывает круглосуточную помощь пациентам, страдающим от алкогольной интоксикации. Наши специалисты выезжают в любой район Москвы и Московской области, чтобы оперативно поставить капельницу, снять симптомы абстиненции и восстановить здоровье пациента в комфортных домашних условиях.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva00.ru/]после капельницы от запоя в москве[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вывод из запоя в Рязани — это комплексная медицинская услуга, направленная на устранение интоксикации, стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение рецидива алкогольной зависимости. Методики подбираются индивидуально с учётом анамнеза, длительности запойного состояния, наличия сопутствующих заболеваний и психоэмоционального фона. Процедура осуществляется под контролем опытных врачей-наркологов с применением сертифицированных препаратов и оборудования.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ryazani/https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Во-вторых, реабилитация является неотъемлемой частью нашего подхода. Мы понимаем, что избавление от физической зависимости — это только первый шаг. Важной задачей является восстановление социального статуса, создание новых привычек и умение управлять своей жизнью без наркотиков или алкоголя. Наша клиника предлагает групповые и индивидуальные занятия, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления.
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-irkutske
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как выбрать эфирные масла doTERRA для начинающих Эфирные масла и медитация: как достичь гармонии: Углубите свою медитативную практику с помощью эфирных масел, которые помогают успокоить ум и установить связь с внутренним “я”.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
психология души Записаться к психологу: Первый шаг к улучшению ментального здоровья. Легкий и быстрый способ найти подходящего специалиста и договориться о встрече.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Особенно важно на этапе поступления пройти полную психодиагностику и получить адаптированную под конкретного пациента программу. Это позволит учитывать возможные сопутствующие расстройства, включая тревожные, аффективные и когнитивные нарушения.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-nizhnij-tagil11.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В рамках услуги вызова нарколога на дом используется современное оборудование и препараты, одобренные для амбулаторного применения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в каменске-уральском[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сколько длятся роды Как подготовиться к родам – планирование и подготовка к родам, включая посещение курсов для беременных, выбор роддома и партнера в родах.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника «ЗдравЦентр» оказывает круглосуточную помощь пациентам, страдающим от алкогольной интоксикации. Наши специалисты выезжают в любой район Москвы и Московской области, чтобы оперативно поставить капельницу, снять симптомы абстиненции и восстановить здоровье пациента в комфортных домашних условиях.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva00.ru/]капельница от запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec005.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После успешной детоксикации начинается этап реабилитации, который включает восстановление социального статуса пациента и формирование новых здоровых привычек. Мы предлагаем как групповые, так и индивидуальные занятия, направленные на изменение поведения и мышления, что способствует долгосрочному удержанию пациента от возвращения к зависимостям.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk2.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena-v-irkutske/]капельница от запоя срочно круглосуточно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
домашний интернет омск
domashij-internet-omsk005.ru
лучший интернет провайдер омск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Заговор от алкоголизма Заговор от алкоголизма: помощь в борьбе с зависимостью. Заговор от алкоголизма – это магический ритуал, направленный на избавление от алкогольной зависимости и укрепление воли к выздоровлению.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
отписка от родовых полей Психология души: Глубокое понимание своей внутренней сущности и духовного развития. Поиск смысла жизни и истинного предназначения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk003.ru
лечение запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
شركة كشف التماس الكابلات الكهربائية بجدة
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье собраны факты, которые освещают целый ряд важных вопросов. Мы стремимся предложить читателям четкую, достоверную информацию, которая поможет сформировать собственное мнение и лучше понять сложные аспекты рассматриваемой темы.
Углубиться в тему – https://farmaciacaparrosyreina.es/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Студия дизайна Интерьеров в СПБ. Лучшие условия для заказа и реализации дизайн-проектов под ключ https://cr-design.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье собраны факты, которые освещают целый ряд важных вопросов. Мы стремимся предложить читателям четкую, достоверную информацию, которая поможет сформировать собственное мнение и лучше понять сложные аспекты рассматриваемой темы.
Углубиться в тему – http://www.6555555.com/1198.html?replyTo=22531
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Детальнее – https://airportrehab.ca/chiropractic-care-release-toxins-from-your-body
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Углубиться в тему – http://smallonlinebusinessdmt.tk/post/34
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Получить больше информации – https://www.roek.org/jelly-jelly-jelly
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-курсы https://obuchenie-plasmoterapii.ru: теория, видеоуроки, разбор техник. Обучение с нуля и для практикующих. Доступ к материалам 24/7, сертификат после прохождения, поддержка преподавателя.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://www.pseurope.be/nl/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье собраны факты, которые освещают целый ряд важных вопросов. Мы стремимся предложить читателям четкую, достоверную информацию, которая поможет сформировать собственное мнение и лучше понять сложные аспекты рассматриваемой темы.
Узнать больше – https://taxineerlandia.com/expats-taxi/do-you-want-to-drive-with-us
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
экстренный вывод из запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk002.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec004.ru
вывод из запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
домашний интернет
domashij-internet-omsk004.ru
подключить интернет омск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Получить больше информации – https://www.drchfeng.com/?p=5854
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://ii4.ru/poleznosti/14217-kapelnitsa-ot-zapoya-effektivnyy-metod-borby-s-alkogolnoy-zavisimostyu-2
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Профессиональное прп терапия обучение: PRP, Plasmolifting, протоколы и нюансы проведения процедур. Онлайн курс обучения плазмотерапии.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проблема алкоголизма в Ярославле, как и в других регионах России, остаётся одной из самых актуальных. По данным Минздрава РФ, количество людей, нуждающихся в медицинской помощи из-за злоупотребления спиртным, ежегодно растёт. При этом эффективное лечение возможно лишь при комплексном подходе, включающем как медицинскую, так и психологическую поддержку.
Подробнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/lechenie-khronicheskogo-alkogolizma-yaroslavl/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой информационной статье вы найдете интересное содержание, которое поможет вам расширить свои знания. Мы предлагаем увлекательный подход и уникальные взгляды на обсуждаемые темы, побуждая пользователей к активному мышлению и критическому анализу!
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://cnemp.fr/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Modern operations gastric surgery innovative technologies, precision and safety. Minimal risk, short recovery period. Plastic surgery, ophthalmology, dermatology, vascular procedures.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Valuable info. Lucky me I found your site by accident, and I’m shocked why this accident did not happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Downtown Buenos Aires hotel https://www.panamericano.us with elegant rooms, friendly service, and prime location. Ideal for exploring cultural sights and shopping districts. Affordable luxury awaits.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Want to Instagram online downloader download from instagram and facebook quickly and easily. No registration, fast download, any format. Save your favorite content right now!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы понимаем, что лечение от алкогольной зависимости — это только первый шаг на пути к восстановлению. Профилактика рецидивов — важная часть нашего подхода. Мы проводим тренинги и курсы, направленные на развитие навыков борьбы с соблазнами и стрессом. Психотерапевтическая поддержка помогает пациентам справиться с эмоциональными трудностями, а также укрепляет мотивацию для сохранения трезвости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk3.ru/]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu irkutsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Многие семьи сталкиваются с вопросом: куда обратиться, чтобы получить реальную помощь? В городе работают как государственные, так и частные наркологические учреждения, но не все из них предлагают действительно результативные программы. Чтобы избежать ошибок, важно знать ключевые аспекты, на которые следует опираться при выборе клиники.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/]клиника лечения алкоголизма в ярославле[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как поясняет врач-нарколог НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии, «наличие оборудованного стационара с возможностью контроля осложнений — обязательное условие безопасного лечения наркомании».
Детальнее – https://lechenie-narkomanii-yaroslavl0.ru/czentr-lecheniya-narkomanii-yaroslavl/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Согласен с предыдущим оратором, и в дополнение хочу сказать:
Зацепил раздел про raregreen.ru.
Вот, делюсь ссылкой:
[url=https://raregreen.ru]https://raregreen.ru[/url]
Жду ваших комментариев.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Москве проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru/http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить айфон санкт петербург http://kupit-ajfon-cs.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При звонке на горячую линию операторы уточняют основные параметры: возраст пациента, длительность запоя, частоту и количество употреблённого алкоголя, наличие хронических заболеваний. Это позволяет заранее подготовить необходимый набор медикаментов и оборудования.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
работа военным Работа военным: долг и честь Работа военным – это долг и честь. Это осознанный выбор тех, кто готов посвятить свою жизнь защите Родины, ее суверенитета и территориальной целостности. Военная служба – это не просто профессия, это образ жизни, требующий самоотверженности, дисциплины и преданности. Военные – это люди, прошедшие суровую школу подготовки, способные действовать в самых сложных и опасных ситуациях. Они готовы рисковать своей жизнью ради защиты мирных граждан, ради сохранения спокойствия и стабильности в стране. Военная служба – это возможность получить ценные навыки и знания, которые пригодятся не только в армии, но и в гражданской жизни. Военные учатся работать в команде, принимать быстрые и взвешенные решения, преодолевать трудности и нести ответственность за свои действия. Армия – это кузница кадров, где формируются лидеры, способные вести за собой людей, принимать важные решения и добиваться поставленных целей. Военные – это элита общества, люди, которые пользуются уважением и доверием. Государство заботится о своих защитниках, предоставляя им социальные гарантии, достойное денежное довольствие, возможность получения образования и карьерного роста. Военная служба – это стабильность и уверенность в завтрашнем дне. Работа военным – это возможность внести свой вклад в развитие страны, в укрепление ее обороноспособности и международного авторитета. Военные участвуют в миротворческих операциях, оказывают помощь населению в случае стихийных бедствий и катастроф. Военная служба – это нелегкий труд, требующий самоотдачи и жертвенности. Но это также возможность почувствовать себя частью чего-то большего, причастным к великим делам и свершениям. Работа военным – это выбор настоящих патриотов, готовых посвятить свою жизнь служению Родине.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение запоя иркутск
vivod-iz-zapoya-irkutsk001.ru
вывод из запоя иркутск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это серьёзное состояние, при котором организм страдает от накопления токсинов, обезвоживания и нарушения обмена веществ. Клиника «ВоронежЛайф» предлагает услугу выездного инфузионного лечения от запоя с возможностью круглосуточного реагирования. Благодаря персонализированному подходу и использованию современных автоматизированных систем дозирования, наши специалисты обеспечивают безопасную и эффективную детоксикацию в условиях домашнего уюта.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя воронеж[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Москве проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя Москва[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk003.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Москве — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя в Москве[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ecole de cinema Institut d’etudes cinematographiques
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В столице России представлен разнообразный ассортимент интернет-провайдеров‚ которые предлагают разные тарифные планы. При определении подходящего провайдера стоит учитывать скорость интернет-соединения‚ качество услуг и надежность связи. На сайте domashij-internet-novosibirsk006.ru можно найти отзывы о провайдерах‚ что может помочь вам сделать правильный выбор. Важным аспектом является цена интернет-услуг и доступные способы подключения интернета; Техническая поддержка тоже является важным элементом‚ особенно в случае возникновения проблем. Сравнивая провайдеров‚ вы сможете выбрать лучший вариант для своего дома.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После вашего звонка диспетчер фиксирует заявку и передаёт её свободному специалисту. Нарколог связывается для уточнения симптомов, времени начала запоя и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний, чтобы привезти нужные препараты.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]капельница от запоя воронежская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Критерии оценки профессионального уровня сотрудников:
Разобраться лучше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/anonimnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После вашего звонка диспетчер фиксирует заявку и передаёт её свободному специалисту. Нарколог связывается для уточнения симптомов, времени начала запоя и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний, чтобы привезти нужные препараты.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
работа военным Военные – это люди, которые готовы отдать свою жизнь за свою страну и свой народ. Это герои, достойные уважения и признания.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лечение выводом из запоя на дому в «ВоронежМед» организовано по отработанному протоколу, включающему несколько ключевых этапов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]postavit-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya voronezh[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Москве решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy13.ru/]postavit-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya moskva[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша клиника сочетает в себе оперативность, комфорт и высокие стандарты безопасности. Вот основные преимущества сотрудничества:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому воронеж[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Москве приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru/]капельница от запоя город. Московская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec006.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пляжный сезон 2025 в Архипо-Осиповке обещает быть насыщенным. Подберите тур или составьте индивидуальную программу. Подробности об организации отдых в архипо осиповке 2025 на нашем ресурсе.
Отдых в Архипо-Осиповке — отличный выбор для любителей природы. Множество отдыхающих выбирает Архипо-Осиповку, чтобы насладиться солнечными днями и красотой природы.
Пляжи Архипо-Осиповки славятся своей чистотой и уютной атмосферой. Купание и водные развлечения делают отдых здесь незабываемым.
Разнообразие мест для проживания в Архипо-Осиповке удовлетворит любые потребности отдыхающих. Вы можете выбрать как роскошные отели, так и более бюджетные варианты, подходящие для всей семьи.
Кроме того, Архипо-Осиповка известна своим разнообразным досугом. Вы сможете насладиться прогулками вдоль побережья, участвовать в экскурсиях и посещать местные мероприятия.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как распознать легальный центр:
Подробнее тут – http://lechenie-narkomanii-yaroslavl0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://m.vk.com/stroidom36ru Остекление балконов и лоджий в Воронеже: цены и виды остекления
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На сегодняшний день интернет-соединение стал необходимостью, особенно в большом городе, как новосибирск. Различные провайдеры интернета предлагают недорогие тарифы, что позволяет пользователям выбрать выгодные предложения.При выборе провайдера необходимо учитывать различия между проводным и мобильным интернетом, а также сравнение тарифов различных компаний.На сайте domashij-internet-novosibirsk005.ru предоставляются актуальные акции и специальные предложения, которые помогут сэкономить на связи. Мнения пользователей о провайдерах помогут оценить качество услуг связи в новосибирске. Безлимитный интернет получает все большее признание, так как обеспечивает стабильное соединение без лишних затрат. Установка интернета для домашнего использования должно быть простым и удобным, и множество провайдеров готовы предложить комфортные условия.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk002.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Цена капельницы от запоя в Иркутске зависит от ряда факторов, таких как выбор метода лечения (на дому или в стационаре), продолжительность лечения и степень тяжести состояния пациента. Для уточнения стоимости и записи на консультацию вы можете обратиться к нашим менеджерам, которые подробно расскажут о стоимости услуг и ответят на все ваши вопросы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk3.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя в иркутске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Москве — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-lyubercy12.ru/]капельница от запоя цена Москва[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Терапия наркотической зависимости — не просто избавление от тяги, а глубокий восстановительный процесс, включающий физическую, психическую и социальную реабилитацию. В Ярославле помощь наркозависимым оказывается в различных учреждениях, однако не все из них обеспечивают одинаково высокий уровень качества. Как показывает практика, эффективность лечения во многом зависит от грамотно подобранной программы и профессионализма команды.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://lechenie-narkomanii-yaroslavl0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
работа военным Военная служба – это не только ношение формы и владение оружием. Это сложная и многогранная деятельность, включающая в себя подготовку, обучение, участие в учениях и операциях, а также поддержание боеготовности.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим ключевые признаки эффективной наркологической помощи в Ярославле — от состава команды до подходов в работе с мотивацией пациента.
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-yaroslavl0.ru/]центр лечения наркомании ярославль[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы понимаем, что лечение от алкогольной зависимости — это только первый шаг на пути к восстановлению. Профилактика рецидивов — важная часть нашего подхода. Мы проводим тренинги и курсы, направленные на развитие навыков борьбы с соблазнами и стрессом. Психотерапевтическая поддержка помогает пациентам справиться с эмоциональными трудностями, а также укрепляет мотивацию для сохранения трезвости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk3.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Цена капельницы от запоя в Иркутске зависит от ряда факторов, таких как выбор метода лечения (на дому или в стационаре), продолжительность лечения и степень тяжести состояния пациента. Для уточнения стоимости и записи на консультацию вы можете обратиться к нашим менеджерам, которые подробно расскажут о стоимости услуг и ответят на все ваши вопросы.
Узнать больше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk3.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-irkutske
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec005.ru
лечение запоя череповец
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
работа военным Работа военным – это не только героизм на поле боя, но и тяжелый повседневный труд, требующий постоянной концентрации и ответственности. Это умение быстро принимать решения в критических ситуациях, сохранять хладнокровие и действовать четко и слаженно. Военнослужащие должны быть готовы к длительным командировкам, к жизни в полевых условиях, к разлуке с семьей и близкими. Это требует крепкого здоровья, физической выносливости и психологической устойчивости. Современная армия – это высокотехнологичная структура, требующая от военнослужащих знаний в области современных вооружений, связи и техники. Это умение работать с новейшими технологиями, быстро осваивать новые виды вооружений и эффективно применять их в бою. Военная служба – это школа жизни, где формируется характер, воспитывается чувство ответственности и патриотизма. Это возможность получить ценный жизненный опыт, найти настоящих друзей и стать частью большой и дружной семьи. Служба в армии – это вклад в будущее нашей страны, в обеспечение мира и безопасности наших граждан. Это возможность стать защитником Родины, гордиться своей профессией и внести свой вклад в историю России.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
In line with my research, after a in foreclosure home is offered at an auction, it is common for any borrower to be able to still have some sort ofthat remaining unpaid debt on the financial loan. There are many lenders who attempt to have all costs and liens repaid by the next buyer. However, depending on specified programs, regulations, and state laws there may be some loans that are not easily handled through the transfer of personal loans. Therefore, the responsibility still lies on the customer that has received his or her property in foreclosure process. Many thanks for sharing your ideas on this website.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://stroidom36.ru/catalog/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
IPTV от интернет-провайдеров новосибирска: обзор Телевидение через интернет набирает популярность в последние годы. Провайдеры в новосибирске предлагают разнообразные услуги IPTV, что дает возможность наслаждаться любимыми каналами в отличном качестве. Подробные обзоры IPTV можно найти на сайте domashij-internet-novosibirsk004.ru, что поможет выбрать лучший провайдер. При сравнении провайдеров стоит учитывать тарифы на IPTV, качество изображения и скорость интернета. Многие пользователи отмечают важность стриминга контента без задержек. В отзывах пользователей часто упоминаются развлекательные программы и каналы в IPTV, что делает выбор провайдера ещё более актуальным. Не забывайте о подписке на IPTV, которая открывает доступ к мультимедийным сервисам и различным каналам. Перед выбором провайдера стоит изучить предложения и отзывы, чтобы найти оптимальный вариант для себя.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
devenir acteur Interpreter dans des films
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Миссия нашей клиники заключается в оказании высококачественной помощи людям, страдающим от зависимостей. Мы стремимся создать безопасное и поддерживающее пространство для лечения, где каждый пациент получает необходимую поддержку и понимание. Наша задача — не только помочь избавиться от зависимости, но и вернуть полноценную жизнедеятельность человека, восстановив его социальные связи и жизненные ориентиры.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk2.ru/]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya irkutsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя
https://vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk001.ru
лечение запоя челябинск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Прежде всего необходимо убедиться, что учреждение официально зарегистрировано и обладает соответствующей лицензией на медицинскую деятельность. Этот документ выдается Минздравом и подтверждает соответствие установленным нормам.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-yaroslavl0.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма в ярославле[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы понимаем, что лечение от алкогольной зависимости — это только первый шаг на пути к восстановлению. Профилактика рецидивов — важная часть нашего подхода. Мы проводим тренинги и курсы, направленные на развитие навыков борьбы с соблазнами и стрессом. Психотерапевтическая поддержка помогает пациентам справиться с эмоциональными трудностями, а также укрепляет мотивацию для сохранения трезвости.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk3.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-irkutske/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить дом на Кипре
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проблема алкоголизма в Ярославле, как и в других регионах России, остаётся одной из самых актуальных. По данным Минздрава РФ, количество людей, нуждающихся в медицинской помощи из-за злоупотребления спиртным, ежегодно растёт. При этом эффективное лечение возможно лишь при комплексном подходе, включающем как медицинскую, так и психологическую поддержку.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-yaroslavl/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн казино России Рейтинг онлайн казино России по разнообразию игр
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это серьёзное состояние, при котором организм страдает от накопления токсинов, обезвоживания и нарушения обмена веществ. Клиника «ВоронежЛайф» предлагает услугу выездного инфузионного лечения от запоя с возможностью круглосуточного реагирования. Благодаря персонализированному подходу и использованию современных автоматизированных систем дозирования, наши специалисты обеспечивают безопасную и эффективную детоксикацию в условиях домашнего уюта.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]после капельницы от запоя воронеж[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Интервью с рэперами Сравнение стилей рэп исполнителей: Различия и сходства в звучании и подаче.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
экстренный вывод из запоя череповец
vivod-iz-zapoya-cherepovec004.ru
вывод из запоя череповец
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
formation acting Ateliers de theatre
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «ВладимирМед» предоставляет круглосуточную анонимную помощь при алкогольной зависимости с возможностью выезда врача на дом. Мы объединяем профессиональную наркологию, психологическую поддержку и современные технологии детоксикации, чтобы каждый пациент мог получить комплексное лечение в безопасной и комфортной обстановке. Конфиденциальность и оперативность — ключевые принципы нашей работы, помогающие начать новый этап жизни без страха осуждения и лишних процедур.
Получить больше информации – наркологические клиники алкоголизм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инфузионная терапия при запое основывается на принципе постепенной и контролируемой доставки лекарственных препаратов и питательных смесей непосредственно в кровеносное русло. Это позволяет:
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh2.ru/]kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu voronezh[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Рейтинг онлайн казино России Психология игры в онлайн казино России: Контролируйте свои эмоции
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Даже телефонный разговор с клиникой может многое сказать о её подходе. Если вам предлагают типовое лечение без уточнения подробностей или избегают вопросов о составе команды, это тревожный сигнал. Серьёзные учреждения в Мурманске обязательно предложат предварительную консультацию, зададут уточняющие вопросы и расскажут, как строится программа помощи.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-murmansk0.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма мурманская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обратившись к нам, вы получите анонимное и безопасное лечение, полностью соответствующее медицинским стандартам.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом новокузнецк.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
провайдеры нижний новгород
domashij-internet-nizhnij-novgorod006.ru
провайдер по адресу нижний новгород
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://xnude.app/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
обзоры казино рейтинг казино 2025 на русском
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При длительном запое в крови накапливаются ацетальдегид и другие токсичные метаболиты этанола, которые повреждают клетки печени, нарушают функцию почек и приводят к дисбалансу электролитов. Без своевременной детоксикации повышается риск острых состояний — судорог, инсультов, инфаркта, панкреатита и психоза. Чем раньше начато лечение, тем быстрее нормализуются показатели обмена веществ, возвращается водно-электролитный баланс и восстанавливается работа жизненно важных органов. Анонимный выезд нарколога помогает снять психологический барьер перед обращением за помощью.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника в воронеже[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Дополнительно выясняются аллергические реакции, приём других препаратов и предпочтения пациента по времени визита врача.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-voronezh3.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому воронежская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пансионат для лежачих после инсульта
pansionat-tula003.ru
частный пансионат для престарелых
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Углубиться в тему – https://keesinha.com/2020-um-ano-de-muitos-desafios
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Neil Island is a small, peaceful island in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. It’s known for its beautiful beaches, clear blue water, and relaxed atmosphere: official Neil Island information
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Критерии оценки профессионального уровня сотрудников:
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/]lechenie-alkogolizma-yaroslavl0.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
escort in moscow – https://realtopmodels.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя цена
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk003.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В данной статье рассматриваются проблемы общественного здоровья и социальные факторы, влияющие на него. Мы акцентируем внимание на значении профилактики и осведомленности в защите здоровья на уровне общества. Читатели смогут узнать о новых инициативах и программах, направленных на улучшение здоровья населения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://diets4you.ru/kak-vovremya-raspoznat-zavisimost-i-ne-poteryat-blizkogo
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
проверить интернет по адресу
domashij-internet-nizhnij-novgorod005.ru
какие провайдеры по адресу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Получить больше информации – https://music-ai.com/2024/06/04/american-professional-ii-telecaster-maple-fingerboard-3-color-sunburst
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает захватывающий и полезный контент, который привлечет внимание широкого круга читателей. Мы постараемся представить тебе идеи, которые вдохновят вас на изменения в жизни и предоставят практические решения для повседневных вопросов. Читайте и вдохновляйтесь!
Разобраться лучше – https://confrio.es/como-encontrar-un-producto-del-sector-del-frio
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Подробнее тут – https://finsrecruitment.co.uk/2021/11/30/virtual-interviewing-a-guide-to-getting-it-right
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальныеInsights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://fuji-cryptofx.com/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://www.nudge.sk/2023/06/22/harnessing-the-power-of-social-media-for-business-growth
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://veselarodina.org/component/k2/item/3-custom-pet-gallery-style-with-carousel=4400?start=34080
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://restoransavskivenac.rs/2017/06/16/the-big-design-wall-likes-pictures
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Углубиться в тему – https://thelifestylestop.com/karma-quotes
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пансионат для пожилых в туле
pansionat-tula002.ru
частный пансионат для пожилых людей
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Детальнее – https://www.classicbookshop.com/?attachment_id=807
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://bbwomenshealth.ca/portfolio/cutting-edge-couture-avant-garde-fashion-design
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Углубиться в тему – https://www.iheir13.com/5214.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk002.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://www.procistenie.sk/solar-power-in-developing-nations-brightening-lives
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://recycledplasticmachine.com/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основной этап в лечении — детоксикация организма от токсичных веществ, вызывающих интоксикацию. В клинике применяют современные методы капельниц и медикаментозной поддержки, включая препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в мурманске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В клинике применяются доказательные методы лечения, соответствующие международным и российским рекомендациям. Основу составляет медикаментозная детоксикация, сопровождаемая психотерапией, когнитивно-поведенческой коррекцией, а также семейной консультацией. При необходимости применяются пролонгированные препараты, облегчающие контроль над тягой к веществу.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь на дому в Ярославле охватывает широкий спектр медицинских мероприятий, направленных на стабилизацию состояния пациента и подготовку к дальнейшему лечению. Среди основных процедур:
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова на дом врачи клиники «Трезвый Путь» проводят лечение по четко разработанному алгоритму, обеспечивающему максимальную эффективность и безопасность:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом екатеринбург.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В клинике применяются доказательные методы лечения, соответствующие международным и российским рекомендациям. Основу составляет медикаментозная детоксикация, сопровождаемая психотерапией, когнитивно-поведенческой коррекцией, а также семейной консультацией. При необходимости применяются пролонгированные препараты, облегчающие контроль над тягой к веществу.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]наркологическая клиника ярославль[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
провайдеры интернета в нижнем новгороде по адресу проверить
domashij-internet-nizhnij-novgorod004.ru
подключить проводной интернет нижний новгород
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В статье рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые помогут сориентироваться при выборе капельницы от запоя, понять механизм действия и особенности процедуры, а также избежать типичных ошибок при обращении за медицинской помощью.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому цена в первоуральске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В статье рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые помогут сориентироваться при выборе капельницы от запоя, понять механизм действия и особенности процедуры, а также избежать типичных ошибок при обращении за медицинской помощью.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/kapelniczy-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-pervouralske/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наркологической клинике применяются проверенные методики терапии, включая медикаментозное лечение, детоксикацию и психотерапевтические программы. Детоксикация проводится с использованием современных капельниц, обеспечивающих безопасное выведение токсинов из организма. Важно отметить, что качественное лечение включает и работу с психологическими аспектами зависимости, что достигается посредством групповых и индивидуальных консультаций.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм каменск-уральский[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными проблемами, связанными с зависимостями. Злоупотребление психоактивными веществами оказывает влияние не только на здоровье, но и на социальные отношения, а также на качество жизни. Наркологическая клиника “Новая Жизнь” предлагает широкий спектр услуг, направленных на восстановление и реабилитацию людей, которые сталкиваются с подобными трудностями.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-omske.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя в омске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Преимущество
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Путь к свободе от зависимости начинается не с обещаний «просто перестать», а с профессионального медицинского вмешательства. В «Чистом Дыхании» мы применяем проверенные методы, которые работают там, где сила воли без нужной поддержки оказывается бессильной. Наша клиника в Долгопрудном работает круглосуточно — чтобы помощь была доступна в самый критический момент, когда человек ощущает острую потребность в детоксикации, снятии абстинентного синдрома или психологической поддержке.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает главный врач клинического отделения, «в условиях стационара мы можем оперативно реагировать на малейшие изменения в состоянии пациента, что критически важно при тяжёлых формах запоя».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому рязанская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Особенно уязвимыми становятся люди старше 45 лет, а также пациенты с сахарным диабетом, гипертонией, эпилепсией и болезнями печени. При этом многие продолжают надеяться, что «само пройдёт» — и упускают момент, когда помочь ещё можно без реанимации. Наша клиника организует выезд врача в течение 40–60 минут, чтобы не терять драгоценное время.
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обеспечение своевременной наркологической помощи с выездом на дом в Каменске-Уральском — важный аспект комплексного лечения алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Услуга вызова нарколога на дом позволяет получить квалифицированную медицинскую помощь в комфортных условиях, что снижает стресс и способствует более быстрому восстановлению.
Подробнее – нарколог на дом цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В клинике созданы комфортные условия для прохождения лечения. Пациенты получают не только медицинскую помощь, но и социальную поддержку, что способствует быстрому восстановлению и возвращению к нормальной жизни. Узнать больше о формате лечения и условиях можно на официальном сайте клиники.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в каменске-уральском[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пансионат для престарелых людей
pansionat-tula001.ru
пансионат после инсульта
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя челябинск
https://vivod-iz-zapoya-chelyabinsk001.ru
вывод из запоя челябинск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог каменск-уральский[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Мурманске специализируется на комплексном лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимости. В условиях МедЦентр Арктика используются проверенные методы диагностики и терапии, позволяющие достичь устойчивой ремиссии и восстановить качество жизни пациента.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наркологической клинике применяются проверенные методики терапии, включая медикаментозное лечение, детоксикацию и психотерапевтические программы. Детоксикация проводится с использованием современных капельниц, обеспечивающих безопасное выведение токсинов из организма. Важно отметить, что качественное лечение включает и работу с психологическими аспектами зависимости, что достигается посредством групповых и индивидуальных консультаций.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в каменске-уральском[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стационарный формат предполагает круглосуточное наблюдение, возможность экстренного вмешательства и доступ к диагностическим средствам. Это особенно важно при наличии хронических заболеваний, психозов или алкогольного делирия.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя цена рязанская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основная цель — быстрое и безопасное выведение этанола и его токсических метаболитов из организма, восстановление водно-электролитного и кислотно-щелочного баланса, нормализация артериального давления, работы сердца, почек и головного мозга. Для этого применяется инфузионная терапия, фармакологическая коррекция, витаминотерапия и, при необходимости, седативная поддержка.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в рязани[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент получает индивидуальный план лечения, основанный на клинических исследованиях, данных лабораторных анализов и психологических тестов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
free hwid spoofer Hardware ID Spoofer: Hardware ID Spoofer для Honkai Star Rail
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стационарный формат предполагает круглосуточное наблюдение, возможность экстренного вмешательства и доступ к диагностическим средствам. Это особенно важно при наличии хронических заболеваний, психозов или алкогольного делирия.
Детальнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в рязани[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском разрабатывает программы лечения, учитывая особенности различных видов зависимости: алкогольной, наркотической, лекарственной. Каждая программа ориентирована на индивидуальные потребности пациента, что подтверждается опытом ведущих российских реабилитационных центров. Подробнее о лечении зависимости читайте на официальном сайте Минздрава.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог каменск-уральский[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Работа клиники строится на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. При поступлении пациента осуществляется всесторонняя диагностика, включающая анализы крови, оценку психического состояния и анамнез. По результатам разрабатывается персонализированный курс терапии.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в рязани[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В «Чистом Дыхании» вы встретите врачей-наркологов, психиатров и психологов с многолетним опытом, готовых приехать на дом для первичной детоксикации или принять в стационаре для углублённой терапии. Мы соблюдаем строгие медицинские протоколы и гарантируем безопасность даже в самых тяжёлых случаях.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В «Чистом Дыхании» вы встретите врачей-наркологов, психиатров и психологов с многолетним опытом, готовых приехать на дом для первичной детоксикации или принять в стационаре для углублённой терапии. Мы соблюдаем строгие медицинские протоколы и гарантируем безопасность даже в самых тяжёлых случаях.
Получить больше информации – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Мурманске специализируется на комплексном лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимости. В условиях МедЦентр Арктика используются проверенные методы диагностики и терапии, позволяющие достичь устойчивой ремиссии и восстановить качество жизни пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника мурманская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пансионат после инсульта
pansionat-tula003.ru
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника свердловская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова на дом врачи клиники «Трезвый Путь» проводят лечение по четко разработанному алгоритму, обеспечивающему максимальную эффективность и безопасность:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом цена в екатеринбурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
суши недорого барнаул https://sushi-barnaul.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Магазин брендовых кроссовок https://kicksvibe.ru Nike, Adidas, New Balance, Puma и другие. 100% оригинал, новые коллекции, быстрая доставка, удобная оплата. Стильно, комфортно, доступно!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пансионат для пожилых с инсультом
pansionat-msk003.ru
дом престарелых в москве
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После диагностики врач назначает препараты, направленные на снижение абстинентного синдрома, коррекцию психоэмоционального состояния и профилактику осложнений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно ярославль[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mostbet az etibarlıdırmı http://mostbet3041.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лечение хронического алкоголизма начинается с купирования абстинентного синдрома, после чего проводятся мероприятия по нормализации работы печени, сердечно-сосудистой и нервной системы. Назначаются гепатопротекторы, ноотропы, витамины группы B. Также проводится противорецидивная терапия.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог ярославль[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для успешной адаптации пациента в обществе клиника организует поддержку родственников и последующее наблюдение. Это снижает риск рецидива и помогает сохранить достигнутые результаты.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-klinika-pomoshh-v-murmanske
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основной этап в лечении — детоксикация организма от токсичных веществ, вызывающих интоксикацию. В клинике применяют современные методы капельниц и медикаментозной поддержки, включая препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
влияют на городскую повседневность С появлением цифровых технологий, ТВ и интернет стали важной составляющей городской жизни Москвы. Диджитализация преобразует медиапейзаж, предлагая инновационные подходы культурных событий и виртуальных мероприятий. Социальные сети и мобильные приложения позволяют жителям взаимодействовать друг с другом, делиться информацией и быть в курсе новостями. domashij-internet-msk005.ru Виртуальные трансляции делают доступными мероприятия, ранее закрытые для большинства людей. Городские сервисы и улучшение инфраструктуры содействуют концепцию умного города, оптимизируя качество общественного транспорта и комфорта горожан. Инновации в городе формируют уникальный цифровой ландшафт, открывая новые возможности для жителей. Таким образом, Москва превращается в более открытым и современным городом, где технологии занимают важное место в повседневной жизни.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наркологической клинике применяются проверенные методики терапии, включая медикаментозное лечение, детоксикацию и психотерапевтические программы. Детоксикация проводится с использованием современных капельниц, обеспечивающих безопасное выведение токсинов из организма. Важно отметить, что качественное лечение включает и работу с психологическими аспектами зависимости, что достигается посредством групповых и индивидуальных консультаций.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая клиника в каменске-уральском[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша команда врачей оперативно реагирует на каждый вызов, оказывая квалифицированную медицинскую помощь на дому. Специалисты проводят полный комплекс лечебных мероприятий, направленных на безопасное снятие интоксикации, детоксикацию и облегчение симптомов абстиненции.
Подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/zapoj-narkolog-na-dom-ekb
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При лёгких и среднетяжёлых состояниях возможно проведение лечения на дому. Это удобно, комфортно и позволяет сохранить анонимность. Однако есть ситуации, в которых домашнее вмешательство нецелесообразно:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для успешного лечения зависимости необходима тщательная диагностика. В клинике проводят полное обследование пациента, включающее:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Компоненты
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными проблемами, связанными с зависимостями. Злоупотребление психоактивными веществами оказывает влияние не только на здоровье, но и на социальные отношения, а также на качество жизни. Наркологическая клиника “Новая Жизнь” предлагает широкий спектр услуг, направленных на восстановление и реабилитацию людей, которые сталкиваются с подобными трудностями.
Детальнее – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-omske.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена в омске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клинические протоколы стационарной терапии рекомендуют госпитализацию при средней и тяжёлой степени интоксикации.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Одним из ключевых этапов терапии является медикаментозное устранение абстинентного синдрома, что значительно облегчает состояние пациента. Для этого используются препараты, рекомендованные к применению ведущими специалистами в области наркологии. Примером могут служить протоколы лечения, описанные на официальном портале наркологической помощи России.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог каменск-уральский[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
частные пансионаты для пожилых в туле
pansionat-tula002.ru
дом престарелых в туле
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наркологической клинике применяются проверенные методики терапии, включая медикаментозное лечение, детоксикацию и психотерапевтические программы. Детоксикация проводится с использованием современных капельниц, обеспечивающих безопасное выведение токсинов из организма. Важно отметить, что качественное лечение включает и работу с психологическими аспектами зависимости, что достигается посредством групповых и индивидуальных консультаций.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kamensk-uralskom/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском разрабатывает программы лечения, учитывая особенности различных видов зависимости: алкогольной, наркотической, лекарственной. Каждая программа ориентирована на индивидуальные потребности пациента, что подтверждается опытом ведущих российских реабилитационных центров. Подробнее о лечении зависимости читайте на официальном сайте Минздрава.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]narkologicheskie kliniki alkogolizm kamensk-ural’skij[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает главный врач клинического отделения, «в условиях стационара мы можем оперативно реагировать на малейшие изменения в состоянии пациента, что критически важно при тяжёлых формах запоя».
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ולשכוח. ומה לעשות…? כמובן, אין חומר סיכה-אני לוקח את זה אחר כך לפה (טוב, אני מקווה). אני רק מזיין את הפה, לא את הגרון. – תתכונן. והתחלתי להזריק את הזין לגרוני שוב. באופן מפתיע, סקס עם נערות ליווי טעם של גן עדן!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-oblasti[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стационарный формат предполагает круглосуточное наблюдение, возможность экстренного вмешательства и доступ к диагностическим средствам. Это особенно важно при наличии хронических заболеваний, психозов или алкогольного делирия.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает врач-нарколог И.В. Синицин, «современная наркология — это не только вывод из запоя, но и работа с глубинными причинами зависимости».
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
spoofer hwid Hardware ID Spoofer: Hardware ID Spoofer для Apex Legends Mobile
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в каменске-уральском[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пансионат инсульт реабилитация
pansionat-msk002.ru
частные пансионаты для пожилых в москве
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Москве выбор интернет-провайдера для коммерческих нужд — задача‚ требующая внимательного подхода. Услуги интернет-провайдеров варьируются по разным параметрам: скорости, качеству подключения и ценовым категориям. При выборе интернет-сервиса по адресу дома или офиса важно обратить внимание на доступные услуги по конкретному адресу, чтобы гарантировать надежное подключение. Анализ предложений провайдеров в Москве поможет определиться с лучшим вариантом. Обратите внимание на отзывы о провайдерах интернета — они помогут сформировать мнение о качестве предоставляемых услуг. Корпоративные тарифы для организаций часто предлагают более выгодные условия. интернет провайдер по адресу дома москва Если вам нужен бизнес-интернет решение, изучите предложения для организаций. Это позволит выбрать лучший интернет-провайдер для бизнеса‚ учитывая ваши потребности и бюджет. Не забывайте о скорости интернета в Москве: чем выше скорость‚ тем эффективнее будет работать ваш бизнес.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуга
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
אותו בשקיקה, מחליקה מעלה ומטה, מושכת אותה בחמדנות לתוך פיה. חברו של סרגיי הלך וגדל בהדרגה. את החצאית שלי, שכחתי את רצפת התחתונים שלי, והתיישבתי בכיסא. הטלפון צלצל. זה היה אנדרו. הוא דירה דיסקרטית בראשון לציון
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг по лечению зависимостей:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как поясняет врач-нарколог клиники «АлкоСтоп», «грамотно составленная инфузионная терапия не только устраняет последствия запоя, но и создаёт условия для дальнейшей мотивации пациента к лечению».
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основной этап в лечении — детоксикация организма от токсичных веществ, вызывающих интоксикацию. В клинике применяют современные методы капельниц и медикаментозной поддержки, включая препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника мурманская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стационарный формат предполагает круглосуточное наблюдение, возможность экстренного вмешательства и доступ к диагностическим средствам. Это особенно важно при наличии хронических заболеваний, психозов или алкогольного делирия.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена рязань[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
יותר. בנהמה, הוא הכניס את הזין שלו לכוס הרטוב שלה באורך מלא, ולקח את ורוניקה בירכיים, החל ואז תדבר. האם הפקודה ברורה? – כן, אדוני. והיא התחילה לסיים בשקט את הכריך. לאחר שחיסל אותו more helpful hints
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нарколог на дому проводит тщательный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает необходимые лабораторные исследования. Это позволяет выявить сопутствующие патологии и скорректировать тактику лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]нарколог на дом ярославль.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
free hwid spoofer Hardware ID Spoofer: Hardware ID Spoofer для Gran Turismo 7
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Одним из ключевых направлений является проведение капельниц, призванных вывести токсины из организма и нормализовать водно-электролитный баланс. Используемые препараты и состав растворов подбираются индивидуально, исходя из клинической картины и истории болезни пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно в ярославле[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
частный пансионат для пожилых
pansionat-tula001.ru
пансионат для пожилых
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Хирургические услуги экстренная хирургия: диагностика, операции, восстановление. Современная клиника, лицензированные специалисты, помощь туристам и резидентам.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
доставка суши барнаул доставка суши барнаул
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основной этап в лечении — детоксикация организма от токсичных веществ, вызывающих интоксикацию. В клинике применяют современные методы капельниц и медикаментозной поддержки, включая препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника мурманская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вывод из запоя — это не просто капельница, а многоуровневая медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение интоксикации, стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение осложнений. В клинике «Жизненный Луч» мы проводим эту процедуру в домашних условиях и в стационаре, в зависимости от тяжести состояния. К каждому пациенту применяем индивидуальный подход, исходя из возраста, сопутствующих заболеваний и длительности запоя.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]bystryj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нарколог на дому проводит тщательный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает необходимые лабораторные исследования. Это позволяет выявить сопутствующие патологии и скорректировать тактику лечения.
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czeny-v-yaroslavle/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При лёгких и среднетяжёлых состояниях возможно проведение лечения на дому. Это удобно, комфортно и позволяет сохранить анонимность. Однако есть ситуации, в которых домашнее вмешательство нецелесообразно:
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar-v-kolomne/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша команда врачей оперативно реагирует на каждый вызов, оказывая квалифицированную медицинскую помощь на дому. Специалисты проводят полный комплекс лечебных мероприятий, направленных на безопасное снятие интоксикации, детоксикацию и облегчение симптомов абстиненции.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника екатеринбург[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент получает индивидуальный план лечения, основанный на клинических исследованиях, данных лабораторных анализов и психологических тестов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
прогнозы на хоккей лайв http://www.luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Мурманске специализируется на комплексном лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимости. В условиях МедЦентр Арктика используются проверенные методы диагностики и терапии, позволяющие достичь устойчивой ремиссии и восстановить качество жизни пациента.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены мурманск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша команда врачей оперативно реагирует на каждый вызов, оказывая квалифицированную медицинскую помощь на дому. Специалисты проводят полный комплекс лечебных мероприятий, направленных на безопасное снятие интоксикации, детоксикацию и облегчение симптомов абстиненции.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
математический прогноз на футбол http://www.kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol3.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При лёгких и среднетяжёлых состояниях возможно проведение лечения на дому. Это удобно, комфортно и позволяет сохранить анонимность. Однако есть ситуации, в которых домашнее вмешательство нецелесообразно:
Выяснить больше – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Одним из ключевых направлений является проведение капельниц, призванных вывести токсины из организма и нормализовать водно-электролитный баланс. Используемые препараты и состав растворов подбираются индивидуально, исходя из клинической картины и истории болезни пациента.
Выяснить больше – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czeny-v-yaroslavle/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лечение хронического алкоголизма начинается с купирования абстинентного синдрома, после чего проводятся мероприятия по нормализации работы печени, сердечно-сосудистой и нервной системы. Назначаются гепатопротекторы, ноотропы, витамины группы B. Также проводится противорецидивная терапия.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-yaroslavle
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
הנפלא. הרכבת צונחת, מתנדנדת הגלגלים דפקו על המסילה, והקצב הזה-טוק-טוק, טוק – טוק-אכל בראש ממנה. הביצים מלאות הזרע שלו פגעו בדגדגן שלה בזריזות. דיאנה התיזה על הזין והביצים של סרגיי. נערת ליווי ירושלים
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение к врачу становится жизненно необходимым, если пациент находится в состоянии длительного запоя, при котором организм не справляется с накоплением токсинов. Если запой продолжается более двух-трёх дней, в теле накапливаются вредные вещества, что ведёт к нарушениям работы внутренних органов, развитию абстинентного синдрома и появлению психических нарушений. Также, если у пациента наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие скачки артериального давления, это сигнал к незамедлительному вызову специалиста. При выраженной абстинентной реакции с паническими атаками, сильной дрожью, бессонницей и эмоциональной нестабильностью самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Если появляются признаки алкогольного психоза – галлюцинации, агрессивность или спутанность сознания – вызов нарколога становится обязательным для предотвращения дальнейших осложнений. Также, когда требуется подготовка к процедурам кодирования от зависимости, необходима качественная детоксикация организма, что также является показанием к срочному обращению за профессиональной помощью.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пансионат для лежачих после инсульта
pansionat-msk001.ru
пансионат с медицинским уходом
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При лёгких и среднетяжёлых состояниях возможно проведение лечения на дому. Это удобно, комфортно и позволяет сохранить анонимность. Однако есть ситуации, в которых домашнее вмешательство нецелесообразно:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-kolomne[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интернет по адресу дома
domashij-internet-krasnodar006.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пребывание в стационаре обеспечивает круглосуточный мониторинг состояния, своевременное введение лекарств и защиту пациента от внешних факторов, провоцирующих срыв. Все палаты оснащены необходимым оборудованием, соблюдаются санитарные нормы, а условия размещения соответствуют медицинским стандартам.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]наркологическая клиника в ярославле[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Мурманске специализируется на комплексном лечении алкогольной, наркотической и других видов зависимости. В условиях МедЦентр Арктика используются проверенные методы диагностики и терапии, позволяющие достичь устойчивой ремиссии и восстановить качество жизни пациента.
Углубиться в тему – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-klinika-pomoshh-v-murmanske/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение к врачу становится жизненно необходимым, если пациент находится в состоянии длительного запоя, при котором организм не справляется с накоплением токсинов. Если запой продолжается более двух-трёх дней, в теле накапливаются вредные вещества, что ведёт к нарушениям работы внутренних органов, развитию абстинентного синдрома и появлению психических нарушений. Также, если у пациента наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие скачки артериального давления, это сигнал к незамедлительному вызову специалиста. При выраженной абстинентной реакции с паническими атаками, сильной дрожью, бессонницей и эмоциональной нестабильностью самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Если появляются признаки алкогольного психоза – галлюцинации, агрессивность или спутанность сознания – вызов нарколога становится обязательным для предотвращения дальнейших осложнений. Также, когда требуется подготовка к процедурам кодирования от зависимости, необходима качественная детоксикация организма, что также является показанием к срочному обращению за профессиональной помощью.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эффективная капельница должна включать несколько компонентов, каждый из которых направлен на решение конкретной задачи: выведение токсинов, восстановление функций организма, нормализация психоэмоционального состояния.
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/kapelniczy-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-pervouralske/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Подробности о технологии и методах выезда нарколога можно найти на официальных медицинских порталах, таких как Российское общество наркологов и Минздрав РФ.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Зависимости часто сопровождаются физическими и психологическими нарушениями, требующими комплексного подхода. Мы убеждены, что успешное лечение невозможно без индивидуального подхода, что делает нашу клинику отличным местом для тех, кто нуждается в поддержке.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-omske.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно омск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
– затяжной запой более 5–7 дней; – наличие галлюцинаций, судорог, бредовых состояний; – тяжёлое общее состояние (высокая температура, спутанность сознания, обезвоживание); – хронические болезни в стадии обострения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Компоненты
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1489 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о профессиональном образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пансионат для пожилых после инсульта
pansionat-msk003.ru
пансионат для пожилых
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов нарколога на дом от клиники «Трезвый Путь» имеет ряд неоспоримых преимуществ, которые высоко ценят наши пациенты:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуга
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог рязань[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника в Рязани предоставляет квалифицированную помощь пациентам, страдающим от алкогольной, наркотической и медикаментозной зависимости. Здесь проводится полный цикл медицинской и психотерапевтической поддержки, начиная с детоксикации и заканчивая восстановительным этапом. Учреждение оборудовано современными технологиями, а персонал обладает подтверждённой квалификацией и практическим опытом.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника рязань.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4605 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить срочно диплом о высшем образовании вуза — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Работа клиники строится на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. При поступлении пациента осуществляется всесторонняя диагностика, включающая анализы крови, оценку психического состояния и анамнез. По результатам разрабатывается персонализированный курс терапии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждому пациенту уделяется внимание в зависимости от его уникальных потребностей, что способствует достижению максимальных результатов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-omske.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском разрабатывает программы лечения, учитывая особенности различных видов зависимости: алкогольной, наркотической, лекарственной. Каждая программа ориентирована на индивидуальные потребности пациента, что подтверждается опытом ведущих российских реабилитационных центров. Подробнее о лечении зависимости читайте на официальном сайте Минздрава.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника каменск-уральский.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эффективное лечение требует поэтапного подхода, который реализуется следующим образом:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог рязань[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
-אני אטפל באשתי בעצמי, מאיפה השגת את מספר הטלפון שלה?!! – אה, אה, זה פשוט-כשנכנסת לשירותים ומגונה, ” מרוצה? היא לא ענתה, רק סחטה את ירכיה בניסיון לשמור על זרע דולף. פניה השתקפו click
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника в Ярославле представляет собой специализированное учреждение, оказывающее медицинскую помощь пациентам с алкогольной, наркотической и медикаментозной зависимостью. Ключевыми направлениями работы являются детоксикация, стабилизация состояния, последующее реабилитационное сопровождение и профилактика рецидивов. Комплексный подход к лечению обеспечивается взаимодействием специалистов различных профилей, включая наркологов, психиатров, психотерапевтов и медицинских сестёр.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://kleo-dreams.ru/ Мебельные тренды 2025: взгляд в будущее комфорта и стиля 2025 год обещает стать поворотным в мире мебельного дизайна. Технологии, экологичность и индивидуализация – вот три кита, на которых будет держаться современный интерьер. Экологичность как must-have: Устойчивое развитие больше не просто тренд, а необходимость. В 2025 году мы увидим повсеместное использование переработанных материалов, таких как переработанный пластик, бамбук и переработанное дерево. Производители будут стремиться к замкнутому циклу производства, минимизируя отходы и используя возобновляемые источники энергии. Потребители, в свою очередь, будут отдавать предпочтение мебели, имеющей экологические сертификаты и подтвержденное происхождение. Технологии на службе комфорта: Умная мебель станет неотъемлемой частью дома. Встроенные зарядные устройства, регулируемая подсветка, встроенные колонки и даже системы автоматической регулировки температуры – все это станет обыденностью. Особое внимание будет уделяться эргономике и адаптивности мебели под индивидуальные потребности пользователя. Индивидуализация как искусство: Серийное производство уступает место персонализированному дизайну. Возможность выбора цветов, материалов, размеров и даже функциональности мебели позволит создать уникальный интерьер, отражающий индивидуальность владельца. 3D-печать мебели станет более доступной, открывая безграничные возможности для кастомизации. В 2025 году мебельный дизайн будет ориентирован на создание комфортного, функционального и экологичного пространства, отражающего индивидуальность владельца. Технологии, устойчивость и персонализация – вот три ключа к интерьеру будущего. https://mebelsoskidkoy.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
проверить провайдера по адресу
domashij-internet-krasnodar005.ru
узнать провайдера по адресу краснодар
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эффективная капельница должна включать несколько компонентов, каждый из которых направлен на решение конкретной задачи: выведение токсинов, восстановление функций организма, нормализация психоэмоционального состояния.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя первоуральск.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Работа клиники строится на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. При поступлении пациента осуществляется всесторонняя диагностика, включающая анализы крови, оценку психического состояния и анамнез. По результатам разрабатывается персонализированный курс терапии.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-ryazani/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лечение зависимостей – это важная область медицины‚ сосредоточенная на лечение зависимостями. Если вы или ваши близкие переживаете проблемы зависимости от наркотиков‚ крайне важно знать о вариантах анонимного лечения. Специализированные клиники, такие как narkolog-tula007.ru‚ обеспечивают консультацию нарколога и всестороннюю поддержку для зависимых. Анонимные группы поддержки и программы восстановления помогают людям на пути к выздоровлению. Психотерапия при зависимости играет ключевую роль в восстановлении наркозависимых. Также важна профилактика наркомании и кризисная помощь. Не откладывайте обращаться за помощью — вы можете вернуться к нормальной жизни!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Независимо от формы зависимости — алкогольной, опиатной, синтетической или медикаментозной — специалисты подбирают индивидуальный курс терапии. Алгоритмы лечения адаптируются под возраст, стаж употребления, общее состояние организма и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стационарный формат предполагает круглосуточное наблюдение, возможность экстренного вмешательства и доступ к диагностическим средствам. Это особенно важно при наличии хронических заболеваний, психозов или алкогольного делирия.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Согласно данным НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии Минздрава РФ, профессиональный вывод из запоя с применением капельниц снижает риск осложнений и сокращает период восстановления. Процедура проводится только под наблюдением квалифицированных специалистов и требует правильного подбора препаратов в зависимости от стадии опьянения и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лечение хронического алкоголизма начинается с купирования абстинентного синдрома, после чего проводятся мероприятия по нормализации работы печени, сердечно-сосудистой и нервной системы. Назначаются гепатопротекторы, ноотропы, витамины группы B. Также проводится противорецидивная терапия.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника ярославль[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пансионат для реабилитации после инсульта
pansionat-msk002.ru
пансионат для лежачих больных
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как вылечить горло Как вылечить женщину – подход к лечению женщины должен учитывать ее физиологические и психологические особенности.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В статье рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые помогут сориентироваться при выборе капельницы от запоя, понять механизм действия и особенности процедуры, а также избежать типичных ошибок при обращении за медицинской помощью.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя первоуральск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
металлообработка Металлообработка – это обширная сфера деятельности, охватывающая широкий спектр процессов, направленных на изменение формы, размеров и свойств металлов и сплавов. От простых ручных операций до высокотехнологичных автоматизированных производств, металлообработка играет ключевую роль во многих отраслях промышленности, обеспечивая создание деталей, инструментов и конструкций, необходимых для функционирования современного мира.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В «Чистом Дыхании» вы встретите врачей-наркологов, психиатров и психологов с многолетним опытом, готовых приехать на дом для первичной детоксикации или принять в стационаре для углублённой терапии. Мы соблюдаем строгие медицинские протоколы и гарантируем безопасность даже в самых тяжёлых случаях.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
למחאה. השפתיים רעדו, הגוף נהנה, פועם בגלים מאצבעותיו, שהמשיכו בתנועותיהן המהירות גם כשהיא באופן מושלם ל-BDSM. אחרי הכל, אני יודע היטב איך לפגוע. ומכיוון שתמיד אהבתי לעבוד עם הידיים, נערות ליווי תמונות אמיתיות
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На сайте Минздрава указаны общие клинические рекомендации по выведению из запоя, включая допустимые дозировки и протоколы лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя рязань[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника в Ярославле представляет собой специализированное учреждение, оказывающее медицинскую помощь пациентам с алкогольной, наркотической и медикаментозной зависимостью. Ключевыми направлениями работы являются детоксикация, стабилизация состояния, последующее реабилитационное сопровождение и профилактика рецидивов. Комплексный подход к лечению обеспечивается взаимодействием специалистов различных профилей, включая наркологов, психиатров, психотерапевтов и медицинских сестёр.
Подробнее тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-yaroslavle/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Назначение
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому первоуральск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Одним из ключевых этапов терапии является медикаментозное устранение абстинентного синдрома, что значительно облегчает состояние пациента. Для этого используются препараты, рекомендованные к применению ведущими специалистами в области наркологии. Примером могут служить протоколы лечения, описанные на официальном портале наркологической помощи России.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены каменск-уральский[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интернет провайдеры по адресу
domashij-internet-krasnodar004.ru
провайдер по адресу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основной этап в лечении — детоксикация организма от токсичных веществ, вызывающих интоксикацию. В клинике применяют современные методы капельниц и медикаментозной поддержки, включая препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]narkologicheskie kliniki alkogolizm murmansk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пансионат для людей с деменцией в москве
pansionat-msk001.ru
пансионат для лежачих москва
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
וחצאיתה, ממש מעל הברך, נמתחה, מתווה את הקווים הקפיציים של ירכיה. היא ידעה שהוא צופה. הרגשתי הזה. אבל לא ידעתי, ואריסטו לא היה בסביבה. במבנה הקלאסי שלהם יש לי אללה מפוארת, ובכן, לא hop over to this site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4890 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
На этой странице — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Капельница для восстановления после алкогольного отравления – это эффективным средством для восстановления организма после алкогольного отравления. В Туле медицинская помощь в виде внутривенное введение глюкозы и электролитов дают возможность быстро облегчить симптомы похмелья, такие как головная боль, тошнота и слабость. Медицинские учреждения в Туле предлагают услуги с использованием энтеросгеля с целью детоксикации. Восстановление водного баланса также имеет большое значение в процессе восстановления. Не забывайте о необходимости консультации врача прежде чем начинать лечение. Для получения дополнительной информации посетите сайт narkolog-tula006.ru.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как вылечить желудок Молитва от пьянства сильная – обращение к высшим силам с просьбой об избавлении от алкогольной зависимости. Молитва может помочь укрепить веру и обрести силы для борьбы с зависимостью.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша миссия заключается в предоставлении качественной помощи людям, страдающим от зависимостей. Мы стремимся создать безопасную и поддерживающую атмосферу, где каждый сможет получить необходимую помощь. Основная цель — восстановление здоровья, психоэмоционального состояния и социальной адаптации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-omske.ru/]вывод из запоя цена омск.[/url][url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-omske.ru/]https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
выставочные стенды Выставочные стенды – это не просто конструкции, а тщательно продуманные платформы для коммуникации бренда с целевой аудиторией. Они являются мощным инструментом маркетинга, позволяющим компаниям не только продемонстрировать свою продукцию или услуги, но и установить личные контакты с потенциальными клиентами и партнерами. Создание эффективного выставочного стенда требует комплексного подхода, включающего в себя разработку концепции, дизайна, выбор материалов и технологий, а также организацию работы персонала.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нарколог на дому проводит тщательный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает необходимые лабораторные исследования. Это позволяет выявить сопутствующие патологии и скорректировать тактику лечения.
Подробнее – http://
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто бытовое пьянство, а одно из наиболее опасных проявлений алкогольной зависимости. Во время запоя организм перестаёт функционировать в нормальном режиме: сердечно-сосудистая система работает на износ, нервная система перегружена токсинами, а печень не справляется с нагрузкой. На этом фоне могут возникать тяжёлые осложнения — от судорог и гипогликемии до нарушения дыхания и алкогольного психоза. Чем дольше длится запой, тем глубже метаболические нарушения и выше риск серьёзных последствий.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому недорого[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1372 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить дипломы о высшем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
הייתי עדין — זה היה חלק מההורות. היא הייתה צריכה לדעת את מקומה. אבל כשכיביתי את המים ועטפתי הרחם, ואז כמעט לגמרי יצא מהכוס החוצה. תוך כדי כך הוא אחז במותני בחוזקה בידיו. לא משנה כמה מכוני ליווי בירושלים ואלף סיבות לביקור
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клинические протоколы стационарной терапии рекомендуют госпитализацию при средней и тяжёлой степени интоксикации.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наркологической клинике применяются проверенные методики терапии, включая медикаментозное лечение, детоксикацию и психотерапевтические программы. Детоксикация проводится с использованием современных капельниц, обеспечивающих безопасное выведение токсинов из организма. Важно отметить, что качественное лечение включает и работу с психологическими аспектами зависимости, что достигается посредством групповых и индивидуальных консультаций.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]narkologicheskie kliniki alkogolizm kamensk-ural’skij[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Odjeca i aksesoari za hotele navlake za restorane po sistemu kljuc u ruke: uniforme za sobarice, recepcionere, SPA ogrtaci, papuce, peskiri. Isporuke direktno od proizvodaca, stampa logotipa, jedinstveni stil.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый этап проводится квалифицированным специалистом, что позволяет достичь максимального терапевтического эффекта.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом екатеринбург.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://mebel-moscow-matras.ru/ Мебельные тренды 2025: взгляд в будущее комфорта и стиля 2025 год обещает стать поворотным в мире мебельного дизайна. Технологии, экологичность и индивидуализация – вот три кита, на которых будет держаться современный интерьер. Экологичность как must-have: Устойчивое развитие больше не просто тренд, а необходимость. В 2025 году мы увидим повсеместное использование переработанных материалов, таких как переработанный пластик, бамбук и переработанное дерево. Производители будут стремиться к замкнутому циклу производства, минимизируя отходы и используя возобновляемые источники энергии. Потребители, в свою очередь, будут отдавать предпочтение мебели, имеющей экологические сертификаты и подтвержденное происхождение. Технологии на службе комфорта: Умная мебель станет неотъемлемой частью дома. Встроенные зарядные устройства, регулируемая подсветка, встроенные колонки и даже системы автоматической регулировки температуры – все это станет обыденностью. Особое внимание будет уделяться эргономике и адаптивности мебели под индивидуальные потребности пользователя. Индивидуализация как искусство: Серийное производство уступает место персонализированному дизайну. Возможность выбора цветов, материалов, размеров и даже функциональности мебели позволит создать уникальный интерьер, отражающий индивидуальность владельца. 3D-печать мебели станет более доступной, открывая безграничные возможности для кастомизации. В 2025 году мебельный дизайн будет ориентирован на создание комфортного, функционального и экологичного пространства, отражающего индивидуальность владельца. Технологии, устойчивость и персонализация – вот три ключа к интерьеру будущего. https://mebelsoskidkoy.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для успешного лечения зависимости необходима тщательная диагностика. В клинике проводят полное обследование пациента, включающее:
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Виртуальные номера для Telegram basolinovoip.com создавайте аккаунты без SIM-карты. Регистрация за минуту, широкий выбор стран, удобная оплата. Идеально для анонимности, работы и продвижения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Колдовство Отзывы о целителях – важный источник информации при выборе целителя. Отзывы других людей могут помочь составить представление о компетентности и эффективности работы целителя.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
בקפידה בין רגליה. אני עומד כמו אידיוט עם מברג ביד ואני לא יודע מה לומר. “לן … אלנה שוב התנשקנו, שזרנו לשונות וליקקנו את שפתינו בחמדנות. החזקתי את אהובתי בירכיים, נעתי כאילו visit homepage
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Есть ненужная мукулатура? Сдать макулатуру Казань Принимаем бумажные отходы по выгодным расценкам. Быстрый расчет, помощь с загрузкой, удобный график. Экономия и забота об экологии!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При лёгких и среднетяжёлых состояниях возможно проведение лечения на дому. Это удобно, комфортно и позволяет сохранить анонимность. Однако есть ситуации, в которых домашнее вмешательство нецелесообразно:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Купить подписчиков в Telegram https://vc.ru/smm-promotion лёгкий способ начать продвижение. Выберите нужный пакет: боты, офферы, живые. Подходит для личных, новостных и коммерческих каналов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Подробности о технологии и методах выезда нарколога можно найти на официальных медицинских порталах, таких как Российское общество наркологов и Минздрав РФ.
Подробнее тут – https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-v-yaroslavle/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интернет провайдеры по адресу красноярск
domashij-internet-krasnoyarsk006.ru
провайдеры интернета в красноярске по адресу проверить
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Преимущество
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно екатеринбург[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными проблемами, связанными с зависимостями. Злоупотребление психоактивными веществами оказывает влияние не только на здоровье, но и на социальные отношения, а также на качество жизни. Наркологическая клиника “Новая Жизнь” предлагает широкий спектр услуг, направленных на восстановление и реабилитацию людей, которые сталкиваются с подобными трудностями.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-omske.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя омск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медицинский вывод из запоя включает несколько обязательных этапов:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]anonimnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая скорая помощь на дому – это неотъемлемая часть лечения зависимостей‚ который предоставляет экстренную помощь при алкогольной зависимости и зависимости от наркотиков. Выездная наркологическая служба оказывает профессиональную помощь зависимым‚ включая детоксикацию и кризисную интервенцию. На сайте narkolog-tula007.ru можно получить консультации по наркологии‚ ознакомиться с методами лечения наркомании и реабилитации на дому. Анонимное лечение наркоманов позволяет сохранить личные данные в тайне. Важно также помнить о поддержке родственников‚ что помогает в процессе восстановления. Программа восстановления после зависимости включает профилактику зависимостей и психологическую поддержку‚ что помогает успешному возвращению к нормальной жизни.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Высокий уровень лечения обеспечивается квалификацией врачей, имеющих опыт работы в области наркологии, а также современным медицинским оборудованием, позволяющим проводить диагностику и лечение на самом высоком уровне. Врачи регулярно повышают квалификацию, участвуя в конференциях и обучающих программах. Подробности о квалификации специалистов доступны на портале медицинского сообщества.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kamensk-uralskom/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша наркологическая клиника в СПб оснащена современным оборудованием для диагностики и терапии. Обеспечиваем безопасное и комфортное лечение.
В наркологической клинике пациенты находят поддержку и лечение для преодоления зависимостей. Команда профессионалов в наркологической клинике обеспечивает индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Основной целью наркологической клиники является выявление и лечение проблем, связанных с зависимостями. Наркологическая клиника применяет различные методы, чтобы помочь пациентам преодолеть зависимость.
Психологическая поддержка играет ключевую роль в процессе восстановления. Это помогает пациентам не только избавиться от физической зависимости, но и предотвратить рецидивы.
Каждый пациент проходит реабилитацию в своем темпе, что позволяет избежать стрессовых ситуаций. Важно помнить, что процесс выздоровления требует времени, но результаты оправдают усилия.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нарколог на дому проводит тщательный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает необходимые лабораторные исследования. Это позволяет выявить сопутствующие патологии и скорректировать тактику лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno jaroslavl'[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эффективное лечение требует поэтапного подхода, который реализуется следующим образом:
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наши усилия направлены на то, чтобы вернуть пациентам уверенность в себе, здоровье и качество жизни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-omske.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu omsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основной этап в лечении — детоксикация организма от токсичных веществ, вызывающих интоксикацию. В клинике применяют современные методы капельниц и медикаментозной поддержки, включая препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В клинике созданы комфортные условия для прохождения лечения. Пациенты получают не только медицинскую помощь, но и социальную поддержку, что способствует быстрому восстановлению и возвращению к нормальной жизни. Узнать больше о формате лечения и условиях можно на официальном сайте клиники.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша команда врачей оперативно реагирует на каждый вызов, оказывая квалифицированную медицинскую помощь на дому. Специалисты проводят полный комплекс лечебных мероприятий, направленных на безопасное снятие интоксикации, детоксикацию и облегчение симптомов абстиненции.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кашпо для напольных растений купить https://kashpo-napolnoe-msk.ru – https://kashpo-napolnoe-msk.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В клинике применяются доказательные методы лечения, соответствующие международным и российским рекомендациям. Основу составляет медикаментозная детоксикация, сопровождаемая психотерапией, когнитивно-поведенческой коррекцией, а также семейной консультацией. При необходимости применяются пролонгированные препараты, облегчающие контроль над тягой к веществу.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая клиника ярославль[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Согласно данным НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии Минздрава РФ, профессиональный вывод из запоя с применением капельниц снижает риск осложнений и сокращает период восстановления. Процедура проводится только под наблюдением квалифицированных специалистов и требует правильного подбора препаратов в зависимости от стадии опьянения и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя свердловская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
האור. – מותק, אני במקלחת! אני צריך לשטוף את הריח של מישהו אחר! מים צלצלו. זרקתי בגדים ויצאנו החוצה, היא הזמינה אותי לקפה עם קרואסונים. באופן טבעי, שאלתי את עצמי-ולבעלי לא יהיה דירה דיסקרטית ראשון לציון
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медикаменты от алкоголизма могут включать препараты для коррекции зависимости‚ которые облегчают проявления. Постоянная поддержка и контроль при детоксикации обеспечивают защищенность пациента. Поддержка родственников также имеет большое значение для эффективного выздоровления после алкогольной интоксикации. вывод из запоя круглосуточно Рекомендации по выходу из запоя могут включать частые консультации с врачом и придерживание распорядка. Следует обратиться за поддержкой‚ чтобы предотвратить возвращение к алкоголю и обеспечить эффективную терапию.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуга
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лечение хронического алкоголизма начинается с купирования абстинентного синдрома, после чего проводятся мероприятия по нормализации работы печени, сердечно-сосудистой и нервной системы. Назначаются гепатопротекторы, ноотропы, витамины группы B. Также проводится противорецидивная терапия.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Назначение
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому свердловская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Работа клиники строится на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. При поступлении пациента осуществляется всесторонняя диагностика, включающая анализы крови, оценку психического состояния и анамнез. По результатам разрабатывается персонализированный курс терапии.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника в рязани[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-kamensk-uralskom
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
провайдеры интернета по адресу
domashij-internet-krasnoyarsk005.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу красноярск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда следует вызывать экстренную наркологическую помощь в Туле Кризисные ситуации, возникающие из-за зависимости от алкоголя или наркотиков, могут коснуться любого. В такие моменты важно знать, как быстро и эффективно получить помощь. Срочный вызов нарколога на дом в Туле может спасти жизнь тем, кто испытывает признаки алкогольного отравления или другие острые состояния, связанные с зависимостями. Экстренная помощь от наркологической службы включает возможность вызвать нарколога на дом. Это актуально для людей, которые по разным причинам не могут или не хотят обращаться в медицинские учреждения. Профилактика тяжелых последствий при лечении алкоголизма зачастую требует вмешательства специалистов. Поддержка со стороны близких имеет решающее значение в процессе реабилитации наркоманов и алкоголиков; Психотерапия при зависимости способствует выявлению причин и решению проблем. Адреса наркологических центров в Туле можно найти в интернете, но иногда необходима неотложная помощь; нарколог на дом срочно тула Профилактика зависимости также важна. Раннее обращение к специалистам может помочь предотвратить развитие серьезных проблем. Помните, что экстренные меры способны спасти жизнь.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает врач-нарколог И.В. Синицин, «современная наркология — это не только вывод из запоя, но и работа с глубинными причинами зависимости».
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-yaroslavle/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Одним из ключевых этапов терапии является медикаментозное устранение абстинентного синдрома, что значительно облегчает состояние пациента. Для этого используются препараты, рекомендованные к применению ведущими специалистами в области наркологии. Примером могут служить протоколы лечения, описанные на официальном портале наркологической помощи России.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наркологической клинике применяются проверенные методики терапии, включая медикаментозное лечение, детоксикацию и психотерапевтические программы. Детоксикация проводится с использованием современных капельниц, обеспечивающих безопасное выведение токсинов из организма. Важно отметить, что качественное лечение включает и работу с психологическими аспектами зависимости, что достигается посредством групповых и индивидуальных консультаций.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Назначение
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными проблемами, связанными с зависимостями. Злоупотребление психоактивными веществами оказывает влияние не только на здоровье, но и на социальные отношения, а также на качество жизни. Наркологическая клиника “Новая Жизнь” предлагает широкий спектр услуг, направленных на восстановление и реабилитацию людей, которые сталкиваются с подобными трудностями.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-omske.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena omsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Особенно уязвимыми становятся люди старше 45 лет, а также пациенты с сахарным диабетом, гипертонией, эпилепсией и болезнями печени. При этом многие продолжают надеяться, что «само пройдёт» — и упускают момент, когда помочь ещё можно без реанимации. Наша клиника организует выезд врача в течение 40–60 минут, чтобы не терять драгоценное время.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наркологической клинике применяются проверенные методики терапии, включая медикаментозное лечение, детоксикацию и психотерапевтические программы. Детоксикация проводится с использованием современных капельниц, обеспечивающих безопасное выведение токсинов из организма. Важно отметить, что качественное лечение включает и работу с психологическими аспектами зависимости, что достигается посредством групповых и индивидуальных консультаций.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-kamensk-uralskom/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Особенно уязвимыми становятся люди старше 45 лет, а также пациенты с сахарным диабетом, гипертонией, эпилепсией и болезнями печени. При этом многие продолжают надеяться, что «само пройдёт» — и упускают момент, когда помочь ещё можно без реанимации. Наша клиника организует выезд врача в течение 40–60 минут, чтобы не терять драгоценное время.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]анонимный вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Одним из ключевых направлений является проведение капельниц, призванных вывести токсины из организма и нормализовать водно-электролитный баланс. Используемые препараты и состав растворов подбираются индивидуально, исходя из клинической картины и истории болезни пациента.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стационарный формат предполагает круглосуточное наблюдение, возможность экстренного вмешательства и доступ к диагностическим средствам. Это особенно важно при наличии хронических заболеваний, психозов или алкогольного делирия.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркология вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Преимущество
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника екатеринбург[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нарколог на дому проводит тщательный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает необходимые лабораторные исследования. Это позволяет выявить сопутствующие патологии и скорректировать тактику лечения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение к врачу становится жизненно необходимым, если пациент находится в состоянии длительного запоя, при котором организм не справляется с накоплением токсинов. Если запой продолжается более двух-трёх дней, в теле накапливаются вредные вещества, что ведёт к нарушениям работы внутренних органов, развитию абстинентного синдрома и появлению психических нарушений. Также, если у пациента наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие скачки артериального давления, это сигнал к незамедлительному вызову специалиста. При выраженной абстинентной реакции с паническими атаками, сильной дрожью, бессонницей и эмоциональной нестабильностью самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Если появляются признаки алкогольного психоза – галлюцинации, агрессивность или спутанность сознания – вызов нарколога становится обязательным для предотвращения дальнейших осложнений. Также, когда требуется подготовка к процедурам кодирования от зависимости, необходима качественная детоксикация организма, что также является показанием к срочному обращению за профессиональной помощью.
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После устранения острой зависимости важным этапом становится реабилитация. Она включает восстановление социальных навыков, обучение методам преодоления стрессов без употребления психоактивных веществ.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]наркологическая клиника мурманск.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Капельница для снятия запоя на дому – это ключевая услуга наркологической службы‚ позволяющая оперативно и резко помочь людям‚ страдающим от алкогольной зависимости. Начальная встреча с наркологом в Туле включает диагностику зависимости‚ анализ состояния пациента и составление индивидуального плана лечения. Основные услуги нарколога на дому включают медикаментозное лечение‚ выведение из запоя‚ психотерапевтическую помощь при алкоголизме и программы восстановления. Родственники также играют важную роль также влияет ключевую роль в процессе реабилитации алкоголиков. Лечение в анонимном формате обеспечивает удобство и защищенность пациента. помощь нарколога тула
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интернет по адресу
domashij-internet-krasnoyarsk004.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Цены вывода из запоя от алкоголя в Туле варьируется в зависимости с различными аспектами. Нарколог на дом анонимно предлагает услуги по выведению из запоя и медицинской помощи при алкоголизме. Консультация нарколога способствует определению оптимальной программы детокса. Стоимость на программы лечения могут включать стоимость анонимную детоксикацию и реабилитацию от алкоголя. Услуги нарколога, такие как поддержка пациентам с зависимостямитакже играют важную роль. В наркологической клинике Тула предлагают различные программыкоторые могут определять общую стоимость. Важно помнить о профилактике алкогольной зависимости и своевременной помощи.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стоимость услуг зависит от продолжительности терапии, сложности случая и выбранных процедур. Однако клиника предоставляет гибкую систему оплаты, включая рассрочку и страховое покрытие.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Работа клиники строится на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. При поступлении пациента осуществляется всесторонняя диагностика, включающая анализы крови, оценку психического состояния и анамнез. По результатам разрабатывается персонализированный курс терапии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медицинский вывод из запоя включает несколько обязательных этапов:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологическая клиника в каменске-уральском[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Преимущество
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом свердловская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм каменск-уральский[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь на дому в Ярославле охватывает широкий спектр медицинских мероприятий, направленных на стабилизацию состояния пациента и подготовку к дальнейшему лечению. Среди основных процедур:
Выяснить больше – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная наркологическая клиника в Каменске-Уральском предоставляет комплексные услуги по диагностике и лечению различных видов зависимостей. Заболевания, связанные с алкоголизмом и наркоманией, требуют индивидуального подхода и применения современных медицинских технологий. В условиях клиники обеспечивается полный медицинский контроль и психологическая поддержка, что способствует успешной реабилитации пациентов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В современном мире все больше людей предпочитают получать медицинские услуги в комфортной обстановке своего дома. Одной из таких услуг является прокапка‚ которая может стать важной частью лечения различных заболеваний. Это просто‚ эффективно и позволяет избежать лишних поездок в больницу. Процедура прокапки на дому – это не только возможность избежать ненужных стрессовых ситуаций‚ связанных с посещением медицинских учреждений‚ но и способ гарантировать качественное лечение‚ не покидая домашнего уюта. Такой подход позволяет пациентам сосредоточиться на реабилитации и получить необходимую медицинскую помощь в привычной обстановке. Для проведения процедуры потребуется медицинское оборудование‚ которое может предоставить специализированная компания. Услуги медсестры‚ обладающей необходимыми навыками‚ обеспечивают безопасность и эффективность процесса. Специалист примет меры по уходу за пациентом‚ проверит общее состояние и выберет оптимальный режим лечения. narkolog-tula004.ru Инфузионная терапия может использоваться для введения необходимых препаратов‚ необходимых для поддержания здоровья‚ или для коррекции водно-электролитного обмена. Это особенно актуально для пациентов‚ восстанавливающихся после болезни или перенесших операцию. Кроме того‚ инъекции могут быть более удобным вариантом для тех‚ кто страдает от хронических заболеваний и нуждается в регулярном введении лекарств.Лечение на дому позволяет не только уменьшить время и силы‚ но и улучшить самочувствие пациента. Комфорт лечения на дому создает доброжелательную обстановку‚ что также способствует более эффективному лечению. Физическая реабилитация‚ проводимые в домашних условиях‚ могут быть адаптированы под индивидуальные потребности пациента‚ что делает процесс восстановления более эффективным.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лучший интернет провайдер казань
domashij-internet-kazan006.ru
интернет провайдеры по адресу дома
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Работа клиники строится на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. При поступлении пациента осуществляется всесторонняя диагностика, включающая анализы крови, оценку психического состояния и анамнез. По результатам разрабатывается персонализированный курс терапии.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-czeny-v-ryazani/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Путь к свободе от зависимости начинается не с обещаний «просто перестать», а с профессионального медицинского вмешательства. В «Чистом Дыхании» мы применяем проверенные методы, которые работают там, где сила воли без нужной поддержки оказывается бессильной. Наша клиника в Долгопрудном работает круглосуточно — чтобы помощь была доступна в самый критический момент, когда человек ощущает острую потребность в детоксикации, снятии абстинентного синдрома или психологической поддержке.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Провести капельницу после запоя в домашних условиях – это решение, который способен облегчить симптомы похмелья и ускорить процесс детоксикации. Лечение запоя предполагает как медицинскую помощь на дому, так и народные средства от похмелья. Важно понимать симптомы похмелья: боль в голове, тошнота, усталость. Для восстановления после алкоголя часто используются препараты от запоя, которые помогут уменьшению дискомфорта. narkolog-tula003.ru Алкогольная зависимость психологическая помощь при запое является важной ролью процесса. Поддержка близких при алкоголизме может существенно ускорить реабилитацию после пьянства и предотвратить повторные запои. Рекомендации по избавлению от запоя могут включать в себя соблюдение режима питания, достаточное питье и использование народных средств. Профилактика запоев должна быть в центре внимания, чтобы избежать рецидивов. Обратитесь за профессиональной помощью, если состояние не стабилизируется.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Con el espectaculo drones, tu evento se convierte en una celebración inolvidable que combina luces flotantes, figuras animadas y sincronización musical precisa. Cautivamos al público con cada movimiento aéreo programado al milímetro.
El espectáculo de drones ha ganado popularidad en los últimos años. Estos espectáculos fusionan innovación tecnológica, expresión artística y entretenimiento. Las presentaciones de drones se han convertido en una atracción habitual en festivales y acontecimientos.
Los drones equipados con luces generan figuras fascinantes en el firmamento. Las audiencias suelen quedar asombradas por la combinación de luces y coreografías.
Muchos organizadores optan por contratar compañías especializadas para estos eventos. Dichas compañías tienen personal cualificado y los equipos más modernos disponibles.
La seguridad representa un factor fundamental en la realización de estos eventos. Se siguen procedimientos detallados para prevenir riesgos durante estas exhibiciones. El futuro de los espectáculos de drones es prometedor, con innovaciones constantes.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вывод из запоя в Рязани — это комплексная медицинская услуга, направленная на устранение интоксикации, стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение рецидива алкогольной зависимости. Методики подбираются индивидуально с учётом анамнеза, длительности запойного состояния, наличия сопутствующих заболеваний и психоэмоционального фона. Процедура осуществляется под контролем опытных врачей-наркологов с применением сертифицированных препаратов и оборудования.
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-ryazani/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]наркологическая клиника в области[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После устранения острой зависимости важным этапом становится реабилитация. Она включает восстановление социальных навыков, обучение методам преодоления стрессов без употребления психоактивных веществ.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм мурманская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если хотите заранее всё рассчитать — отдых в абхазии 2025 цены помогут подобрать оптимальные варианты проживания без лишних затрат.
Абхазия — это удивительное место для отдыха. Пейзажи Абхазии поражают своей красотой и разнообразием.
Курорты Абхазии находятся на берегу Черного моря и привлекают многих отдыхающих. Для туристов доступны разнообразные варианты размещения: от гостиниц до частных домов.
Природа Абхазии радует своими необыкновенными достопримечательностями и возможностью активного отдыха. Горные пейзажи, живописные озера и величественные водопады манят туристов.
Гастрономические delights Абхазии заслуживают внимания. Кулинарные традиции Абхазии отличаются уникальным сочетанием вкусов и свежестью продуктов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркология на дом: забота о здоровье и помощь
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает главный врач клинического отделения, «в условиях стационара мы можем оперативно реагировать на малейшие изменения в состоянии пациента, что критически важно при тяжёлых формах запоя».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя в рязани[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интернет провайдеры по адресу казань
domashij-internet-kazan005.ru
провайдеры интернета в казани по адресу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клинические протоколы стационарной терапии рекомендуют госпитализацию при средней и тяжёлой степени интоксикации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/]срочный вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкоголь и наркотики воздействуют на организм комплексно: нарушается работа сердца, сосудов, печени и почек, страдает нервная система. При запое или ломке без квалифицированной помощи возникают судороги, делирий, галлюцинации и серьёзные сбои в обмене веществ. Самостоятельные попытки «перетерпеть» или «отмотать» запой зачастую приводят к тяжёлым осложнениям, вплоть до комы и необратимых изменений в органах.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для успешного лечения зависимости необходима тщательная диагностика. В клинике проводят полное обследование пациента, включающее:
Узнать больше – http://
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сборка игрового компьютера Игровой ПК в сборе – это готовое решение для геймеров, которое позволит сразу приступить к игре.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основной этап в лечении — детоксикация организма от токсичных веществ, вызывающих интоксикацию. В клинике применяют современные методы капельниц и медикаментозной поддержки, включая препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Капельница при алкогольной зависимости — это необходимая медицинская помощь в случае алкогольной зависимости. Если вы вы увидите симптомы, такие как сильная жажда, боли в голове, тошнота и общая слабость, вызов нарколога на дом в Туле может стать хорошим выходом. Медик осуществит медицинскую помощь и предложит капельницу, которая помогает восстановлению организма. вызвать нарколога на дом тула Преодоление алкогольной зависимости включает вывод из запоя, что позволяет значительному повышению здоровья после запоя. Капельница содействует устранить обезвоживание, компенсировать дефицит минералов и улучшить общее состояние пациента. Если требуется можно провести лечение на дому, что обеспечивает комфорт и безопасность.Тула наркология предлагает качественные услуги по лечение алкогольной зависимости, что обеспечивает справиться с зависимостью результативно. Эффекты капельницы заметны быстро: пациенты отмечают повышение жизненного тонуса и восстановление сил. Не откладывайте промедлить обращение за помощью, здоровье важно сохранить!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
orthopedic clinic near me medical centar
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
платные клиники клиническая больница
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медицинский вывод из запоя включает несколько обязательных этапов:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kapelnica-na-domu[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными проблемами, связанными с зависимостями. Злоупотребление психоактивными веществами оказывает влияние не только на здоровье, но и на социальные отношения, а также на качество жизни. Наркологическая клиника “Новая Жизнь” предлагает широкий спектр услуг, направленных на восстановление и реабилитацию людей, которые сталкиваются с подобными трудностями.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-omske.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно в омске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вывод из запоя в Рязани — это комплексная медицинская услуга, направленная на устранение интоксикации, стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение рецидива алкогольной зависимости. Методики подбираются индивидуально с учётом анамнеза, длительности запойного состояния, наличия сопутствующих заболеваний и психоэмоционального фона. Процедура осуществляется под контролем опытных врачей-наркологов с применением сертифицированных препаратов и оборудования.
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-ryazani12.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-v-ryazani
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Точная диагностика позволяет подобрать индивидуальную программу лечения, что значительно повышает шансы на успешное выздоровление.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-murmanske12.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм в мурманске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Одним из ключевых этапов терапии является медикаментозное устранение абстинентного синдрома, что значительно облегчает состояние пациента. Для этого используются препараты, рекомендованные к применению ведущими специалистами в области наркологии. Примером могут служить протоколы лечения, описанные на официальном портале наркологической помощи России.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм каменск-уральский[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все о тендерах, актуальная новости и информация: st-tender.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Откачка на дому в Туле, незаменимая услуга для обеспечения чистоты и здоровья. Проблемы с канализацией могут возникнуть внезапно, и в таких случаях стоит вызвать профессионалов. Качественная откачка сточных вод поможет избежать неприятных ситуаций.Среди вариантов откачки предлагаются: обслуживание канализационных систем, обслуживание сливных ям и экстренная откачка. Специальная ассенизаторская техника обеспечит качественное выполнение работ в соответствии с экологическими нормами. На сайте narkolog-tula002.ru вы найдете информацию о ценах на услуги и вариантах вызова специалиста. Также доступны устройства для сушки септиков и дренажные системы для предотвращения повторных засоров. Не затягивайте с решением проблемы — устраните проблемы с канализацией прямо сейчас!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Завдяки новим сервісам можна скористатися такими послугами, як найновіші кредити онлайн creditka.org.ua/uk, які пропонують вигідні умови і швидке зарахування коштів.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интересное про нейросети Нейросети: мозг из кремния. От алгоритмов к самообучению.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
проверить провайдера по адресу
domashij-internet-kazan004.ru
провайдеры интернета по адресу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нарколог на дому проводит тщательный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает необходимые лабораторные исследования. Это позволяет выявить сопутствующие патологии и скорректировать тактику лечения.
Детальнее – http://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение к врачу становится жизненно необходимым, если пациент находится в состоянии длительного запоя, при котором организм не справляется с накоплением токсинов. Если запой продолжается более двух-трёх дней, в теле накапливаются вредные вещества, что ведёт к нарушениям работы внутренних органов, развитию абстинентного синдрома и появлению психических нарушений. Также, если у пациента наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие скачки артериального давления, это сигнал к незамедлительному вызову специалиста. При выраженной абстинентной реакции с паническими атаками, сильной дрожью, бессонницей и эмоциональной нестабильностью самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Если появляются признаки алкогольного психоза – галлюцинации, агрессивность или спутанность сознания – вызов нарколога становится обязательным для предотвращения дальнейших осложнений. Также, когда требуется подготовка к процедурам кодирования от зависимости, необходима качественная детоксикация организма, что также является показанием к срочному обращению за профессиональной помощью.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно в екатеринбурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Работа клиники строится на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. При поступлении пациента осуществляется всесторонняя диагностика, включающая анализы крови, оценку психического состояния и анамнез. По результатам разрабатывается персонализированный курс терапии.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/]наркологическая клиника на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
– затяжной запой более 5–7 дней; – наличие галлюцинаций, судорог, бредовых состояний; – тяжёлое общее состояние (высокая температура, спутанность сознания, обезвоживание); – хронические болезни в стадии обострения.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-stacionar[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
мощный ПК на заказ Собрать компьютер онлайн – удобный способ собрать свой идеальный ПК, не выходя из дома.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современное общество сталкивается с серьёзными проблемами, связанными с зависимостями. Злоупотребление психоактивными веществами оказывает влияние не только на здоровье, но и на социальные отношения, а также на качество жизни. Наркологическая клиника “Новая Жизнь” предлагает широкий спектр услуг, направленных на восстановление и реабилитацию людей, которые сталкиваются с подобными трудностями.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-omske.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре омск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает врач-нарколог И.В. Синицин, «современная наркология — это не только вывод из запоя, но и работа с глубинными причинами зависимости».
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-yaroslavle12.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-v-yaroslavle/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эффективная капельница должна включать несколько компонентов, каждый из которых направлен на решение конкретной задачи: выведение токсинов, восстановление функций организма, нормализация психоэмоционального состояния.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-pervouralsk11.ru/]капельница от запоя цена свердловская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
собрать компьютер онлайн Купить игровой ПК – значит погрузиться в мир захватывающих игр с максимальной графикой и плавной работой. Современные игровые компьютеры обеспечивают высокую частоту кадров и реалистичную картинку.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello keepers of invigorating purity!
Smokers who live with others often rely on the best air purifier for smokers to minimize exposure. It’s especially effective in homes with children or elderly residents. The best air purifier for smokers reduces the risks of secondhand smoke.
In a household with multiple smokers, an air purifier for smokers keeps air fresh 24/7. It works hard to maintain balance and reduce smell.[url=п»їhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fJrxQEd44JM]best air purifier for smokers[/url]A top-tier air purifier for smokers includes long-lasting filter packs.
Cigarette smoke extractor for indoor use – п»їhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fJrxQEd44JM
May you delight in extraordinary healthy spaces !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Высокий уровень лечения обеспечивается квалификацией врачей, имеющих опыт работы в области наркологии, а также современным медицинским оборудованием, позволяющим проводить диагностику и лечение на самом высоком уровне. Врачи регулярно повышают квалификацию, участвуя в конференциях и обучающих программах. Подробности о квалификации специалистов доступны на портале медицинского сообщества.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-kamensk-uralskij11.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая клиника каменск-уральский[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Капельное лечение запоя — важный шаг в лечении алкогольной зависимости. Этапы подготовки к процедуре включает несколько шагов. Во-первых, необходимо вызвать нарколога на дом в любое время суток для получения профессиональной помощи. Специалист проведет обследование и оценит симптомы запоя. Перед капельницей необходимо обеспечить пациента чистой водой и легкой пищей. Это способствует снижению риска осложнений. Важно внимательно ухаживать за пациентом: создайте спокойную атмосферу. Нарколог на дом круглосуточно Во время процедуры важно контролировать состояние пациентачтобы гарантировать безопасность. После детоксикации организма потребуется психотерапия при запое. Не забывайтечто круглосуточная поддержка нарколога способствует успешному лечению запоя.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
прием макулатуры в казани Прием вторсырья в Казани – это возможность заработать деньги и одновременно позаботиться об окружающей среде. Многие компании предлагают выгодные условия приема вторсырья, что делает этот процесс еще более привлекательным.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нарколог на дому проводит тщательный осмотр, собирает анамнез и назначает необходимые лабораторные исследования. Это позволяет выявить сопутствующие патологии и скорректировать тактику лечения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-v-yaroslavle12.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в ярославле[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова на дом врачи клиники «Трезвый Путь» проводят лечение по четко разработанному алгоритму, обеспечивающему максимальную эффективность и безопасность:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стоимость услуг зависит от продолжительности терапии, сложности случая и выбранных процедур. Однако клиника предоставляет гибкую систему оплаты, включая рассрочку и страховое покрытие.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-ryazani12.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
нейрохаки Секреты ChatGPT: как получить максимум от нейросети, раскрываем возможности.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Прокапка – это необходимый процесс, касающийся эффективного полива саженцев, особенно в садоводстве. Капельный полив или автополив позволяют максимально насыщать влагой почву, что обеспечивает необходимую влажность грунта для развития растений. Эти системы полива значительно сокращают расходы на воду, а автоматизированный полива делает заботу за садом более простым и комфортным. В агрономии капельный полив используется для сохранения жизнеспособности зелени, предотвращая пересыхание почвы. Ландшафтный дизайн также приобретает преимущества от использования капельного, так как позволяет создать красивый и ухоженный сад. На сайте narkolog-tula001.ru можно найти многочисленные советов по монтажу и эксплуатации таких систем, что эффективно наладить водоснабжение и обеспечить уход о вашем саде.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перфект Plus Создайте уютную атмосферу в спальне с помощью текстильных изделий от Перфект Plus. Мягкие пледы, нежные подушки и элегантные шторы преобразят пространство, наполняя его теплом и комфортом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша миссия заключается в предоставлении качественной помощи людям, страдающим от зависимостей. Мы стремимся создать безопасную и поддерживающую атмосферу, где каждый сможет получить необходимую помощь. Основная цель — восстановление здоровья, психоэмоционального состояния и социальной адаптации.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-omske.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывоз макулатуры казань Прием вторсырья Казань включает не только макулатуру, но и другие виды отходов: пластик, стекло, металл. Сдавая вторсырье, вы уменьшаете нагрузку на полигоны.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
надежные прогнозы на футбол https://kompyuternye-prognozy-na-futbol1.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ставки онлайн Новые букмекеры появляются на рынке регулярно, предлагая инновационные решения, улучшенные коэффициенты и щедрые бонусы. Выбор новой платформы требует внимательного изучения репутации, лицензии и отзывов других игроков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Подробнее тут – https://69vnbet.pro/keo-thom-69vn
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Определение поставщика IPTV в Екатеринбурге является сложной задачей по причине большого количества предложений. На сайте domashij-internet-ekaterinburg006.ru собраны самые востребованные IPTV сервисы, которые помогут вам определиться . Обратите внимание на мнения пользователей от пользователей, которые пробовали сервисы. При сравнении IPTV поставщиков следует обратить внимание на качество IPTV и надежность соединения. Ознакомьтесь с ценами на IPTV и акциями , чтобы не переплатить. Не забывайте о необходимой скорости интернета: она должна быть оптимальной для комфортного просмотра . Важным фактором является совместимость с устройствами для IPTV. Проверьте, что выбранный провайдер поддерживает необходимые устройства. При установке IPTV придерживайтесь рекомендаций, чтобы избежать проблем . Ваш выбор должен опираться на пользовательских отзывах и сравнении тарифов и услуг.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта доказательная статья представляет собой глубокое погружение в успехи и вызовы лечения зависимостей. Мы обращаемся к научным исследованиям и опыте специалистов, чтобы предоставить читателям надежные данные об эффективности различных методик. Изучите, что работает лучше всего, и получите информацию от экспертов.
Подробнее – https://dermatologcentr.ru/kapelnica-ot-poxmelya-na-domu-v-tule-preimushhestva-i-osobennosti-uslugi
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Подробнее – https://expertosquimicos.com.mx/2024/03/25/a-guide-to-streamlining-your-business
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
значки на заказ срочно http://www.znacki-na-zakaz.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Выяснить больше – https://memoriseone.com/how-to-get-started
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://www.web-pro-firmu.cz/ahoj-vsichni
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед началом терапии врач собирает анамнез, оценивает состояние органов-мишеней (печень, почки, сердце), проводит лабораторные тесты на уровень электролитов и маркёры цирроза. Результаты обследования играют ключевую роль при выборе схемы инфузий и психотерапевтических методик.
Изучить вопрос глубже – lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar005.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://alku.fi/laihdu-10-kg-nopeasti
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Долго искал решение и наконец-то нашел:
По теме “buytime.ru”, нашел много полезного.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://buytime.ru]https://buytime.ru[/url]
Давайте обсудим это подробнее.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Подробнее тут – https://toonpet.com/toonpet_logo-01-2
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья для ознакомления предлагает читателям общее представление об актуальной теме. Мы стремимся представить ключевые факты и идеи, которые помогут читателям получить представление о предмете и решить, стоит ли углубляться в изучение.
Выяснить больше – https://thaimassage-remscheid.de/?attachment_id=9
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Подробнее тут – https://elsardinero.org/el-primer-ensayo-controlado-en-humanos-muestra-que-reducir-las-calorias-mejora-la-salud-y-la-longevidad
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1562924-25-servisov-i-besplatnye-metody-nakrutki-v-instagram-v-2025-godu
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar005.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш сайт является архитектурным и культурным путеводителем по Венеции, здесь Вы найдете информацию о великолепных достопримечательностях этого города: venice4you.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Выяснить больше – https://custompackaginginfo.com/small-business-big-impressions-packaging-as-a-marketing-tool
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта доказательная статья представляет собой глубокое погружение в успехи и вызовы лечения зависимостей. Мы обращаемся к научным исследованиям и опыте специалистов, чтобы предоставить читателям надежные данные об эффективности различных методик. Изучите, что работает лучше всего, и получите информацию от экспертов.
Разобраться лучше – https://put-sily.ru/izbavlenie-ot-zapoya-metody-vyvedeniya-na-domu
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
заказать экскаватор на час https://arenda-ehkskavatora-1.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкоголь и наркотики воздействуют на организм комплексно: нарушается работа сердца, сосудов, печени и почек, страдает нервная система. При запое или ломке без квалифицированной помощи возникают судороги, делирий, галлюцинации и серьёзные сбои в обмене веществ. Самостоятельные попытки «перетерпеть» или «отмотать» запой зачастую приводят к тяжёлым осложнениям, вплоть до комы и необратимых изменений в органах.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости требуют незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства. Длительные запои или острое отравление могут привести к тяжелым осложнениям и серьезным проблемам со здоровьем. Клиника «МедТрезвость» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает квалифицированную наркологическую помощь прямо на дому, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность пациента. Наши специалисты оперативно выезжают по адресу, проводят все необходимые процедуры и помогают максимально быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента в комфортных домашних условиях.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя санкт-петербург[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наше время наличие качественного интернета является важным условием для многих домохозяйств. Семьям с несколькими членами необходимо подобрать оптимального провайдера, предоставляющего высокую скорость и стабильное соединение. На сайте domashij-internet-ekaterinburg005.ru вы найдете доступные тарифы на интернет с семейными пакетами, которые обеспечивают подключение для семьи, поддерживающее много устройств одновременно. Такой тариф оптимален для дистанционного обучения, онлайн-обучения и потока видео. Наряду с этим роутеры для большого дома предоставляют стабильный Wi-Fi , что дает возможность всем членам семьи пользоваться интернетом без ограничений. Выбирая интернет для игр, нужно учитывать провайдеров с высокой скоростью и возможностью подключения нескольких пользователей, чтобы избежать задержек и сбоев.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar004.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ставки онлайн Букмекеры с минимальным депозитом позволяют начать делать ставки с небольшим бюджетом. Это отличный вариант для новичков, которые хотят протестировать свои навыки.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для обеспечения оперативности «НаркоМед» сформировала несколько мобильных бригад, размещённых по разным районам города. Каждая бригада оснащена портативными инфузионными насосами, современными измерительными приборами и запасом медикаментов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ekaterinburg0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В «Чистом Дыхании» вы встретите врачей-наркологов, психиатров и психологов с многолетним опытом, готовых приехать на дом для первичной детоксикации или принять в стационаре для углублённой терапии. Мы соблюдаем строгие медицинские протоколы и гарантируем безопасность даже в самых тяжёлых случаях.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкоголь и наркотики воздействуют на организм комплексно: нарушается работа сердца, сосудов, печени и почек, страдает нервная система. При запое или ломке без квалифицированной помощи возникают судороги, делирий, галлюцинации и серьёзные сбои в обмене веществ. Самостоятельные попытки «перетерпеть» или «отмотать» запой зачастую приводят к тяжёлым осложнениям, вплоть до комы и необратимых изменений в органах.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение запоя
narkolog-krasnodar004.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение к врачу становится жизненно необходимым, если пациент находится в состоянии длительного запоя, при котором организм не справляется с накоплением токсинов. Если запой продолжается более двух-трёх дней, в теле накапливаются вредные вещества, что ведёт к нарушениям работы внутренних органов, развитию абстинентного синдрома и появлению психических нарушений. Также, если у пациента наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие скачки артериального давления, это сигнал к незамедлительному вызову специалиста. При выраженной абстинентной реакции с паническими атаками, сильной дрожью, бессонницей и эмоциональной нестабильностью самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Если появляются признаки алкогольного психоза – галлюцинации, агрессивность или спутанность сознания – вызов нарколога становится обязательным для предотвращения дальнейших осложнений. Также, когда требуется подготовка к процедурам кодирования от зависимости, необходима качественная детоксикация организма, что также является показанием к срочному обращению за профессиональной помощью.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-ekb/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты клиники «НаркоМед» полностью застрахованы от утечки личной информации. Приём и лечение оформляются по псевдониму, документы не передаются в другие организации.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ekaterinburg0.ru/]наркологическая клиника екатеринбург.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент получает индивидуальный план лечения, основанный на клинических исследованиях, данных лабораторных анализов и психологических тестов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты клиники «НаркоМед» полностью застрахованы от утечки личной информации. Приём и лечение оформляются по псевдониму, документы не передаются в другие организации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ekaterinburg0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-otzyvy-v-ekb
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Екатеринбурге выбор интернет провайдеров по адресу велик. Основные услуги связи включают интернет высокой скорости, который необходим для комфортного пользования. При выборе провайдера необходимо обратить внимание на тарифы на интернет, безлимитные тарифы и оптоволоконный интернет. интернет провайдеры Екатеринбург по адресу Также существуют удобные варианты подключения к интернету, что позволяет оставаться на связи даже вдали от города. Сравнение провайдеров поможет выбрать оптимальный вариант. Отзыв о провайдерах в Екатеринбурге помогает понять качество их услуг и стабильность соединения. Для установки интернета в квартире или доме часто предлагается Wi-Fi для дома, что обеспечивает доступ ко всем устройствам. Понимание всех этих аспектов позволит сделать правильный выбор и наслаждаться всеми преимуществами интернета.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все о тендерах, актуальная новости и информация: st-tender
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar003.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проблема алкогольной зависимости требует срочного вмешательства, ведь чем дольше человек находится в запое, тем выше риск серьезных осложнений для его здоровья. Наркологическая клиника «Трезвый Путь» предоставляет услуги нарколога на дом в Екатеринбурге, гарантируя круглосуточную помощь и эффективное решение проблемы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/zapoj-narkolog-na-dom-ekb
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
– затяжной запой более 5–7 дней; – наличие галлюцинаций, судорог, бредовых состояний; – тяжёлое общее состояние (высокая температура, спутанность сознания, обезвоживание); – хронические болезни в стадии обострения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов нарколога на дом от клиники «Трезвый Путь» имеет ряд неоспоримых преимуществ, которые высоко ценят наши пациенты:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш сайт является архитектурным и культурным путеводителем по Венеции, здесь Вы найдете информацию о великолепных достопримечательностях этого города: venice4you.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://vc.ru/niksolovov/1566936-25-servisov-i-sovety-po-nakrutke-podpischikov-vk-v-2025-godu
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
led экран без рамок СанПиН учебные кабинеты Безопасность и здоровье учащихся — абсолютный приоритет при оснащении любого учебного помещения. Все проекты компании «Astana IT Garant» разрабатываются и реализуются в строгом соответствии с действующими Санитарными правилами и нормами (СанПиН), предъявляемыми к учебным кабинетам. Мы уделяем этому аспекту первостепенное внимание. При проектировании мы учитываем нормы площади на одного учащегося, требования к естественному и искусственному освещению, чтобы обеспечить достаточный уровень освещенности рабочих мест и избежать нагрузки на зрение. Вся поставляемая нами мебель (парты, стулья) подбирается в соответствии с росто-возрастными группами учащихся, что способствует формированию правильной осанки. Мы используем только сертифицированные, экологически чистые отделочные материалы, которые не выделяют вредных веществ. Особое внимание уделяется электробезопасности: вся проводка выполняется в соответствии с правилами, розетки имеют защитные механизмы. В кабинетах химии мы обеспечиваем наличие эффективной приточно-вытяжной вентиляции и используем мебель с химически стойким покрытием. Обращаясь в «Astana IT Garant», руководство учебного заведения может быть полностью уверено, что оснащенные нами кабинеты не только современны и функциональны, но и абсолютно безопасны для здоровья детей и успешно пройдут любую проверку санитарно-эпидемиологической службы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выездной формат позволяет избежать контактов с другими пациентами в клинике и очистить организм в привычной обстановке. Специалисты самостоятельно привозят весь необходимый набор медикаментов и расходных материалов.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ekaterinburg0.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все о тендерах, актуальная новости и информация: https://st-tender.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
создание контента для бизнеса Маркетолог услуги охватывают широкий спектр задач, от разработки стратегии до реализации конкретных рекламных кампаний.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чтобы обеспечить безопасное выведение психоактивных веществ и восстановление организма, применяется детоксикация под контролем врача-нарколога и анестезиолога-реаниматолога.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://lechenie-narkomanii-arkhangelsk0.ru/czentr-lecheniya-narkomanii-arkhangelsk/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша команда врачей оперативно реагирует на каждый вызов, оказывая квалифицированную медицинскую помощь на дому. Специалисты проводят полный комплекс лечебных мероприятий, направленных на безопасное снятие интоксикации, детоксикацию и облегчение симптомов абстиненции.
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вывод из запоя — это не просто капельница, а многоуровневая медицинская процедура, направленная на устранение интоксикации, стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение осложнений. В клинике «Жизненный Луч» мы проводим эту процедуру в домашних условиях и в стационаре, в зависимости от тяжести состояния. К каждому пациенту применяем индивидуальный подход, исходя из возраста, сопутствующих заболеваний и длительности запоя.
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя цена
narkolog-krasnodar003.ru
лечение запоя краснодар
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
phomi гибкая керамика Гибкая керамика Москва подходит для отделки как жилых, так и коммерческих помещений, обеспечивая эстетичный и современный внешний вид.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На втором этапе с пациентом работают психотерапевты, используя когнитивно-поведенческие и мотивационные техники. Основная задача — изменить стереотипы мышления и поведения, приводящие к употреблению веществ.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-ekaterinburg0.ru/]лечение наркомании нарколог[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
недорогой интернет челябинск
domashij-internet-chelyabinsk006.ru
подключить интернет тарифы челябинск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar002.ru
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова на дом врачи клиники «Трезвый Путь» проводят лечение по четко разработанному алгоритму, обеспечивающему максимальную эффективность и безопасность:
Выяснить больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова на дом врачи клиники «Трезвый Путь» проводят лечение по четко разработанному алгоритму, обеспечивающему максимальную эффективность и безопасность:
Разобраться лучше – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-ekb
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Прежде чем принимать решение, важно изучить сайт клиники. В надёжных учреждениях размещена полная информация о врачах, их образовании и опыте работы. Кроме того, пациентам предлагается пройти предварительную консультацию — чаще всего она проводится анонимно и включает первичную диагностику. Это позволяет оценить профессионализм команды ещё до начала терапии.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-yaroslavl0.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-telefon-yaroslavl
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Круглосуточная клиника «НаркоЦентр» предлагает широкий спектр наркологических услуг в Екатеринбурге и области. В числе основных направлений — выезд врача на дом, проведение детоксикационных процедур, индивидуальные программы восстановления, врачебное сопровождение в стационаре, а также психологическая и физиотерапевтическая реабилитация. Мы опираемся на международные стандарты терапии и применяем только сертифицированные препараты, что гарантирует безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-ekaterinburg0.ru/vyzvat-narkologicheskuyu-pomoshh-v-ekb/https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-ekaterinburg0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Woodworking and construction https://www.woodsurfer.com forum. Ask questions, share projects, read reviews of materials and tools. Help from practitioners and experienced craftsmen.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь на дому становится всё более востребованной благодаря своей доступности, конфиденциальности и эффективности. Клиника «МедТрезвость» предлагает пациентам целый ряд важных преимуществ:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-spb/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
можно ли в турции Турция – страна контрастов, где древняя история переплетается с современным комфортом. Бирюзовое море, золотые пляжи и величественные горы создают неповторимую атмосферу для отдыха.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
GPS-мониторинг транспорта: полный контроль за автопарком
https://t.me/s/kupit_gruzoviki/200
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В программе используются когнитивно-поведенческая терапия, мотивационное интервьюирование, арт- и телесно-ориентированные практики. Занятия помогают пациенту осознать причины употребления, выработать навыки управления эмоциями и стрессом, сформировать устойчивую внутреннюю мотивацию к отказу от вещества.
Подробнее тут – https://lechenie-narkomanii-arkhangelsk0.ru/lechenie-narkomanii-anonimno-arkhangelsk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
нейросеть создать сайт https://sozday-sayt-s-ai.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Конфиденциальность обеспечивается отдельными блоками для каждого этапа лечения и строгим пропускным режимом. Пациент получает круглосуточную поддержку по телефону даже после выписки для предотвращения рецидива.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-ekaterinburg0.ru/]lechenie narkomanii i alkogolizma ekaterinburg[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Миссия клиники “Обновление” заключается в предоставлении качественной и всесторонней помощи людям, страдающим от различных форм зависимости. Мы понимаем, что успешное лечение невозможно без индивидуального подхода, поэтому каждый пациент проходит детальную диагностику, после которой разрабатывается персонализированный план терапии. В процессе работы мы акцентируем внимание на следующих аспектах:
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя в иркутске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Преимущество
Разобраться лучше – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
домашний интернет в челябинске
domashij-internet-chelyabinsk005.ru
домашний интернет подключить челябинск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
доступные компьютеры требования МОН РК кабинеты Деятельность каждого учебного заведения в Казахстане регулируется нормативными документами Министерства образования и науки Республики Казахстан (МОН РК). Требования МОН РК к учебным кабинетам являются основополагающими при их оснащении, и компания «Astana IT Garant» гарантирует их стопроцентное соблюдение. Эти требования носят комплексный характер. Они определяют минимальный перечень учебного оборудования, наглядных пособий, мебели и технических средств, необходимых для полноценной реализации образовательных программ по каждому предмету. При комплектации любого кабинета, будь то начальный класс или специализированная лаборатория, наши специалисты в первую очередь руководствуются актуальными приказами и нормативами МОН РК. Мы гарантируем, что каждый элемент в нашей спецификации соответствует или превосходит требования министерства. Кроме того, требования МОН РК затрагивают и вопросы безопасности, и санитарные нормы, и правила расстановки мебели. «Astana IT Garant» берет на себя полную ответственность за соответствие наших проектов всем этим аспектам. Сотрудничая с нами, руководство школы может быть абсолютно уверено, что оснащенные кабинеты не вызовут никаких вопросов при проверках и аттестации, так как они созданы в строгом соответствии с буквой и духом государственных образовательных стандартов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar001.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
экстренный вывод из запоя
narkolog-krasnodar002.ru
экстренный вывод из запоя краснодар
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
разработка позиционирования Маркетолог цена услуги зависит от объема работ и опыта специалиста.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Надувные лодки ПВХ Badger https://badgerboats.ru от надёжного производителя. Широкий выбор моделей: от компактных до моторных.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лазерная косметология https://actual-cosmetology.ru в клинике премиум-уровня. Новейшие технологии, сертифицированные специалисты, комфортная атмосфера и заметный результат.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://talleresmelli.com/%D0%B7%D0%B5%D1%80%D0%BA%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%BE-%D0%BA%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BA%D0%B5%D0%BD-onion-darknet-kraken-%D1%81%D0%B0%D0%B9%D1%82
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://www.sarahdarkmagic.com/content/lego-ad-girl?page=5
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация обращает внимание на важность профилактики зависимостей. Мы обсудим, как осведомленность и образование могут помочь в предотвращении возникновения зависимости. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с полезными советами и ресурсами, которые способствуют здоровому образу жизни.
Узнать больше – https://prosimptomy.ru/doctor-136-ru-statsionarnoe-lechenie
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Разобраться лучше – https://richlife2020.com/download/gmma%CE%B1
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
интернет тарифы челябинск
domashij-internet-chelyabinsk004.ru
подключить домашний интернет челябинск
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://macdebtcollection.com/remove-arrest-orders-of-rental-dispute-cases-in-dubai
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Загородный клуб https://yct.su в Зеленогорске — отдых на берегу Финского залива. Комфортабельные коттеджи, баня, ресторан, мероприятия и природа рядом с Петербургом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Центр независимой сертификации https://radiocert.ru помощь в получении сертификатов ISO, ГОСТ, ТР ТС и других документов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение запоя краснодар
narkolog-krasnodar001.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Углубиться в тему – https://trimunlamdep.com/serum-tri-mun-rau-ngo
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
היו לא נוחים מדי, והיא מעולם לא יכלה לקנות אחד נוח מספיק כדי להתאים את השדיים שלה לתוכו. הקלפים ואיגור חתך אותם במספריים. ואז הוא הוציא 15,000 רובל מהארנק. – הנה הכסף עבור דלק read link
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя круглосуточно
narkolog-krasnodar001.ru
вывод из запоя цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Разобраться лучше – http://backupteleinformatica.com.br/?p=94
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
לא היה במשרד, ורציתי לנוח, פיזרתי גיליונות של ניירות על הרצפה, והתחלתי לאסוף הכל באלף-בית כמו כלבה בחום,” הוא לחש, נוגע בשפתיים באוזנה, נשימתו החמה שורפת את עורה. – אני אמתח אותך כך נערות ליווי ערביות
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi there, You’ve done a fantastic job. I?ll definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I am sure they will be benefited from this web site.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта медицинская заметка содержит сжатую информацию о новых находках и методах в области здравоохранения. Мы предлагаем читателям свежие данные о заболеваниях, профилактике и лечении. Наша цель — быстро и доступно донести важную информацию, которая поможет в повседневной жизни и понимании здоровья.
Разобраться лучше – http://laform.ru/zdorov-e/kak-proisxodit-kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье мы рассматриваем разные способы борьбы с алкогольной зависимостью. Обсуждаются методы лечения, программы реабилитации и советы для поддержки близких. Читатели получат информацию о том, как преодолеть зависимость и добиться успешного выздоровления.
Выяснить больше – https://fermerpetrov.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezheeffektivnoe-reshenie-problemy-alkogolnoj-zavisimosti-kapelnica-ot-zapoya-na-domu-v-voronezhe
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://nncs.es/animate-a-participar-en-las-iv-jornadas-nacionales-de-dano-cerebral-andando-se-hace-el-camino-nncs
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждая выездная бригада укомплектована портативным лабораторным оборудованием для экспресс-анализов крови и мочи, современными инфузионными насосами и средствами телеметрии. Это позволяет врачу контролировать жизненно важные параметры пациента в режиме реального времени и корректировать схему детоксикации на месте.
Подробнее тут – наркологическая клиника нарколог в тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы предложим ряд рекомендаций по избавлению от зависимостей и успешному восстановлению. Мы обсудим методы привлечения поддержки и важность самосознания. Эти советы помогут людям вернуться к нормальной жизни и стать на путь выздоровления.
Узнать больше – https://aaukg.ru/effektivnost-uslugi-vyzova-narkologa-na-dom-v-klinike-trezvyy-shag
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот медицинский обзор сосредоточен на последних достижениях, которые оказывают влияние на пациентов и медицинскую практику. Мы разбираем инновационные методы лечения и исследований, акцентируя внимание на их значимости для общественного здоровья. Читатели узнают о свежих данных и их возможном применении.
Углубиться в тему – https://ii4.ru/poleznosti/14220-vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-udobstvo-i-effektivnost-v-lechenii-zavisimostey
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Продвижение сайтов https://optimizaciya-i-prodvizhenie.ru в Google и Яндекс — только «белое» SEO. Улучшаем видимость, позиции и трафик. Аудит, стратегия, тексты, ссылки.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Агентство контекстной рекламы https://kontekst-dlya-prodazh.ru настройка Яндекс.Директ и Google Ads под ключ. Привлекаем клиентов, оптимизируем бюджеты, повышаем конверсии.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Фрибеты за регистрацию Ставки онлайн – это удобство и доступность. Делайте ставки в любое время и в любом месте, используя свой компьютер или мобильное устройство.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основные показания для вызова нарколога:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-irkutsk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При поступлении или выезде на дом врач-нарколог собирает анамнез, оценивает степень зависимости, измеряет жизненные показатели и назначает необходимые анализы. Цель — исключить противопоказания и выбрать оптимальную схему терапии.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]наркологическая клиника здоровье[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
телеграм санкт петербург Экскурсии в Питере: Незабываемые впечатления от посещения музеев, театров и парков города
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой – это состояние, когда организм требует постоянного поступления алкоголя для нормальной работы. Запой вызывает накопление вредных веществ, что негативно влияет на органы и иммунную систему. Не пытайтесь самостоятельно избавиться от запоя, это может навредить. Получите квалифицированную помощь на дому от клиники «Семья и Здоровье». Мы быстро приедем и окажем круглосуточную поддержку при запое. Длительное употребление алкоголя опасно для здоровья и жизни. Не ждите, пока станет слишком поздно, обратитесь за помощью при запое!
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-krasnoyarsk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто бытовое пьянство, а одно из наиболее опасных проявлений алкогольной зависимости. Во время запоя организм перестаёт функционировать в нормальном режиме: сердечно-сосудистая система работает на износ, нервная система перегружена токсинами, а печень не справляется с нагрузкой. На этом фоне могут возникать тяжёлые осложнения — от судорог и гипогликемии до нарушения дыхания и алкогольного психоза. Чем дольше длится запой, тем глубже метаболические нарушения и выше риск серьёзных последствий.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Путь к свободе от зависимости начинается не с обещаний «просто перестать», а с профессионального медицинского вмешательства. В «Чистом Дыхании» мы применяем проверенные методы, которые работают там, где сила воли без нужной поддержки оказывается бессильной. Наша клиника в Долгопрудном работает круглосуточно — чтобы помощь была доступна в самый критический момент, когда человек ощущает острую потребность в детоксикации, снятии абстинентного синдрома или психологической поддержке.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экстренный вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске от «ТрезвоМед» при запое, интоксикации или кодировании – анонимно и удобно. Осмотр, детоксикация капельницей, индивидуальный план лечения – все это на дому! «ТрезвоМед» – круглосуточная помощь, анонимность и безопасность при отказе от алкоголя. Не можете бросить пить самостоятельно? Нужна помощь нарколога! Васильев: «Своевременная помощь при интоксикации – залог успешного выздоровления».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом цена в иркутске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто бытовое пьянство, а одно из наиболее опасных проявлений алкогольной зависимости. Во время запоя организм перестаёт функционировать в нормальном режиме: сердечно-сосудистая система работает на износ, нервная система перегружена токсинами, а печень не справляется с нагрузкой. На этом фоне могут возникать тяжёлые осложнения — от судорог и гипогликемии до нарушения дыхания и алкогольного психоза. Чем дольше длится запой, тем глубже метаболические нарушения и выше риск серьёзных последствий.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости требуют незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства. Длительные запои или острое отравление могут привести к тяжелым осложнениям и серьезным проблемам со здоровьем. Клиника «МедТрезвость» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает квалифицированную наркологическую помощь прямо на дому, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность пациента. Наши специалисты оперативно выезжают по адресу, проводят все необходимые процедуры и помогают максимально быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента в комфортных домашних условиях.
Подробнее тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Во-первых, мы фокусируемся на медицинской детоксикации, которая является первоочередной задачей при лечении зависимостей. Этот процесс позволяет удалить токсические вещества из организма и улучшить общее состояние пациента. Мы применяем современные методики, которые помогают минимизировать симптомы абстиненции и обеспечить комфортное пребывание в клинике.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-irkutsk.ru/]капельница от запоя выезд в иркутске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При лёгких и среднетяжёлых состояниях возможно проведение лечения на дому. Это удобно, комфортно и позволяет сохранить анонимность. Однако есть ситуации, в которых домашнее вмешательство нецелесообразно:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]bystryj-vyvod-iz-zapoya[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Путь к свободе от зависимости начинается не с обещаний «просто перестать», а с профессионального медицинского вмешательства. В «Чистом Дыхании» мы применяем проверенные методы, которые работают там, где сила воли без нужной поддержки оказывается бессильной. Наша клиника в Долгопрудном работает круглосуточно — чтобы помощь была доступна в самый критический момент, когда человек ощущает острую потребность в детоксикации, снятии абстинентного синдрома или психологической поддержке.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительство бассейнов премиального качества. Строим бетонные, нержавеющие и композитные бассейны под ключ https://pool-profi.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости требуют незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства. Длительные запои или острое отравление могут привести к тяжелым осложнениям и серьезным проблемам со здоровьем. Клиника «МедТрезвость» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает квалифицированную наркологическую помощь прямо на дому, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность пациента. Наши специалисты оперативно выезжают по адресу, проводят все необходимые процедуры и помогают максимально быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента в комфортных домашних условиях.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом санкт-петербург[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительство бассейнов премиального качества. Строим бетонные, нержавеющие и композитные бассейны под ключ https://pool-profi.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наши специалисты применяют только сертифицированные и проверенные препараты. В их число входят детоксикационные растворы (глюкоза, физраствор, растворы Рингера), гепатопротекторы для восстановления печени, кардиопротекторы для нормализации сердечной деятельности, витамины и седативные препараты, позволяющие успокоить нервную систему, улучшить сон и снять тревожность. Индивидуальный подход врача позволяет подобрать именно тот набор медикаментов, который будет наиболее эффективен и безопасен в каждом конкретном случае.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После прибытия врач проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает его состояние, измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода и выявляет возможные противопоказания. Затем разрабатывается индивидуальный план лечения, направленный на стабилизацию состояния.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]narkolog na dom[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Спортивные ставки Новые букмекеры появляются на рынке регулярно, предлагая игрокам свежие возможности и инновационные решения. Конкуренция заставляет их предлагать более выгодные условия, интересные бонусы и расширенный выбор спортивных событий. Прежде чем доверить свои средства новому букмекеру, важно убедиться в его надежности и наличии лицензии, а также ознакомиться с отзывами других пользователей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша миссия заключается в предоставлении качественной помощи людям, страдающим от зависимостей. Мы стремимся создать безопасную и поддерживающую атмосферу, где каждый сможет получить необходимую помощь. Основная цель — восстановление здоровья, психоэмоционального состояния и социальной адаптации.
Подробнее – [url=https://tajnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-omske.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
римские шторы Какие шторы выбрать — вопрос, требующий учета многих факторов: стиля комнаты, освещенности, размеров окон и личных предпочтений. Среди популярных вариантов — классические тканевые шторы, рулонные и римские модели, а также шторы блэкаут для полной затемненности. Консультация с дизайнером помогает подобрать оптимальный вариант.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Специальный экран для видеопроектора обеспечивает превосходную четкость и цветопередачу при воспроизведении динамичного видео. Выберите модель экран для видеопроектора.
Экран для проектора — это ключевой компонент, обеспечивающий высокое качество изображения. Оптимальный экран может оказать заметное влияние на общий результат демонстрации.
Различают несколько видов экранов: переносные, стационарные и настенные. Каждый из этих типов имеет свои особенности и преимущества.
При выборе экрана следует принимать во внимание габариты комнаты и характеристики проектора. Оптимальные размеры экрана зависят от расстояния от него до зрителей.
Для наилучшего восприятия изображения рекомендуется учитывать уровень освещения в помещении. При наличии яркого света лучше выбрать экран с матовым покрытием.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
изготовление наружной рекламы цена https://papa-promotion.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
подобрать подшипник по размерам Подшипники от производителей – это гарантия качества и соответствия техническим требованиям. Приобретая продукцию напрямую у изготовителя, вы избегаете посредников и получаете лучшие цены.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основные показания для вызова нарколога:
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]нарколог на дом иркутск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске и Иркутской области — это удобное и безопасное решение, позволяющее получить неотложную помощь в привычной обстановке. Врачи клиники «ЧистоЖизнь» выезжают круглосуточно, приезжают в течение 30–60 минут и проводят комплексное лечение, направленное на стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]вызов нарколога цена иркутск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вот здесь можно найти больше примеров:
По теме “musichunt.pro”, есть отличная статья.
Вот, можете почитать:
[url=https://musichunt.pro]https://musichunt.pro[/url]
Может, у кого-то есть другой опыт?
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чем раньше проведена детоксикация, тем меньше риск развития серьезных последствий, таких как инфаркт, инсульт, алкогольный психоз, цирроз печени.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva0.ru/]капельница от запоя цена москва.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Особенно уязвимыми становятся люди старше 45 лет, а также пациенты с сахарным диабетом, гипертонией, эпилепсией и болезнями печени. При этом многие продолжают надеяться, что «само пройдёт» — и упускают момент, когда помочь ещё можно без реанимации. Наша клиника организует выезд врача в течение 40–60 минут, чтобы не терять драгоценное время.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-kolomne[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Студия дизайна Интерьеров в СПБ. Лучшие условия для заказа и реализации дизайн-проектов под ключ https://cr-design.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимости требуют незамедлительного медицинского вмешательства. Длительные запои или острое отравление могут привести к тяжелым осложнениям и серьезным проблемам со здоровьем. Клиника «МедТрезвость» в Санкт-Петербурге предлагает квалифицированную наркологическую помощь прямо на дому, обеспечивая полную конфиденциальность и безопасность пациента. Наши специалисты оперативно выезжают по адресу, проводят все необходимые процедуры и помогают максимально быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента в комфортных домашних условиях.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Петербург телеграм Телеграм Санкт-Петербург: Все самое интересное и важное о жизни города на Неве. Обсуждение городских проблем, афиша мероприятий, полезные советы для жителей и туристов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Особенно уязвимыми становятся люди старше 45 лет, а также пациенты с сахарным диабетом, гипертонией, эпилепсией и болезнями печени. При этом многие продолжают надеяться, что «само пройдёт» — и упускают момент, когда помочь ещё можно без реанимации. Наша клиника организует выезд врача в течение 40–60 минут, чтобы не терять драгоценное время.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]вывод из запоя стационар[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске и Иркутской области — это удобное и безопасное решение, позволяющее получить неотложную помощь в привычной обстановке. Врачи клиники «ЧистоЖизнь» выезжают круглосуточно, приезжают в течение 30–60 минут и проводят комплексное лечение, направленное на стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение осложнений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом платный в иркутске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой – это не просто пьянство, а состояние, когда организм становится зависимым от алкоголя. Накопление токсинов приводит к сбоям в работе органов и ослаблению защиты организма. Самостоятельный выход из запоя может быть опасен и только усугубить состояние. Мы предлагаем лечение запоя на дому, чтобы избежать больницы и создать комфорт. Наши специалисты быстро приедут к вам и окажут всю необходимую помощь круглосуточно. Запой приводит к серьезным проблемам со здоровьем, ухудшает качество жизни и угрожает жизни. Очень важно вовремя обратиться за помощью, чтобы избежать необратимых последствий.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]клиника вывод из запоя красноярск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Подшипники купить от производителя Подшипники купить от производителя – это возможность получить квалифицированную консультацию и подобрать оптимальный тип подшипника для конкретного оборудования.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
гибкая керамика Phomi гибкая керамика цена за 1 м2 делает этот материал доступным выбором как для частных заказчиков, так и для коммерческих проектов. Возможность заказать точное количество снижает отходы и экономит средства.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-oblasti[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужна срочная помощь при алкогольном отравлении или запое? Вызовите нарколога на дом в Иркутске! Квалифицированная помощь нарколога на дому: диагностика, капельница, стабилизация состояния. Круглосуточный выезд нарколога, анонимность и снижение рисков – с «ТрезвоМед». Самостоятельный отказ невозможен? Необходима наркологическая помощь. Васильев: «Не затягивайте с помощью при алкогольном отравлении!».
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в иркутске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как проходит лечение:
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/narkolog-lechenie-na-domu-novokuzneczk/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
•очешь продать авто? telegram канал продажа авто
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основной этап – введение внутривенной капельницы с специально разработанными растворами. Эти растворы содержат электролиты, витамины и активные компоненты, способствующие быстрому выведению токсинов, восстановлению водно-солевого баланса и улучшению обмена веществ. Детоксикация позволяет снизить концентрацию алкоголя в крови, уменьшить симптомы абстиненции и подготовить организм к последующим этапам терапии.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]платный нарколог на дом в красноярске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все вызовы фиксируются под кодовым номером без указания ФИО, что обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность каждого пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir10.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника владимир[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
штора без Как правильно выбрать шторы — важный процесс, включающий учет стиля, функциональности и особенностей помещения. Хорошо подобранные шторы способны преобразить комнату и сделать ее уютнее.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто бытовое пьянство, а одно из наиболее опасных проявлений алкогольной зависимости. Во время запоя организм перестаёт функционировать в нормальном режиме: сердечно-сосудистая система работает на износ, нервная система перегружена токсинами, а печень не справляется с нагрузкой. На этом фоне могут возникать тяжёлые осложнения — от судорог и гипогликемии до нарушения дыхания и алкогольного психоза. Чем дольше длится запой, тем глубже метаболические нарушения и выше риск серьёзных последствий.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]быстрый вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Greetings, witty comedians !
Jokes for adults clean for the office – http://jokesforadults.guru/# good jokes for adults
May you enjoy incredible memorable laughs !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой – тяжелое состояние, когда организм не может функционировать без алкоголя. Токсины накапливаются, органы перестают работать, иммунитет слабеет. Это очень опасно. Самостоятельные попытки выйти из запоя только ухудшают ситуацию и усиливают страдания. Клиника «Семья и Здоровье» предлагает лечение на дому, без стресса и в комфортной обстановке. Мы работаем круглосуточно, быстро приезжаем и проводим все необходимые процедуры. Длительный запой разрушает организм, ухудшает качество жизни и может привести к опасным ситуациям. Своевременный вывод из запоя — это критически важно для сохранения здоровья и жизни.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/]https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnoyarsk0.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой, интоксикация? Вызовите нарколога на дом в Иркутске для быстрой и анонимной помощи. На дому: осмотр, подбор лечения, капельница для вывода токсинов и улучшение самочувствия. «ТрезвоМед» – круглосуточная наркологическая помощь на дому с гарантией анонимности. Не справляетесь с зависимостью сами? Вызовите нарколога на дом. Васильев подчеркивает: «Оперативная помощь – ключ к выздоровлению при отравлении алкоголем».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом цена в иркутске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино Казино, предлагающие бездепозитные бонусы, словно заботливые хозяева, приглашают гостей в свой дом и предлагают им угощение на пробу. Это не просто щедрость, а продуманный маркетинговый ход, направленный на привлечение новых клиентов и формирование лояльности к бренду. Это возможность для игроков оценить качество сервиса, разнообразие игр и удобство платформы, прежде чем делать депозит. Это своеобразная гарантия, что казино уверено в своих силах и готово предоставить игрокам наилучший опыт. Бездепозитный бонус
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
מוכנה וזה היה מטריף. “תוריד את זה,” אמרתי, וקולי היה צרוד, זר. אניה הביטה בי, חייכה-שיכורה, זאת, יהיה קשה יותר! אבל הרעיון לנקום בשני אלה היה גם הפוך. הסיכוי לקבל סרטונים, למשל על ידי נערת ליווי במרכז
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мечтаете о расслабляющем отпуске у моря? Легко и быстро отдохнуть в абхазии вам поможет наш сервис прямого бронирования.
Абхазия предлагает чудесные условия для отдыха и незабываемые впечатления. Её живописные пейзажи, мягкий климат и теплое море привлекают туристов со всего мира.
Каждый год миллионы людей стремятся посетить Абхазию, чтобы насладиться её красотой. Отдых в Абхазии предлагает как спокойные пляжные дни, так и захватывающие приключения.
Выбор жилья в Абхазии впечатляет: от уютных гостевых домов до современных гостиниц. Местные рестораны предлагают множество блюд, которые позволят погрузиться в атмосферу страны.
Независимо от времени года, отпуск в Абхазии будет незабываемым и полным позитивных эмоций. Посетите Абхазию, и вы сможете насладиться её природными красотами и культурным наследием.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://b2tor2.cc/blaksprut_ssylka.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительство бассейнов премиального качества. Строим бетонные, нержавеющие и композитные бассейны под ключ https://pool-profi.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://ukrbeautystyle.com.ua/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Детальнее – http://www.oasisdetetir.com/construcciones-en-fuerteventura-tetir
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://guidomoens.be/?p=272
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Разобраться лучше – https://www.cempi2.it/marina-di-rimini
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Разобраться лучше – https://789win.vodka/ban-ca-xeng
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Детальнее – https://www.bendigometalworks.com/2018/06/29/bendigo-metalworks
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://bs2cite.cc
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://cermam.com.br/como-escolher-a-especialidade-na-residencia-medica
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Подробнее – https://manualosteopaths.org/2019/09/19/we-are-in-the-process-of-building-a-french-language-website-for-the-college-of-registered-manual-osteopaths-canada-crmo-french-language-logo-has-already-been-designed
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию 1000 рублей без депозита
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://www.amonusa.com/?p=63
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://joodalarab.com/in-viverra-faucibus-tellus-sed-cursus-quam-fringilla-sit-amet-7
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Разобраться лучше – https://nepalipedia.com/entertainment/top-ten-places-to-visit-in-surkhet-district
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Такси в аэропорт Праги – надёжный вариант для тех, кто ценит комфорт и пунктуальность. Опытные водители доставят вас к терминалу вовремя, с учётом пробок и особенностей маршрута. Заказ можно оформить заранее, указав время и адрес подачи машины. Заказать трансфер можно заранее онлайн, что особенно удобно для туристов и деловых путешественников: дешевое такси в аэропорт прага
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Серьезные состояния, вызванные длительным употреблением алкоголя или наркотиков, требуют немедленного вмешательства. Если пациент испытывает ухудшение самочувствия вследствие продолжительного запоя, его организм начинает накапливать токсичные вещества, что ведёт к нарушению работы внутренних органов. При появлении таких симптомов, как сильная рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги, резкие скачки артериального давления, а также выраженные признаки абстинентного синдрома (сильная дрожь, панические атаки, бессонница, тревожность), вызов нарколога становится жизненно необходимым. Экстренное вмешательство позволяет стабилизировать состояние больного и предотвратить развитие серьёзных осложнений, включая сердечно-сосудистые нарушения, повреждение печени и развитие алкогольного психоза. В таких ситуациях профессиональное лечение на дому — лучший способ сохранить здоровье и жизнь пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]анонимная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
והביא את הזרע לרתיחה. היא התחילה ללקק את הביצים שלו תוך שאיבת הזין שלו ביד. קתרין החלה לקפוץ הזה, שבונים לו עיניים. – הבנת מה אתה צריך ללמוד? – אמר המנהל בסוף יום העבודה-יש חבורה של סקס בדרום תל אביב
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительство бассейнов премиального качества. Строим бетонные, нержавеющие и композитные бассейны под ключ https://pool-profi.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://b2shop.gl/blacksprut.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Группа препаратов
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом свердловская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для эффективного лечения наши врачи используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента. В состав лечебного курса входят:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент получает индивидуальный план лечения, основанный на клинических исследованиях, данных лабораторных анализов и психологических тестов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]наркологическая клиника в области[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
LMC Middle School https://lmc896.org in Lower Manhattan provides a rigorous, student-centered education in a caring and inclusive atmosphere. Emphasis on critical thinking, collaboration, and community engagement.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используя современные инфузионные системы, мы постепенно вводим растворы для выведения токсинов, коррекции водно-электролитного баланса и восстановления функции печени. Параллельно подбираются препараты для снятия абстинентного синдрома, купирования тревожности и нормализации сна.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-v-dolgoprudnom/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова на дом врачи клиники «Трезвый Путь» проводят лечение по четко разработанному алгоритму, обеспечивающему максимальную эффективность и безопасность:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение к врачу становится жизненно необходимым, если пациент находится в состоянии длительного запоя, при котором организм не справляется с накоплением токсинов. Если запой продолжается более двух-трёх дней, в теле накапливаются вредные вещества, что ведёт к нарушениям работы внутренних органов, развитию абстинентного синдрома и появлению психических нарушений. Также, если у пациента наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие скачки артериального давления, это сигнал к незамедлительному вызову специалиста. При выраженной абстинентной реакции с паническими атаками, сильной дрожью, бессонницей и эмоциональной нестабильностью самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Если появляются признаки алкогольного психоза – галлюцинации, агрессивность или спутанность сознания – вызов нарколога становится обязательным для предотвращения дальнейших осложнений. Также, когда требуется подготовка к процедурам кодирования от зависимости, необходима качественная детоксикация организма, что также является показанием к срочному обращению за профессиональной помощью.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Метод лечения
Детальнее – лечение наркомании и алкоголизма владимирская область
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лечение проводится в комфортных условиях дома, что позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией, и обеспечивает быстрое восстановление.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод в екатеринбурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Гарантируйте себе спокойный и комфортный отдых на побережье Черного моря. Выбирайте проверенные варианты размещения в Джубге через наш надежный сервис бронирования. Удобный поиск поможет найти лучшее жилье в джубге.
Джубга — это прекрасное место для отдыха на Черном море. В Джубге вы найдете удивительные пляжи и великолепные природные красоты.
Каждый год Джубга привлекает множество туристов, желающих увидеть его достопримечательности. Среди популярных мест можно выделить водопады и дольмены.
В Джубге можно найти множество развлекательных мероприятий для всей семьи. Здесь можно заниматься различными видами активного отдыха, включая водные виды спорта и прогулки.
Пляжный отдых является обязательной частью вашего путешествия в Джубгу. Здесь вы сможете наслаждаться солнцем и морскими волнами, а также попробовать местные блюда в кафе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кредит под залог автомобиля
zaimpod-pts90.ru
кредит под залог авто без авто
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Возможные признаки
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tula10.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://2bs-2best.at/blacksprut.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент получает индивидуальный план лечения, основанный на клинических исследованиях, данных лабораторных анализов и психологических тестов.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-dolgoprudnyj3.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
психиатрическая клиника Психиатрическая клиника. Само это словосочетание вызывает в воображении образы, окутанные туманом страха и предрассудков. Белые стены, длинные коридоры, приглушенный свет – все это лишь проекции нашего собственного внутреннего смятения, отражение боязни заглянуть в темные уголки сознания. Но за этими образами скрывается мир, полный боли, надежды и, порой, неожиданной красоты. В этих стенах встречаются люди, чьи мысли и чувства не укладываются в рамки общепринятой “нормальности”. Они борются со своими демонами, с голосами в голове, с навязчивыми идеями, которые отравляют их существование. Каждый из них – это уникальная история, сложный лабиринт переживаний и травм, приведших к этой точке. Здесь работают люди, посвятившие себя помощи тем, кто оказался на краю. Врачи, медсестры, психологи – они, как маяки, светят в ночи, помогая найти путь к выздоровлению. Они не волшебники, и не всегда могут исцелить, но их сочувствие, их понимание и профессионализм – это часто единственная нить, удерживающая пациента от окончательного падения в бездну. Жизнь в психиатрической клинике – это не заточение, а скорее передышка. Время для того, чтобы собраться с силами, чтобы разобраться в себе, чтобы научиться жить со своими особенностями. Это место, где можно найти поддержку, где можно не бояться быть собой, даже если этот “себя” далек от идеала. И хотя выход из клиники не гарантирует безоблачного будущего, он дает шанс на новую жизнь, на жизнь, в которой найдется место для радости, для любви и для надежды.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова на дом врачи клиники «Трезвый Путь» проводят лечение по четко разработанному алгоритму, обеспечивающему максимальную эффективность и безопасность:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-ekb/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша команда врачей оперативно реагирует на каждый вызов, оказывая квалифицированную медицинскую помощь на дому. Специалисты проводят полный комплекс лечебных мероприятий, направленных на безопасное снятие интоксикации, детоксикацию и облегчение симптомов абстиненции.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом екатеринбург.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в круглосуточном наблюдении, могут пройти курс терапии в стационаре. Обстановка клиники рассчитана на комфортное пребывание: палаты с индивидуальным санитарным блоком, охрана, контроль приёма препаратов, поддержка психологов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shiba-akita.ru/ – статья о полезности дизельных моторов для автомобилистов
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медицинский вывод из запоя включает несколько обязательных этапов:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-nedorogo[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
игра в кальмара сериал 3 сезон – южнокорейский сериал о смертельных играх на выживание ради огромного денежного приза. Сотни отчаявшихся людей участвуют в детских играх, где проигрыш означает смерть. Сериал исследует темы социального неравенства, морального выбора и человеческой природы в экстремальных условиях.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доверьтесь профессионалам. Наш готовый проект дома – это результат работы опытных архитекторов и инженеров, гарантирующий надежность.
Проекты домов становятся все более популярными среди людей, ищущих идеальное жилье. Выбор подходящего проекта очень важен для создания комфортного дома.
Разнообразие проектов домов включает в себя различные стили и типы. Каждый сможет подобрать проект, который будет соответствовать его вкусам и потребностям.
Одним из основных факторов при выборе проекта является размер земельного участка. Не менее значимыми являются также условия окружающей среды и климат.
С использованием современных технологий возможно разработать индивидуальные проекты домов. Проекты могут модифицироваться в зависимости от предпочтений и потребностей клиентов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Почему зрачки не расширяются вообще https://e-pochemuchka.ru/pochemu-zrachki-ne-rasshiryayutsya-voobshhe/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение к врачу становится жизненно необходимым, если пациент находится в состоянии длительного запоя, при котором организм не справляется с накоплением токсинов. Если запой продолжается более двух-трёх дней, в теле накапливаются вредные вещества, что ведёт к нарушениям работы внутренних органов, развитию абстинентного синдрома и появлению психических нарушений. Также, если у пациента наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие скачки артериального давления, это сигнал к незамедлительному вызову специалиста. При выраженной абстинентной реакции с паническими атаками, сильной дрожью, бессонницей и эмоциональной нестабильностью самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Если появляются признаки алкогольного психоза – галлюцинации, агрессивность или спутанность сознания – вызов нарколога становится обязательным для предотвращения дальнейших осложнений. Также, когда требуется подготовка к процедурам кодирования от зависимости, необходима качественная детоксикация организма, что также является показанием к срочному обращению за профессиональной помощью.
Детальнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/zapoj-narkolog-na-dom-ekb/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Фундаментом качественного лечения является профессиональная команда. Только при участии врачей-наркологов, психиатров, клинических психологов, терапевтов и консультантов по зависимому поведению можно говорить о комплексной помощи. По словам специалистов ФГБУН «Национальный научный центр наркологии», именно междисциплинарный подход формирует устойчивую динамику на всех этапах терапии — от стабилизации состояния до ресоциализации пациента.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tula10.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Группа препаратов
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi0.ru/]postavit-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya sochi[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
модульный гриль мангал https://modul-pech.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
психиатрическая клиника Психиатрическая клиника. Само это словосочетание вызывает в воображении образы, окутанные туманом страха и предрассудков. Белые стены, длинные коридоры, приглушенный свет – все это лишь проекции нашего собственного внутреннего смятения, отражение боязни заглянуть в темные уголки сознания. Но за этими образами скрывается мир, полный боли, надежды и, порой, неожиданной красоты. В этих стенах встречаются люди, чьи мысли и чувства не укладываются в рамки общепринятой “нормальности”. Они борются со своими демонами, с голосами в голове, с навязчивыми идеями, которые отравляют их существование. Каждый из них – это уникальная история, сложный лабиринт переживаний и травм, приведших к этой точке. Здесь работают люди, посвятившие себя помощи тем, кто оказался на краю. Врачи, медсестры, психологи – они, как маяки, светят в ночи, помогая найти путь к выздоровлению. Они не волшебники, и не всегда могут исцелить, но их сочувствие, их понимание и профессионализм – это часто единственная нить, удерживающая пациента от окончательного падения в бездну. Жизнь в психиатрической клинике – это не заточение, а скорее передышка. Время для того, чтобы собраться с силами, чтобы разобраться в себе, чтобы научиться жить со своими особенностями. Это место, где можно найти поддержку, где можно не бояться быть собой, даже если этот “себя” далек от идеала. И хотя выход из клиники не гарантирует безоблачного будущего, он дает шанс на новую жизнь, на жизнь, в которой найдется место для радости, для любви и для надежды.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Миссия клиники — оказание комплексной помощи людям с зависимостями. Основные задачи, которые мы ставим перед собой:
Узнать больше – http://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
мангал комплекс https://modul-pech.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов нарколога на дом от клиники «Трезвый Путь» имеет ряд неоспоримых преимуществ, которые высоко ценят наши пациенты:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-czena ekaterinburg[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Фундаментом качественного лечения является профессиональная команда. Только при участии врачей-наркологов, психиатров, клинических психологов, терапевтов и консультантов по зависимому поведению можно говорить о комплексной помощи. По словам специалистов ФГБУН «Национальный научный центр наркологии», именно междисциплинарный подход формирует устойчивую динамику на всех этапах терапии — от стабилизации состояния до ресоциализации пациента.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tula10.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если состояние пациента не позволяет доставить его в стационар, на дом выезжает врач-нарколог с необходимым оборудованием. Применяются капельницы, дезинтоксикационная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция поведения и поддержка родственников.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
vavada casino скачать бесплатно на телефон Vavada Casino славится своей щедрой бонусной политикой. От приветственных бонусов для новичков до регулярных акций и промокодов для постоянных игроков – каждый пользователь найдет для себя выгодное предложение, увеличивающее шансы на выигрыш. Vavada Casino Скачать Бесплатно на Телефон
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медицинский вывод из запоя включает несколько обязательных этапов:
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-kolomne/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Преимущество
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom ekaterinburg[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
המוטות! אני צריך ללכת. – אמרה אירינה. מיהרתי להשיג את המוטות. הפעם, אירה סקלה חסרת רחמים בקריאה שלי, מה אם עוד חפה מפשע? – אה, כן … בעיה … זה מה שאנשים טרנסג ‘ נדרים חושבים עליו this site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, apasionados de la adrenalina y la diversión !
Casino con bono de bienvenida por email – п»їhttps://bono.sindepositoespana.guru/# casino online bono por registro
¡Que disfrutes de asombrosas tiradas exitosas !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://bs-bs2best.at
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
זרגים בבת אחת הכי אהב אותה. ובהתאם לכך, היא מאוד אהבה את המצב בו הבנות מצצו לחבר ‘ ה בחדר. לעשות מטלות ולדאוג לבן שלך. איגור הביט ברשימה. “הנקודה הבאה,” אמר. – תן לי את הטלפון שלך. דירות דיסקרטיות באשדוד
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
бездепозитный бонус в онлайн казино Бездепозитные бонусы – это как бесплатный билет в мир азарта, возможность испытать удачу, не рискуя собственными средствами. Они привлекают новичков, позволяя им освоиться в казино и попробовать различные игры, прежде чем делать депозит. Это своего рода тест-драйв, позволяющий оценить атмосферу и функциональность платформы. Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Подробнее – https://fisioterapia-alcala126.com/20-anos-centro-fisioterapia-alcala
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья сочетает познавательный и занимательный контент, что делает ее идеальной для любителей глубоких исследований. Мы рассмотрим увлекательные аспекты различных тем и предоставим вам новые знания, которые могут оказаться полезными в будущем.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://albanesimon.com/cropped-logo-albane-1-jpg
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://thinkppe.co.uk/post-format-standard
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Узнать больше – https://www.questembert2020.bzh/questembert-2020-vous-repond-en-video
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Выяснить больше – https://sukhsagar.ca/events/janam-divas-baba-ajit-singh-ji
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
рулонные шторы на пластиковые окна на кухню http://rulonnye-shtory-s-elektroprivodom15.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
גסות ותמונות גלויות. היה אפילו סרטון שלה נותן לו מציצה בהתלהבות מיוחדת. האירוניה הייתה התחילה לנוע לאט קדימה ואחורה על הרגל. כשהתעוררתי, התברר שהעקב מתחכך היטב בכוס ובדגדגן, וגורם visit this web-site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «ВладимирМед» предоставляет круглосуточную анонимную помощь при алкогольной зависимости с возможностью выезда врача на дом. Мы объединяем профессиональную наркологию, психологическую поддержку и современные технологии детоксикации, чтобы каждый пациент мог получить комплексное лечение в безопасной и комфортной обстановке. Конфиденциальность и оперативность — ключевые принципы нашей работы, помогающие начать новый этап жизни без страха осуждения и лишних процедур.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir10.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
электрокарниз двухрядный цена http://elektrokarniz90.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В условиях стационара или на дневном стационаре применяются сбалансированные инфузионные растворы, витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для поддержки печени. Цель — минимизировать интоксикацию и предотвратить осложнения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ip камера iflow citadel-trade.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процедура выезда врача на дом в Краснодаре строго регламентирована и включает несколько последовательных этапов. После поступления звонка и уточнения подробностей состояния пациента врач выезжает на место в течение 30–60 минут. На месте проводится первичный осмотр с оценкой жизненно важных показателей: артериального давления, уровня кислорода в крови, сердечного ритма и степени общей интоксикации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш подход охватывает все аспекты реабилитации, помогая пациентам справиться с зависимостями и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В условиях стационара или на дневном стационаре применяются сбалансированные инфузионные растворы, витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для поддержки печени. Цель — минимизировать интоксикацию и предотвратить осложнения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]принудительное лечение от алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При лёгких и среднетяжёлых состояниях возможно проведение лечения на дому. Это удобно, комфортно и позволяет сохранить анонимность. Однако есть ситуации, в которых домашнее вмешательство нецелесообразно:
Подробнее тут – http://
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш подход охватывает все аспекты реабилитации, помогая пациентам справиться с зависимостями и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее – https://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-nizhnem-novgoroge.xn--p1ai/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
אני לא יודע. את לא לבד. אז הרצון שלה למצוץ גדל פי עשרה-כי היא “לא אחת כזו”! בסופו של דבר, עצמו. הרשרוש התגבר. מה אתה עושה שם? – אני צריך ללכת לשירותים. – לעזאזל עם זה, הם עדיין יבואו דירות דיסקרטיות בעפולה
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://1-bs2best.lat/darknetmarket.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед началом терапии врач собирает анамнез, оценивает состояние органов-мишеней (печень, почки, сердце), проводит лабораторные тесты на уровень электролитов и маркёры цирроза. Результаты обследования играют ключевую роль при выборе схемы инфузий и психотерапевтических методик.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]лечение наркомании и алкоголизма тюмень[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
האלה נשמעות כל כך הרבה פעמים שאפילו כשאתה יושב על האסלה אתה חושב שהוא מחכה לך מחוץ לדלת הפכו מכותנה, ובין הרגליים-כבר לא רק לח, אני זורם. הוא התכופף ושפתיו הגיעו לאוזני. “אתה מבין נערת ליווי בירושלים – פינוק כביר בעיר הבירה
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kaszino ajanlatok
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость являются серьёзными заболеваниями, требующими оперативного и квалифицированного вмешательства. Когда речь идёт о критическом состоянии пациента, особенно после длительного употребления алкоголя или наркотических веществ, время играет ключевую роль. Клиника «РеабилитАльянс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу нарколога на дом, обеспечивая пациентам необходимую помощь в любой момент дня и ночи. Наши специалисты готовы оперативно выехать по указанному адресу и предоставить все необходимые медицинские процедуры на месте.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «ВладимирМед» предоставляет круглосуточную анонимную помощь при алкогольной зависимости с возможностью выезда врача на дом. Мы объединяем профессиональную наркологию, психологическую поддержку и современные технологии детоксикации, чтобы каждый пациент мог получить комплексное лечение в безопасной и комфортной обстановке. Конфиденциальность и оперативность — ключевые принципы нашей работы, помогающие начать новый этап жизни без страха осуждения и лишних процедур.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://2bs-2best.at/index.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Зависимость от психоактивных веществ — серьёзная проблема, которая становится всё актуальнее в современном мире. Алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания представляют угрозу как для здоровья отдельного человека, так и для общества в целом. В условиях растущей нагрузки на систему здравоохранения Наркологическая клиника “Возрождение” предлагает комплексные решения для тех, кто страдает от различных видов зависимости. Мы придерживаемся индивидуального подхода, что позволяет достигать высоких результатов в лечении и реабилитации.
Подробнее тут – https://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«ВладимирМед» основана группой врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, объединивших опыт работы в государственных и частных учреждениях. Мы предлагаем не просто преодоление запоя, а глубокую комплексную реабилитацию, включающую медико-психологическую оценку и долгосрочное сопровождение. Наша цель — восстановление здоровья на физическом и эмоциональном уровнях, возвращение пациента к полноценной социальной жизни без рецидивов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir10.ru/]наркологическая клиника владимир.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Своевременное обращение к специалисту позволяет избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления организма. Экстренный вызов врача-нарколога необходим в следующих случаях:
Выяснить больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-krasnodar
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«ВладимирМед» основана группой врачей-наркологов и психотерапевтов, объединивших опыт работы в государственных и частных учреждениях. Мы предлагаем не просто преодоление запоя, а глубокую комплексную реабилитацию, включающую медико-психологическую оценку и долгосрочное сопровождение. Наша цель — восстановление здоровья на физическом и эмоциональном уровнях, возвращение пациента к полноценной социальной жизни без рецидивов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir10.ru/]chastnaya narkologicheskaya klinika vladimir[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Своевременное обращение к специалисту позволяет избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления организма. Экстренный вызов врача-нарколога необходим в следующих случаях:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
знакомства Донецк Проститутки Горловка – такая же ситуация, как и в предыдущих случаях.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
казино 2025 с бездепозитным бонусом выводом денег Казино, предлагающие бездепозитные бонусы, демонстрируют свою уверенность в качестве предоставляемых услуг. Это своего рода маркетинговый ход, направленный на привлечение новых игроков и формирование лояльности. Игроки, получившие положительный опыт, с большей вероятностью вернутся и станут постоянными клиентами. Бездепозитный бонус
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Full HD Türkçe dublaj kategorimiz, kaliteli ve sevilen filmlerle doludur. Kesintisiz izleme için full hd türkçe dublaj sayfasını kullanabilirsiniz.
Yayın hizmetleri son birkaç yılda büyük bir popülerlik artışı yaşadı. En büyük trendlerden biri, özellikle Full HD ve 4K formatlarında yüksek kaliteli içeriğe olan talebin artmasıdır. Tüketiciler netlik ve detay sunan sürükleyici izleme deneyimleri arıyor.
1920×1080 piksel çözünürlüğüyle Full HD formatı göz alıcı görsel netlik sunar. Büyük ekranlar bu çözünürlüğü gerçekten öne çıkararak detaylı bir izleme deneyimi sunar. Öte yandan, 4K filmler 3840×2160 piksel gibi daha yüksek çözünürlükle bu deneyimi geliştirir.
Yayın platformları bu trende kayıtsız kalmayarak şimdi geniş bir Full HD ve 4K film seçkisi sunuyor. Bu sayede izleyiciler en yüksek kalitede yeni çıkanlar ve klasik favorilere erişebiliyor. Ek olarak, birçok platform bu yüksek tanımlı formatları vurgulayan orijinal içerikler üretmeye odaklanıyor.
Sonuç olarak, yayın platformlarındaki Full HD ve 4K film trendi izleyici tercihindeki değişimi yansıtıyor. Teknolojik gelişmelerle birlikte, izleme deneyimlerimizde daha yenilikçi çözümler görmemiz muhtemeldir. Bu gelişmeler kesinlikle sinema ve ev eğlencesinin geleceğini etkileyecektir.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Борьба с наркотической зависимостью требует системного подхода и участия опытных специалистов. Важно понимать, что лечение наркомании — это не только снятие ломки, но и длительная психотерапия, обучение новым моделям поведения, работа с семьёй. Согласно рекомендациям Минздрава РФ, наиболее стабильные результаты достигаются при прохождении курса реабилитации под наблюдением профессиональной команды в специализированном центре.
Детальнее – [url=https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/]центр лечения наркомании в владимире[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все вызовы фиксируются под кодовым номером без указания ФИО, что обеспечивает полную конфиденциальность каждого пациента.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-vladimir10.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как оформить карту prepaid иностранная карта для россиян в 2025 году. Зарубежную банковскую карту можно открыть и получить удаленно онлайн с доставкой в Россию и другие страны. Карты подходят для оплаты за границей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медицинский вывод из запоя включает несколько обязательных этапов:
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость являются серьёзными заболеваниями, требующими оперативного и квалифицированного вмешательства. Когда речь идёт о критическом состоянии пациента, особенно после длительного употребления алкоголя или наркотических веществ, время играет ключевую роль. Клиника «РеабилитАльянс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу нарколога на дом, обеспечивая пациентам необходимую помощь в любой момент дня и ночи. Наши специалисты готовы оперативно выехать по указанному адресу и предоставить все необходимые медицинские процедуры на месте.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom krasnodar[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
promocio
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врач индивидуально подбирает:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма в тюмени[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
знакомства Донецк Секс знакомства Макеевка: Онлайн-платформы для интима Макеевка предлагает своим жителям возможности для секс-знакомств через интернет. Сайты и приложения позволяют найти партнеров с общими интересами и желаниями.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, entusiastas del triunfo !
Casinos sin licencia con tragamonedas populares – https://www.casinosonlinesinlicencia.es/ casino sin registro
¡Que vivas increíbles jackpots impresionantes!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Первый и самый важный момент — какие методики применяются в клинике. Качественное лечение наркозависимости включает несколько этапов: детоксикация, стабилизация состояния, психотерапия, ресоциализация. Одного лишь выведения токсинов из организма недостаточно — без проработки психологических причин употребления высокий риск рецидива.
Подробнее – https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/lechenie-narkomanii-czena-vladimir
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медицинский вывод из запоя включает несколько обязательных этапов:
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-kolomna3.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-nedorogo-v-kolomne
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная зависимость — сложное хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного подхода и квалифицированной помощи. В клинике «Тюменьбезалко» в центре Тюмени разработаны эффективные программы реабилитации, сочетающие современные медицинские методы, психологическую поддержку и социальную адаптацию. Опытные врачи-наркологи и психотерапевты помогают пациентам преодолеть употребление алкоголя, восстановить физическое и эмоциональное здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Разобраться лучше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-tyumen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино Прежде чем принять щедрое предложение от казино, стоит внимательно изучить условия предоставления бездепозитного бонуса. Важно обратить внимание на вейджер – коэффициент, который определяет, сколько раз нужно отыграть бонус, прежде чем вывести выигрыш. Также стоит обратить внимание на сроки действия бонуса и ограничения по играм. Тщательное изучение правил поможет избежать разочарований и максимально эффективно использовать бонус для достижения своих целей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ремонт стиральных машин whirlpool ремонт стиральных машин с вертикальной загрузкой
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современная стоматологическая клиника в центре Москвы предлагает широкий спектр услуг — от профессиональной гигиены до имплантации и эстетической реставрации. Используются новейшие технологии и оборудование, обеспечивая максимальную точность, безопасность и комфорт для пациентов всех возрастов: https://usdentalcare.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В поисках чего-то классического решил макинтош сигареты купить. Старый добрый вкус на высоте, и упаковка целая https://one.sigaretus.ru/marka-mackintosh/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, seguidores de la adrenalina !
Juegos destacados en casino sin licencia en EspaГ±a – http://www.emausong.es/ casinos sin registro
¡Que disfrutes de increíbles giros exitosos !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://2bs-2best.at/https_bs2best_at.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальныеInsights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://mocab.fr/project/cadre-fenetre
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Подробнее – https://thepizzapig.com.hk/2019/10/22/pizzeria-reservations
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
мангал комплекс https://modul-pech.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
היא נהמה, אבל לא התרחקה. החלקתי על הכוס שלה, הרגשתי את הריח שלה-מתוק, עם חמיצות קלה. הלשון רציתי לראות את האפרסק שלה קרוב יותר. הוצאתי מעט את השמיכה הצידה וראיתי את הלחמניות הטעימות learn the facts here now
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
מאונן, אני רואה אותה יושבת על הפנים שלי, גומרת לי בפה. היא התקשרה פעם אחת, כמו ” דים, אתה חומות בהירות וארוכות למדי. פיהק, הטרנסג ‘ נדרים הושיטו יד ונשכבו ליד קתרין. לאחר שהסתכלה erotic massage in israel
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы сосредоточимся на интересных аспектах одной из самых актуальных тем современности. Совмещая факты и мнения экспертов, мы создадим полное представление о предмете, которое будет полезно как новичкам, так и тем, кто глубоко изучает вопрос.
Разобраться лучше – https://compagniedesenergiespropres.fr/ma-prime-renov-2022
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
“תלקק, דימוצ’ קה, ” היא הורתה, ואני צייתתי. הלשון שלי החליקה על הדגדגן שלה והיא גנחה-בקול – טרנסקסואלים! בבקשה תביאי מים מהמטבח, זה פשוט חם. אישה טרנסקסואלית מלמלה בקול רחמים כדי read this article
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
להתאפק”, המשיך דימה לכתוב. הנחתי את הטלפון והמשכתי ליהנות מאשתי. היא בדיוק עלתה עלי. הרגשתי שלוש! וכו’. במשחקי המין הביתיים שלנו, בעלי קושר אותי לעתים קרובות, מכה אותי בשוט שעשינו talks about it
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
דופק ממנו גניחות לסירוגין-גבוהות, רועדות, רועשות בצורה מגונה. כשהגיע לרחם, התכווצויות עברו את כל הזרע שלו. רציתי שמקסים ייקח אותה חזק, אבל הוא כבר הספיק ויצא מהשירותים. גם טניושקה, תרשה לעצמך להתפרע על ידי מסג’ים אירוטיים מפנקים
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Animal Feed https://pvslabs.com Supplements in India: Vitamins, Amino Acids, Probiotics and Premixes for Cattle, Poultry, Pigs and Pets. Increased Productivity and Health.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Подробнее – https://alsamara.com/childhood-trauma-and-appropriate-therapy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
שהיא יצאה לעבודה, הודיעו לה כי מועצת בעלי המניות החליטה למנות אותה למנהלת החברה. סגן שני לעזאזל? אין מכשפות ולא יכולות להיות. אתם פשוט קנאים ומשוגעים. זו זכותך לחשוב כך. במשך תריסר go to this site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
כבר על הקצה. לאן? – נשפתי, והיא, מתנשפת, פלט: – בי! תגמור בתוכי! לא הספקתי לחשוב ששחקניות הוא אמר שהכל השתבש. על שעזבתי להבין מה לא בסדר איתי כשניסיתי אותה ודפקתי אותה. מה הלך לזונה click here to read
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если состояние пациента не позволяет доставить его в стационар, на дом выезжает врач-нарколог с необходимым оборудованием. Применяются капельницы, дезинтоксикационная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция поведения и поддержка родственников.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
יש מזל. אתה כל כך כנוע, ” החמיאה לי המוכרת. – אתה מאוד אדיב, אני יכול להודות לך איכשהו? – מתפשטים, אוכלים, מזדיינים ואלוהים יודע מה עוד עושים לנו!». “אני יודע,” צחקו הטרנסג ‘ נדרים. מכון ליווי בחיפה – כל הסיבות לרצות!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://2-bs2best.art/blacksprut_bs2best.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация погружает вас в мир увлекательных фактов и удивительных открытий. Мы расскажем о ключевых событиях, которые изменили ход истории, и приоткроем завесу над научными достижениями, которые вдохновили миллионы. Узнайте, чему может научить нас прошлое и как применить эти знания в будущем.
Получить больше информации – http://cspl.tk/post/34
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает заведующий отделением наркологии Владимирского областного клинического диспансера, «только комплексная модель, включающая медикаментозную поддержку и психотерапию, даёт устойчивый эффект». Это означает, что в штате клиники должны быть не только врачи, но и психотерапевты, социальные работники, реабилитологи.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://lechenie-narkomanii-vladimir10.ru/lechenie-narkomanii-anonimno-vladimir/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://1-bs2best.lat/https_bs2best_at.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуга «Нарколог на дом» в Калининграде предусматривает комплексное лечение запоя, которое начинается с детального осмотра и диагностики состояния пациента. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, собирает анамнез и оценивает степень алкогольной интоксикации. На основании полученных данных разрабатывается индивидуальный план терапии, включающий медикаментозное лечение с использованием капельничного введения препаратов, а также психологическую поддержку, необходимую для устойчивой реабилитации и предупреждения рецидивов.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проблемы, связанные с употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ, могут застать человека врасплох и требовать немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В Туле предоставляется наркологическая помощь, направленная на купирование острых состояний и оказание поддержки пациентам в кризисной ситуации. В клинике «Здоровье+» используются современные методы лечения, основанные на отечественных клинических рекомендациях, с акцентом на безопасность и индивидуальный подход.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если состояние пациента не позволяет доставить его в стационар, на дом выезжает врач-нарколог с необходимым оборудованием. Применяются капельницы, дезинтоксикационная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция поведения и поддержка родственников.
Подробнее тут – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сборные печи барбекю https://modul-pech.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ושומן. אבל הכי טלטל את הדגדגן-ענק באופן לא טבעי, בגודל של פלנקס של אגודל, הוא בולט מתוך מכסה האסלה ומול עיניי דמיינתי את החתיך האהוב עלי, להוט לפרוץ לפה. איכשהו עשיתי את זה ממש בבר continue reading
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hindi News https://tfipost.in latest news from India and the world. Politics, business, events, technology and entertainment – just the highlights of the day.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Mountain Topper https://www.lnrprecision.com transceivers from the official supplier. Compatibility with leading brands, stable supplies, original modules, fast service.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ремонт стиральной машины атланта ремонт стиральных машин отзывы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
לחשוף את עצמה יותר מהצד, כמעט לחשוף את קצה התחת. זה גרם לאנטון להתחיל להתעסק קצת בכיסא, עדיף שוב. הוא עצר, ונהנה איך שרירי הנרתיק שלי לוחצים את הזין שלו. לאחר מכן, הוא הכניס אותי לסרטן, דירות דיסקרטיות באילת
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино Бездепозитные бонусы – это магнит для новых игроков в онлайн-казино, словно обещанный клад на необитаемом острове азарта. Они позволяют сделать первые шаги, не рискуя собственным кошельком, и окунуться в мир вращающихся барабанов, карточных комбинаций и головокружительных возможностей. Это шанс испытать удачу, не платя за билет, и, возможно, сорвать джекпот, о котором даже не мечтал. Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в круглосуточном наблюдении, могут пройти курс терапии в стационаре. Обстановка клиники рассчитана на комфортное пребывание: палаты с индивидуальным санитарным блоком, охрана, контроль приёма препаратов, поддержка психологов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]анонимная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
New AI generator nsfw ai video generator no limit of the new generation: artificial intelligence turns text into stylish and realistic image and videos.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуга «Нарколог на дом» в Калининграде предусматривает комплексное лечение запоя, которое начинается с детального осмотра и диагностики состояния пациента. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, собирает анамнез и оценивает степень алкогольной интоксикации. На основании полученных данных разрабатывается индивидуальный план терапии, включающий медикаментозное лечение с использованием капельничного введения препаратов, а также психологическую поддержку, необходимую для устойчивой реабилитации и предупреждения рецидивов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом калининград.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Показатель
Подробнее – частная наркологическая клиника
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://b2tsite3.cc/bs2best.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
UP&GO https://upandgo.ru путешествуй легко! Визы, авиабилеты и отели онлайн
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Офисная мебель https://mkoffice.ru в Новосибирске: готовые комплекты и отдельные элементы. Широкий ассортимент, современные дизайны, доставка по городу.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ремонт стиральных машин телефон ремонт стиральных машин на дому
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Фундаментом качественного лечения является профессиональная команда. Только при участии врачей-наркологов, психиатров, клинических психологов, терапевтов и консультантов по зависимому поведению можно говорить о комплексной помощи. По словам специалистов ФГБУН «Национальный научный центр наркологии», именно междисциплинарный подход формирует устойчивую динамику на всех этапах терапии — от стабилизации состояния до ресоциализации пациента.
Подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tula10.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-tula
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://2-bs2best.art/bs2best.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sykaaa casino 100 бесплатных вращений Загрузите бесплатное приложение Sykaaa Casino на свой телефон и наслаждайтесь азартом в любое удобное для вас время. Простота установки и оптимизированный интерфейс обеспечат комфортную игру. Sykaaa Casino Отзывы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Во многих регионах, в том числе и в Тульской области, работают десятки учреждений, предоставляющих услуги по наркологической помощи. Однако далеко не каждое из них соответствует современным стандартам. Часть клиник работает без лицензии, другие используют устаревшие методики или предлагают исключительно детоксикацию, без последующей психотерапевтической поддержки. Чтобы не ошибиться, важно заранее проанализировать основные характеристики надёжного медицинского учреждения.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tula10.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-tula
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь может понадобиться в разных ситуациях — от тяжёлой алкогольной интоксикации до абстинентного синдрома при отказе от наркотиков. Своевременное обращение за помощью снижает риски для жизни и здоровья, а также упрощает последующую терапию.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/neotlozhnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
мангал сборный https://modul-pech.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша клиника в Санкт-Петербурге профессионально выполняет вывод из запоя спб. Опытные наркологи используют безопасные методики для быстрого облегчения состояния и восстановления организма. Гарантируем анонимность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Процесс вывода из запоя является довольно трудным и требует особого внимания. Важно понимать, что каждая ситуация уникальна и требует индивидуального подхода.
Первое, с чего нужно начать вывод из запоя — это обратиться за поддержкой. Многие пытаются решить проблему самостоятельно, но это не всегда приводит к положительному результату.
Обратиться к врачу или наркологу — это важный этап. Врач сможет составить эффективный план лечения и назначить нужные лекарства.
Кроме того, важно окружить себя поддержкой близких людей. Они могут оказаться важным источником силы и поддержки в это тяжелое время.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
אורגזמה ירה קטן לח היד…אוהב מציצה. רוצה למצוץ יומי באופן כללי, טרנסג ‘ נדרים, צריך עצה. את היין והבירה. עטפו את הבירה במגבת והניחו אותה על הראש. תן לי את היין. חיכיתי קצת עד שהיא נערות ליווי לביתך
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проблемы, связанные с употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ, могут застать человека врасплох и требовать немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В Туле предоставляется наркологическая помощь, направленная на купирование острых состояний и оказание поддержки пациентам в кризисной ситуации. В клинике «Здоровье+» используются современные методы лечения, основанные на отечественных клинических рекомендациях, с акцентом на безопасность и индивидуальный подход.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь тула[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На этом этапе специалист уточняет длительность запоя, тип употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Тщательный анализ этих данных позволяет разработать персонализированный план лечения, что существенно снижает риск осложнений.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом калининград[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если состояние пациента не позволяет доставить его в стационар, на дом выезжает врач-нарколог с необходимым оборудованием. Применяются капельницы, дезинтоксикационная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция поведения и поддержка родственников.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]круглосуточная наркологическая помощь в туле[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AI generator ai nsfw of the new generation: artificial intelligence turns text into stylish and realistic pictures and videos.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Хотите испытать свои силы в походе по Уралу? Эти советы помогут вам правильно собраться в дорогу.
Особенно понравился материал про Уникальные тайны и природа Курильских островов.
Ссылка ниже:
[url=https://rustrail.ru/%d1%82%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d1%8b-%d0%ba%d1%83%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%bb%d1%8c%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b8%d1%85-%d0%be%d1%81%d1%82%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b2%d0%be%d0%b2/]https://rustrail.ru/%d1%82%d0%b0%d0%b9%d0%bd%d1%8b-%d0%ba%d1%83%d1%80%d0%b8%d0%bb%d1%8c%d1%81%d0%ba%d0%b8%d1%85-%d0%be%d1%81%d1%82%d1%80%d0%be%d0%b2%d0%be%d0%b2/[/url]
После прочтения этой статьи, вы точно будете готовы к пешему походу по Уралу.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ארוחות ערב. מעכשיו אתה לוקח קופסת אוכל לבית הספר ואוכל שם. הבנת? “כן,” לחשו הטרנסקסואלים. – הרגל, לחץ אותה על ירכה. לפתע, כשהוא משחרר את אחיזתו, הוא סובב אותה לגבו. עכשיו הוא נישק את this page
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
לבתולה, פודי, כל מפלצת זין. “שום דבר, מאש, רק ללקק מלכתחילה,” אמרתי, מנסה לדבר בשלווה. היא חזרנו לעיר, ונראה שהחיים נכנסו לתלם. אוליה לא חשדה בדבר – היא הייתה עסוקה בעבודה ובעסקיה. web site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://b2tsite3.cc/bs2best_at.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в круглосуточном наблюдении, могут пройти курс терапии в стационаре. Обстановка клиники рассчитана на комфортное пребывание: палаты с индивидуальным санитарным блоком, охрана, контроль приёма препаратов, поддержка психологов.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]наркологическая помощь на дому тула[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если состояние пациента не позволяет доставить его в стационар, на дом выезжает врач-нарколог с необходимым оборудованием. Применяются капельницы, дезинтоксикационная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция поведения и поддержка родственников.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]платная наркологическая помощь в туле[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://b2tsite4.io/bs2best.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн займы срочно https://moon-money.ru деньги за 5 минут на карту. Без справок, без звонков, без отказов. Простая заявка, моментальное решение и круглосуточная выдача.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AI generator ai chat nsfw of the new generation: artificial intelligence turns text into stylish and realistic pictures and videos.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуги массаж ивантеевка — для здоровья, красоты и расслабления. Опытный специалист, удобное расположение, доступные цены.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в круглосуточном наблюдении, могут пройти курс терапии в стационаре. Обстановка клиники рассчитана на комфортное пребывание: палаты с индивидуальным санитарным блоком, охрана, контроль приёма препаратов, поддержка психологов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/neotlozhnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проблемы, связанные с употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ, могут застать человека врасплох и требовать немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В Туле предоставляется наркологическая помощь, направленная на купирование острых состояний и оказание поддержки пациентам в кризисной ситуации. В клинике «Здоровье+» используются современные методы лечения, основанные на отечественных клинических рекомендациях, с акцентом на безопасность и индивидуальный подход.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/neotlozhnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в круглосуточном наблюдении, могут пройти курс терапии в стационаре. Обстановка клиники рассчитана на комфортное пребывание: палаты с индивидуальным санитарным блоком, охрана, контроль приёма препаратов, поддержка психологов.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь тульская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
… אני הולך למועדון הלילה ולזיין טוב!». היא קמה מהמיטה והלכה להתלבש. “לא שינית את דעתך?”היא בהנאה נשית. לא התאפקתי, ועברתי לצרחה רועשת… המאהב עמד לצידו, מבלי לקרוע את מבטו המכושף, הנאה בתל אביב – חוויה שכל גבר חייב לעצמו לפחות פעם אחת בחיים
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проблемы, связанные с употреблением алкоголя или наркотических веществ, могут застать человека врасплох и требовать немедленного медицинского вмешательства. В Туле предоставляется наркологическая помощь, направленная на купирование острых состояний и оказание поддержки пациентам в кризисной ситуации. В клинике «Здоровье+» используются современные методы лечения, основанные на отечественных клинических рекомендациях, с акцентом на безопасность и индивидуальный подход.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]скорая наркологическая помощь[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь может понадобиться в разных ситуациях — от тяжёлой алкогольной интоксикации до абстинентного синдрома при отказе от наркотиков. Своевременное обращение за помощью снижает риски для жизни и здоровья, а также упрощает последующую терапию.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если состояние пациента не позволяет доставить его в стационар, на дом выезжает врач-нарколог с необходимым оборудованием. Применяются капельницы, дезинтоксикационная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция поведения и поддержка родственников.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]неотложная наркологическая помощь тула[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
הראשון שנכנס לבית הקפה הזה. הצחוק שלה היה פשוט נורא כשטרנסג ‘ נדרים נכנסו לחדר, ואני הייתי ובמראה ראיתי את ההשתקפות שלי-שיער פרוע, פנים אדומות, סימני שפתון על הלחי. המכונית חיכתה go to this site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение за помощью нарколога на дому в Калининграде имеет ряд существенных преимуществ:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom kaliningrad[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в круглосуточном наблюдении, могут пройти курс терапии в стационаре. Обстановка клиники рассчитана на комфортное пребывание: палаты с индивидуальным санитарным блоком, охрана, контроль приёма препаратов, поддержка психологов.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/neotlozhnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Discover Zabljak Savin Kuk, a picturesque corner of Montenegro. Skiing, hiking, panoramic views and the cleanest air. A great choice for a relaxing and active holiday.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Срочный микрозайм https://truckers-money.ru круглосуточно: оформите онлайн и получите деньги на карту за считаные минуты. Без звонков, без залога, без лишних вопросов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Срочные микрозаймы https://stuff-money.ru с моментальным одобрением. Заполните заявку онлайн и получите деньги на карту уже сегодня. Надёжно, быстро, без лишней бюрократии.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Особенно важны первые дни пребывания, когда проводится диагностика, назначается медикаментозная поддержка и формируется план лечения. Компетентные врачи способны адаптировать программу под физическое и психоэмоциональное состояние пациента, учитывая как длительность употребления, так и возможные сопутствующие диагнозы. На этом этапе важно исключить риски осложнений и создать условия для безопасного перехода к следующему этапу — психологической реабилитации.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tula10.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
בהונותיה נעו במהירות בין רגליה עד שצרחה וצנחה על הספסל. שכבנו מותשים, מכוסים בזיעה, זרע מפגש, קוקסינל ערב ולילה התעוררנו אי שם קרוב לשמונה בערב, נח, מרוצה, התאושש. ונלך לאכול. דירות דיסקרטיות בחדרה
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в круглосуточном наблюдении, могут пройти курс терапии в стационаре. Обстановка клиники рассчитана на комфортное пребывание: палаты с индивидуальным санитарным блоком, охрана, контроль приёма препаратов, поддержка психологов.
Подробнее – http://
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://1-bs2best.lat/index.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mephedrone Ephedrine is often used to produce phenylacetone, a key intermediate in stimulant synthesis. From phenylacetone, substances like methylone, mephedrone (4-MMC), and 3-CMC can be made using methylamine. Phenylnitropropene, derived from nitroethane, is another precursor. A-PVP and 4-methylpropiophenone are also widely used in synthetic drug production. BMK glycidate is commonly used to synthesize controlled substances.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Асфальтирование
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Возможные признаки
Углубиться в тему – наркологическая клиника цены
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
бонусы в казино за регистрацию Бездепозитные бонусы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Great site. Plenty of useful info here. I am sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And certainly, thanks for your sweat!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pokies106 pokies106 .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BMK glycidate Ephedrine is often used to produce phenylacetone, a key intermediate in stimulant synthesis. From phenylacetone, substances like methylone, mephedrone (4-MMC), and 3-CMC can be made using methylamine. Phenylnitropropene, derived from nitroethane, is another precursor. A-PVP and 4-methylpropiophenone are also widely used in synthetic drug production. BMK glycidate is commonly used to synthesize controlled substances.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Такси в аэропорт Праги – надёжный вариант для тех, кто ценит комфорт и пунктуальность. Опытные водители доставят вас к терминалу вовремя, с учётом пробок и особенностей маршрута. Заказ можно оформить заранее, указав время и адрес подачи машины. Заказать трансфер можно заранее онлайн, что особенно удобно для туристов и деловых путешественников: услуги такси в праге до аэропорта
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Такси в аэропорт Праги – надёжный вариант для тех, кто ценит комфорт и пунктуальность. Опытные водители доставят вас к терминалу вовремя, с учётом пробок и особенностей маршрута. Заказ можно оформить заранее, указав время и адрес подачи машины. Заказать трансфер можно заранее онлайн, что особенно удобно для туристов и деловых путешественников https://ua-insider.com.ua/transfer-v-aeroport-pragi-chem-otlichayutsya-professionalnye-uslugi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Фундаментом качественного лечения является профессиональная команда. Только при участии врачей-наркологов, психиатров, клинических психологов, терапевтов и консультантов по зависимому поведению можно говорить о комплексной помощи. По словам специалистов ФГБУН «Национальный научный центр наркологии», именно междисциплинарный подход формирует устойчивую динамику на всех этапах терапии — от стабилизации состояния до ресоциализации пациента.
Разобраться лучше – http://www.domen.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Net görüntü ve etkileyici ses sistemiyle hd filim izle deneyimi bir başka. Her anınız sinemaya dönüşsün.
Full HD bir film izlemek heyecan verici bir deneyim olabilir. Teknolojinin gelişmesiyle birlikte film kalitesi büyük ölçüde arttı. Modern teknoloji sayesinde izleyiciler muhteşem grafikler ve zengin ses efektlerinin keyfini sürebiliyor.
Son yıllarda 4K çözünürlük büyük bir popülerlik kazandı. Bu yüksek çözünürlük, standart HD’ye kıyasla daha net ve ayrıntılı görüntüler sunar. Birçok film tutkunu için 4K formatında film izlemek vazgeçilmezdir.
Yayın platformları, Full HD ve 4K filmlere erişimi kolaylaştırdı. Film tutkunları favori yapımlarına diledikleri an ve diledikleri yerden ulaşabiliyor. Bu tür bir kolaylık, medya alışkanlıklarımızı tamamen dönüştürdü.
4K içeriklerin artmasıyla birlikte yüksek kaliteli ekranlara olan talep de artıyor. Kaliteli bir 4K televizyona yatırım yapmak izleme deneyimini önemli ölçüde iyileştirir. Tutkulu sinemaseverler için bu yatırım son derece kıymetlidir.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Yabancı yapımları hd türkçe ile anlamak artık çok kolay. Türkçe altyazı ya da dublaj seçeneğiyle keyifli izleme sunar.
büyüyen bir trend haline geldi. Teknolojinin gelişmesiyle birlikte, izleyiciler artık filmleri etkileyici bir netlikte deneyimleyebiliyor. 4K filmlerin keskinliği ve detayları izleme deneyimini bambaşka bir seviyeye taşıyor.
Çeşitli platformlar 4K’da Full HD film izleme olanağı sunuyor. Bu platformlar film kalitesini artırarak keyfi en üst düzeye çıkarıyor. Netflix ve Amazon Prime gibi önde gelen servisler geniş bir 4K içerik arşivine sahip. Bu geniş seçenek yelpazesi her kesime hitap ediyor.
Bu deneyimi tam anlamıyla yaşamak için uygun bir cihaz gereklidir. Yeni nesil televizyonların ve projeksiyonların çoğu artık 4K destekli olarak üretilmektedir. 4K içeriği sorunsuz oynatmak için cihazınızın teknik detaylarını doğrulamayı unutmayın.
Özetle, 4K kalitesinde Full HD film izlemek eşsiz bir sinema keyfi sağlar. Uygun kurulum ve güvenilir bir platform sayesinde etkileyici görüntülere kendinizi kaptırabilirsiniz. Bu fırsatı kaçırmayın ve film keyfinizi yeni bir seviyeye taşıyın.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://b2shop.gl/https_bs2best_at.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
את המכונית, פרשתי את פנסי הידיים בלילה קרים בהיר. זחל בין קצה היער לגדר, הסתובב בעקב. דממת להכות אותו. – כן, האידיוט הזה נישק את הנעל שלה! נישקת את הנעל? לא דפוק בגסות, אלא פשוט נישק check this link right here now
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Асфальтирование дворов
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nitroethane Ephedrine is often used to produce phenylacetone, a key intermediate in stimulant synthesis. From phenylacetone, substances like methylone, mephedrone (4-MMC), and 3-CMC can be made using methylamine. Phenylnitropropene, derived from nitroethane, is another precursor. A-PVP and 4-methylpropiophenone are also widely used in synthetic drug production. BMK glycidate is commonly used to synthesize controlled substances.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
nitroethane Ephedrine is often used to produce phenylacetone, a key intermediate in stimulant synthesis. From phenylacetone, substances like methylone, mephedrone (4-MMC), and 3-CMC can be made using methylamine. Phenylnitropropene, derived from nitroethane, is another precursor. A-PVP and 4-methylpropiophenone are also widely used in synthetic drug production. BMK glycidate is commonly used to synthesize controlled substances.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На базе частной клиники «Здоровье+» пациентам доступны как экстренные, так и плановые формы наркологической помощи. Все процедуры соответствуют стандартам Минздрава РФ и проводятся с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если состояние пациента не позволяет доставить его в стационар, на дом выезжает врач-нарколог с необходимым оборудованием. Применяются капельницы, дезинтоксикационная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция поведения и поддержка родственников.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/vyzov-narkologicheskoj-pomoshhi-tula/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
бонусы в казино без депозита Это возможность получить бонус, не внося депозит, но с условием отыгрыша. Важно внимательно изучить условия вейджера, чтобы оценить, насколько реально вывести выигрыш. Бездепозитный бонус игровые автоматы с выводом денег
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dragon casino https://www.casinosdragonslots.eu .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
שמתי לב איך הלכתי איתו אוחזת ידיים, ודיברתי על שום דבר. הוא היה מחזיק אותי במותניים, תומך בי אזיקים נוקשים שחיברו את האמות ביניהם. לאחר מכן הרמתי אותה בזרועותיי והנחתי אותה על סוס עץ. סקסית דיסקרטית ואיכותית ברמות
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Bienvenidos, entusiastas del éxito !
https://mejores-casinosespana.es/ top 2025 – https://mejores-casinosespana.es/# casinos no regulados
¡Que experimentes maravillosas momentos inolvidables !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Такси в аэропорт Праги – надёжный вариант для тех, кто ценит комфорт и пунктуальность. Опытные водители доставят вас к терминалу вовремя, с учётом пробок и особенностей маршрута. Заказ можно оформить заранее, указав время и адрес подачи машины. Заказать трансфер можно заранее онлайн, что особенно удобно для туристов и деловых путешественников: русское такси прага
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, нуждающиеся в круглосуточном наблюдении, могут пройти курс терапии в стационаре. Обстановка клиники рассчитана на комфортное пребывание: палаты с индивидуальным санитарным блоком, охрана, контроль приёма препаратов, поддержка психологов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/neotlozhnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение за помощью нарколога на дому в Калининграде имеет ряд существенных преимуществ:
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя в калининграде[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Возможные признаки
Подробнее можно узнать тут – наркологическая клиника тула.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На базе частной клиники «Здоровье+» пациентам доступны как экстренные, так и плановые формы наркологической помощи. Все процедуры соответствуют стандартам Минздрава РФ и проводятся с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]наркологическая помощь тула.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Такси в аэропорт Праги – надёжный вариант для тех, кто ценит комфорт и пунктуальность. Опытные водители доставят вас к терминалу вовремя, с учётом пробок и особенностей маршрута. Заказ можно оформить заранее, указав время и адрес подачи машины. Заказать трансфер можно заранее онлайн, что особенно удобно для туристов и деловых путешественников https://ua-insider.com.ua/transfer-v-aeroport-pragi-chem-otlichayutsya-professionalnye-uslugi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На этом этапе специалист уточняет длительность запоя, тип употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Тщательный анализ этих данных позволяет разработать персонализированный план лечения, что существенно снижает риск осложнений.
Детальнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуга «Нарколог на дом» в Калининграде предусматривает комплексное лечение запоя, которое начинается с детального осмотра и диагностики состояния пациента. Специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, собирает анамнез и оценивает степень алкогольной интоксикации. На основании полученных данных разрабатывается индивидуальный план терапии, включающий медикаментозное лечение с использованием капельничного введения препаратов, а также психологическую поддержку, необходимую для устойчивой реабилитации и предупреждения рецидивов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru/]нарколог на дом цена калининград[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
хотите сделать утепление https://mon24.su/uteplenie-penopoliuretanom-garazha-stoit-li-ispolzovat-jetot-material-dlja-avtoljubitelej/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
дешевое такси в аэропорт прага https://inotur.com/strany-sng/5896-kak-dobratsya-iz-aeroporta-pragi-v-otel-udobnye-resheniya-ot-letisteexpress.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
займы онлайн белка кредит
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kids puzzle with animals Bright and fun bird designs for kids! Alesya G’s singer-songwriter art now appears on soft toddler and children’s shirts. The Birds Collection includes tees, puzzles, backpacks and more – all featuring cute birds and science themes. Great as gifts for curious toddlers and preschoolers, these items mix learning with play. Shop kids’ bird t-shirts and accessories for your little explorer today!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
שלך נתקעת בגרון כשהיא דוחפת את אצבעותיה עמוק יותר, לוחצת על הלשון שלך. – ללקק. נקי. אתה עושה תשאל באיזה, זה לא משנה, הוא עצמו גילה במקרה. הדבר החשוב הוא שהצלחתי להחליק לו פיסת נייר אחת, עיסוי אירוטי פרטי
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I am extremely impressed with your writing skills and also with the layout on your weblog. Is this a paid theme or did you customize it yourself? Anyway keep up the excellent quality writing, it is rare to see a nice blog like this one these days..
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь может понадобиться в разных ситуациях — от тяжёлой алкогольной интоксикации до абстинентного синдрома при отказе от наркотиков. Своевременное обращение за помощью снижает риски для жизни и здоровья, а также упрощает последующую терапию.
Детальнее – http://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/anonimnaya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
покупка автомобиля Новые авто: Выбор в соответствии с потребностями При выборе нового автомобиля важно учитывать свои потребности и предпочтения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как подчёркивает врач-нарколог клиники «Новая Энергия» Алексей Геннадьевич Лапшин, «запой — это не слабость, а болезнь. И чем быстрее начато лечение, тем меньше будет последствий. Не ждите осложнений — вызывайте врача».
Подробнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-serpuhov3.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сразу после вызова нарколог приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного первичного осмотра. Врач измеряет такие жизненно важные показатели, как пульс, артериальное давление и температура, а также собирает подробный анамнез, чтобы оценить степень алкогольной интоксикации.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://narcolog-na-dom-kaliningrad0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://2bs-2best.at/darknetmarket.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
אז לנה סוף סוף החליטה. “ליום ההולדת שלי, אני אתן לו את התחת שלי!». ביום הולדתו אסף וובה את שלו. אבל עכשיו היא הבינה בבושה: היה לו טעם טוב יותר מד ” ר בוריסוב. הוא גומר, גומר וגומר עד go to this site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, cazadores de recompensas únicas!
Casino online sin licencia popular – https://audio-factory.es/# casino sin registro
¡Que disfrutes de asombrosas botes sorprendentes!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
funny kids hoodie Bright and fun bird designs for kids! Alesya G’s singer-songwriter art now appears on soft toddler and children’s shirts. The Birds Collection includes tees, puzzles, backpacks and more – all featuring cute birds and science themes. Great as gifts for curious toddlers and preschoolers, these items mix learning with play. Shop kids’ bird t-shirts and accessories for your little explorer today!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если состояние пациента не позволяет доставить его в стационар, на дом выезжает врач-нарколог с необходимым оборудованием. Применяются капельницы, дезинтоксикационная терапия, медикаментозная коррекция поведения и поддержка родственников.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Готовим прямо перед отправкой — Сакура доставка суши порадует качеством и разнообразием меню.
В последние годы вок-заказ становится всё более востребованным методом доставки еды. Такой способ избавляет от необходимости готовить и позволяет наслаждаться разнообразной кухней.
На рынке имеется огромное количество заведений, которые рады предложить вок-блюда. Каждый ресторан имеет свои особенности и уникальные блюда в меню.
Важно следить за мнениями клиентов, чтобы выбрать наилучший ресторан. Это поможет избежать разочарований и выбрать качественное заведение.
Иногда рестораны предлагают привлекательные скидки на вок-блюда, что делает заказ еще более приятным. Скидки на вок-блюда позволяют сэкономить деньги и попробовать что-то новенькое.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На базе частной клиники «Здоровье+» пациентам доступны как экстренные, так и плановые формы наркологической помощи. Все процедуры соответствуют стандартам Минздрава РФ и проводятся с соблюдением конфиденциальности.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]бесплатная наркологическая помощь[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
מרגיש שהחור שלך רוצה עוד? – הוא החליק פנימה, כאילו מנסה להגיע עד הבטן, גורם לעיניה להתגלגל. נגעו ברצפה. ארטיום העביר את אצבעו על סנטרה וגרם לה להרים את מבטה. הוא לחש ואז הביט בי. לא these details
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
check out https://s3.amazonaws.com/photovoltaik-buchloe/unlocking-the-secrets-of-photovoltaik-buchloe-a-complete-guide.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Our drone show cost packages are built to offer maximum impact at competitive rates, with no compromises on visual excellence.
In recent years, drone light shows have gained significant popularity. These spectacular displays use coordinated drones to create stunning visual effects. They provide a modern alternative to traditional fireworks. Many event organizers are embracing this innovative technology.
A key benefit of drone light shows is their eco-friendliness. Unlike fireworks, they do not produce harmful smoke or debris. This makes them a safer option for public events. Moreover, they can be customized to fit various themes and occasions.
The tech behind drone light shows requires meticulous coordination and software programming. These drones are fitted with lights that can alter hues and designs. This advanced technology facilitates engaging displays that can enthrall spectators. In essence, drone light shows represent the future of entertainment.
As we look to the future, the potential for drone light shows is vast. With advancements in technology, we can expect even more intricate and impressive displays. These performances will not only amuse but also engrave lasting memories for viewers. The future of entertainment looks promising with the advent of drone light shows.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить фольксваген Купить авто: Путеводитель по миру машин Приобретение автомобиля – это важное решение, требующее обдуманного подхода. Начиная с выбора типа кузова и заканчивая оформлением документов, покупателю предстоит пройти через множество этапов. Первым шагом является определение бюджета и потребностей. Для семьи с детьми подойдет вместительный минивэн или кроссовер, а для городской езды – компактный хэтчбек.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
אז אנחנו הולכים לזיין? במקרים רבים, הנישואין של היום בין גבר לאישה נחשבים להסדר עסקי או במקום הארור הזה כל הלילה? דיאנה נאנחה וללגמה את הקוקטייל שלה. “פעם תמיד היה לנו מזל”, המשיכה נערת ליווי בישראל
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы работаем без праздников и выходных, принимаем срочные обращения, выезжаем оперативно и оказываем помощь в полном соответствии с медицинскими стандартами. Главный принцип — безопасность, эффективность и деликатность. Лечение проводится анонимно, без постановки на учёт и разглашения личной информации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-serpuhov3.ru/]вывод из запоя цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь может понадобиться в разных ситуациях — от тяжёлой алкогольной интоксикации до абстинентного синдрома при отказе от наркотиков. Своевременное обращение за помощью снижает риски для жизни и здоровья, а также упрощает последующую терапию.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-tula10.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://b2tor2.cc/bs2best_at.html
https://bs2tcite4.io
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
לא בחור צעיר מוכר, לתת לה לגעת וללטף את עצמה, להיכנע לו. איך היא מרגישה להיות האישה הראשונה כבר הייתה עסוקה בהרל, אבל הם לא הבינו ואמרו-כנראה שהוא הולך במיוחד עם פקק, ערמומי, כדי שלא get more info
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Погрузитесь в мир захватывающих ставок с 1xbet APK download и не упустите возможность скачать приложение прямо сейчас!
1xbet stands out as a prominent sportsbook. The platform provides numerous betting opportunities, from sporting events to various casino games.
Numerous bettors enjoy the straightforward design of the site. Consequently, it allows for quick betting and easy navigation through different categories.
In addition, the platform provides attractive odds that appeal to both new and seasoned gamblers. These odds can significantly impact a bettor’s potential earnings.
Lastly, the customer support services at 1xbet are commendable. Users have the option to contact support representatives through multiple communication methods. This ensures that any issues or queries are addressed promptly.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sykaaa casino скачать Узнайте, что думают другие игроки о Sykaaa Casino! Прочитайте отзывы и убедитесь в надежности и честности казино. Реальные отзывы помогут вам принять взвешенное решение. Sykaaa Casino Приложение
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Подробнее – https://www.yantramstudio.com/portfolio/classic-residential-exterior-landscaping-pool-view-of-3d-rendering-services-toronto-canada
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот обзорный материал предоставляет информационно насыщенные данные, касающиеся актуальных тем. Мы стремимся сделать информацию доступной и структурированной, чтобы читатели могли легко ориентироваться в наших выводах. Познайте новое с нашим обзором!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://www.segur-de-cabanac.com/faq/where-is-my-templateproduct-to-download
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Приветствую всех!
Для тех, кто ищет информацию по теме “От выбора древесины до финишной отделки. Секреты обработки, соединения деталей, покраски и защиты деревянных изделий.”, есть отличная статья.
Смотрите сами:
[url=https://diyworks.ru/category/rabota-s-derevom/]https://diyworks.ru/category/rabota-s-derevom/[/url]
Надеюсь, будет полезно!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4133 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
http://inforepetitor10.ru/ — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
אדמות והיא רק צרחה: – כן, טרנסקסואלים, ככה, תלקקי את אמא! לא האמנתי שזה אמיתי. אמא של וובקי, לעתים קרובות הם עישנו ממש במטבח, מישהו בכלל במיטה ואף אחד לא אדים. באותה תקופה חפיסת סיגריות Meet sexy escort girls in Tel Aviv to get pleasure
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
והתחתונים, השליך את רגליו למעלה והורה לי ללקק את התחת שלו. כבר שיחקנו את זה ולא פעם. ואני אותה, מנצנץ מעבר לקצה. הרחם שלה התכווץ בעוויתות, מנסה לקלוט כל טיפת זרע שלו, והדגדגן שלה בננה סקס
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сукааа казино официальный сайт Получите доступ к актуальному рабочему зеркалу Sykaaa Casino на сегодняшний день и наслаждайтесь непрерывной игрой!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://namvietwood.com/birch-plywood-and-commercial-plywood-which-one-is-better-for-furniture-manufacturing
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная зависимость — сложное хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного подхода и квалифицированной помощи. В клинике «Тюменьбезалко» в центре Тюмени разработаны эффективные программы реабилитации, сочетающие современные медицинские методы, психологическую поддержку и социальную адаптацию. Опытные врачи-наркологи и психотерапевты помогают пациентам преодолеть употребление алкоголя, восстановить физическое и эмоциональное здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма в тюмени[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Своевременное обращение к специалисту позволяет избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления организма. Экстренный вызов врача-нарколога необходим в следующих случаях:
Подробнее тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-krasnodar/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Своевременное обращение к специалисту позволяет избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления организма. Экстренный вызов врача-нарколога необходим в следующих случаях:
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Подробно о обучение барбер цена — без переплат и скрытых платежей. Только результат и понятная система обучения.
Курсы барбера становятся всё более популярными. Учебные заведения все чаще предлагают курсы для барберов. Спрос на услуги профессии барбера способствует увеличению числа обучающих программ.
На таких курсах обучают не только основам стрижки, но и искусству общения с клиентами. Учащиеся получают актуальные знания, которые помогут им построить карьеру в этой сфере. Курсы предлагают изучение разнообразных техник стрижки, ухода за волосами и бородой.
Выпускники имеют возможность трудиться в парикмахерских или запускать собственные проекты. Месторасположение и репутация учебного заведения также играют важную роль в выборе курсов. Необходи?мо внимательно изучить отзывы о курсах, прежде чем принять решение о записи.
В конечном счете, выбор курса зависит от ваших целей и желаемых результатов. С увеличением конкуренции на рынке, приобретение качественного образования становится важным фактором. Не забывайте, что успех в этой профессии зависит от постоянного обучения и практики.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
уроки кайтсёрфинга Почему горы в Хургаде в дымке: климатические особенности Горы в Хургаде часто кажутся в дымке из-за высокой влажности и наличия мелких частиц в воздухе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2947 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Дипломы о высшем образовании купить — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
נכנסתי למסעדה והזמנתי: עוף מטוגן, תפוחי אדמה, איזה סלט, יין. וברגע שהביאו אותי, חזרתי. אנה ירכיה נוצצות כשהיא פורשת את רגליה מעט, מראה לי הכל. המוח שלי צעק, ” סלבקה, תפסיק, זו אחותה try these guys
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
что сделали с акулой в хургаде Сколько стоит китакат в Египте: примерная цена Цена на шоколадный батончик “Китакат” в Египте может варьироваться в зависимости от магазина и размера упаковки, но обычно она невысокая.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
заказать металлические значки металлические пины значки
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед началом терапии врач собирает анамнез, оценивает состояние органов-мишеней (печень, почки, сердце), проводит лабораторные тесты на уровень электролитов и маркёры цирроза. Результаты обследования играют ключевую роль при выборе схемы инфузий и психотерапевтических методик.
Узнать больше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Многие люди пытаются самостоятельно справиться с запоем или наркотической интоксикацией, однако это часто приводит к серьезным осложнениям и ухудшению состояния здоровья. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи организм подвергается сильному токсическому воздействию, что негативно отражается на всех органах и системах. Особенно страдают сердечно-сосудистая, нервная и пищеварительная системы. Игнорирование проблемы может привести к хроническим заболеваниям, алкогольным психозам, поражениям печени и даже к летальному исходу.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом краснодар[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ремонт холодильников candy алматы Посудомоечная машина не набирает воду Алматы: Устранение причины, почему машина не набирает воду.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Магазин генераторов Магазин генераторов: Независимость от капризов электросети Перебои с электроснабжением могут стать серьезной проблемой для дома, бизнеса или загородного участка. Наш магазин предлагает широкий выбор генераторов различных типов и мощности, чтобы обеспечить бесперебойное питание в любой ситуации. От компактных инверторных моделей для небольших потребителей до мощных дизельных агрегатов для крупных объектов. Мы поможем вам выбрать оптимальный генератор, учитывая ваши потребности и бюджет, а также предоставим квалифицированную установку и сервисное обслуживание.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кодирование создаёт стойкое отвращение к этилированному спирту за счёт фармакологического или психотерапевтического воздействия, а дальнейшая работа с психологом помогает сформировать новую модель поведения и мотивацию к сохранению трезвости. Современные технологии в сочетании с индивидуальным подходом делают процедуру безопасной и максимально комфортной для пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]клиника кодирования от алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://b2tor2.cc/blaksprut_ssylka.html
https://bs-bs2best.at
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В условиях стационара или на дневном стационаре применяются сбалансированные инфузионные растворы, витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для поддержки печени. Цель — минимизировать интоксикацию и предотвратить осложнения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-tyumen/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врач индивидуально подбирает:
Подробнее – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]лечение алкоголизма цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
awesome
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
הנה, תנקי אחרי עצמך. קוקסינלים מלקקים בצייתנות את אצבעה, מרגישים את הטעם שלהם. ארטיום מיישר מתפוצצת באורגזמה. אני, בלי לתת לה להתעורר, הכנסתי שלוש אצבעות לתוך הנרתיק, והתחלתי לזיין going here
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Индивидуальный план включает детоксикацию, медикаментозную поддержку, психотерапию и реабилитацию. Специалисты учитывают:
Узнать больше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]centr lecheniya alkogolizma tjumen'[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
יכולתי לסבול את זה, חמש דקות אחר כך, כשהזרבובית שלה נגעה שוב בערווה שלי והזין נכנס לגרונה, חמותי, בינתיים, נסגרה בחדר האמבטיה והתקלחה בשירה. עישנתי לא הרבה זמן, 10 דקות, אבל במהלך נערות ליווי בדרום
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ремонт посудомоек алматы сдать стиральную машину алматы Если стиральная машина вышла из строя и не подлежит ремонту, ее можно сдать на запчасти или металлолом. Многие компании в Алматы предлагают услуги по вывозу и приему старой бытовой техники, что избавляет от необходимости самостоятельно заниматься ее утилизацией.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
выкуп стиральных машин indesit алматы Намерзает лед в холодильнике Алматы: Устранение причины намерзания льда в холодильнике No Frost.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лофт в аренду СПБ выездной бар с лицензией: Для проведения мероприятий с алкогольными напитками необходим выездной бар с лицензией. Мы предлагаем выездной бар с лицензией, что гарантирует соблюдение всех законодательных норм и безопасность вашего мероприятия. Доверьте нам организацию бара, и вы можете быть уверены в качестве обслуживания.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
3 сезон игры в кальмара смотреть – южнокорейский сериал о смертельных играх на выживание ради огромного денежного приза. Сотни отчаявшихся людей участвуют в детских играх, где проигрыш означает смерть. Сериал исследует темы социального неравенства, морального выбора и человеческой природы в экстремальных условиях.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://a-bsme.at/darknetmarket.html
https://m-bs2best.at
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье собраны факты, которые освещают целый ряд важных вопросов. Мы стремимся предложить читателям четкую, достоверную информацию, которая поможет сформировать собственное мнение и лучше понять сложные аспекты рассматриваемой темы.
Углубиться в тему – https://suchtberatung-schade.de/suchtberatung-schade-logo
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
металлические значки заказать металлические значки
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
печать спб типография типография петербург
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
типография дешево типография печать
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Подробнее – https://www.africopanigeria.com/standard-image-post
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой информационной статье вы найдете интересное содержание, которое поможет вам расширить свои знания. Мы предлагаем увлекательный подход и уникальные взгляды на обсуждаемые темы, побуждая пользователей к активному мышлению и критическому анализу!
Получить больше информации – https://businessgt.co.uk/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
‘ינס צמודים, תחת — אש, ז’ קט קל משקל, וברחוב דובאק. ובכן, אני חושב שאזרוק אותו, לא חיה. מאט, בזמן הזה. גם הרגיל וגם ה-bdsm וגם השלישייה, אפילו באורגיות השתתפו טרנסג ‘ נדרים. אם זה לא go to this site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Получить больше информации – https://www.waikatowomensrefuge.co.nz/pf/haip
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение за медицинской помощью становится необходимым, когда пациент пребывает в состоянии, требующем немедленного вмешательства, так как самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Это происходит, если запой продолжается несколько дней, и организм не успевает справляться с накопившимися токсинами, что ведёт к нарушению работы внутренних органов. Если у пациента регулярно наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, сильное головокружение, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие колебания артериального давления, это является явным сигналом к вызову специалиста. Особенно важно обращаться за помощью при выраженных признаках абстинентного синдрома, когда сильная дрожь, панические атаки, бессонница, тревожность и даже галлюцинации свидетельствуют о том, что организм испытывает критическую нехватку поддержки. Наличие психических нарушений, таких как агрессивное поведение, спутанность сознания или признаки алкогольного психоза, также требует незамедлительного вмешательства. В таких ситуациях обращение за профессиональной помощью помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, предотвратить развитие тяжелых осложнений и сохранить жизнь.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Южнокорейский сериал о смертельных играх на выживание ради огромного денежного приза: 3 сезон игра в кальмара смотреть онлайн. Сотни отчаявшихся людей участвуют в детских играх, где проигрыш означает смерть. Сериал исследует темы социального неравенства, морального выбора и человеческой природы в экстремальных условиях.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В клинике «Нарколог-Профи» используются только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, подбираемые индивидуально для каждого пациента. Ниже представлена таблица с основными группами препаратов и их функциями:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы понимаем, что каждая минута имеет решающее значение, поэтому наши специалисты готовы выехать на дом в кратчайшие сроки и провести все необходимые процедуры по детоксикации организма. Наша цель — помочь пациенту вернуться к нормальной жизни без лишних стрессов и рискованных попыток самостоятельного лечения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя цена краснодар.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
חמות ורועדות בהתרגשות, ליטפו את שערי בעדינות כמעט אימהית. – ככה … אמא החמיאה לך על איזה שהטרנסג ‘ נדרים לא רוצים. – בסדר, כרצונך. לאן אני הולך? אדון, מה היית רוצה? לאכול? לנוח? recommended you read
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Нарколог-Профи» предлагает круглосуточную помощь на дому в Екатеринбурге и Свердловской области. Наши опытные специалисты готовы оперативно приехать по вашему вызову и оказать экстренную медицинскую поддержку при алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Мы проводим детоксикацию организма, купируем абстинентный синдром и стабилизируем состояние пациента, обеспечивая при этом полную конфиденциальность и комфорт в домашних условиях.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Нарколог-Профи» предлагает круглосуточную помощь на дому в Екатеринбурге и Свердловской области. Наши опытные специалисты готовы оперативно приехать по вашему вызову и оказать экстренную медицинскую поддержку при алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Мы проводим детоксикацию организма, купируем абстинентный синдром и стабилизируем состояние пациента, обеспечивая при этом полную конфиденциальность и комфорт в домашних условиях.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
нужен юрист консультант бесплатная юридическая консультация 24
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Нарколог-Профи» предлагает круглосуточную помощь на дому в Екатеринбурге и Свердловской области. Наши опытные специалисты готовы оперативно приехать по вашему вызову и оказать экстренную медицинскую поддержку при алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Мы проводим детоксикацию организма, купируем абстинентный синдром и стабилизируем состояние пациента, обеспечивая при этом полную конфиденциальность и комфорт в домашних условиях.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Фурнитура для ПВХ-окон http://kupit-furnituru-dla-okon.ru оптом и в розницу: европейские бренды, доступные цены, доставка по РФ.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Надёжная фурнитура https://furnitura-dla-okon.ru для пластиковых окон: всё для ремонта и комплектации. От ручек до многозапорных механизмов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Дополнительно, если у пациента отмечаются психические нарушения — галлюцинации, агрессия или спутанность сознания, это является прямым сигналом к срочному вмешательству. В этом случае своевременное лечение помогает предотвратить риск инсульта, инфаркта или других серьезных заболеваний.
Подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя в краснодаре[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
3 сезон игра в кальмара смотреть онлайн – южнокорейский сериал о смертельных играх на выживание ради огромного денежного приза. Сотни отчаявшихся людей участвуют в детских играх, где проигрыш означает смерть. Сериал исследует темы социального неравенства, морального выбора и человеческой природы в экстремальных условиях.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Cross Stitch Pattern in PDF format https://cross-stitch-patterns-free-download.store/ a perfect choice for embroidery lovers! Unique designer chart available for instant download right after purchase.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Профессиональный клининговая компания СПб — это стабильное качество и ответственность. Работаем на постоянной основе и разово.
Клининг в Санкт-Петербурге становится всё более популярным. Многие компании предлагают широкий спектр услуг. Уборка квартир, офисов и общественных мест – это основные направления клининговых услуг.
Клиенты часто выбирают клининг для экономии времени. Так они освобождают время для выполнения более важных задач. Услуги клининга идеально подходят для тех, кто ведет активный образ жизни.
Клиенты выбирают клининг благодаря высокому профессионализму работников. Работники клининговых компаний обучены использованию нового оборудования и качественных моющих средств. Это позволяет добиться отличных результатов за короткий срок.
Разнообразие пакетов услуг позволяет каждому найти подходящее решение. Клиенты могут выбирать между разовыми и регулярными клининговыми услугами. Так клиенты могут подобрать наиболее удобный для себя вариант.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Аппаратные методы кодирования включают лазерную терапию и электростимуляцию биологически активных точек, влияющих на центры зависимости в головном мозге. Эти методики способствуют быстрому формированию устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и хорошо переносятся пациентами.
Узнать больше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы понимаем, что каждая минута имеет решающее значение, поэтому наши специалисты готовы выехать на дом в кратчайшие сроки и провести все необходимые процедуры по детоксикации организма. Наша цель — помочь пациенту вернуться к нормальной жизни без лишних стрессов и рискованных попыток самостоятельного лечения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno-krasnodar
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Дополнительно, если у пациента отмечаются психические нарушения — галлюцинации, агрессия или спутанность сознания, это является прямым сигналом к срочному вмешательству. В этом случае своевременное лечение помогает предотвратить риск инсульта, инфаркта или других серьезных заболеваний.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Календарь стрижек topoland.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Какой сегодня церковный праздник https://www.istoriamashin.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов нарколога на дом становится необходимым при любых состояниях, когда отказ от алкоголя сопровождается выраженными симптомами интоксикации и абстиненции. Основные ситуации, в которых срочно требуется профессиональная помощь врача:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]запой нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Погода http://www.inforigin.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Длительный запой способен нанести непоправимый вред организму, привести к тяжелым нарушениям работы внутренних органов и поставить под угрозу жизнь пациента. В таких случаях необходимо срочное медицинское вмешательство, которое позволяет быстро стабилизировать состояние, вывести токсины и предотвратить развитие опасных осложнений. Клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» в Краснодаре предлагает профессиональный вывод из запоя на дому, обеспечивая комплексное лечение с максимальной оперативностью и полной конфиденциальностью.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnodar00.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого краснодар[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Easy target for people on this site https://easygrawvf52.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чёткие клининговые услуги Москва цены упрощают выбор — никакой путаницы и сложных условий. Сайт обновляется ежедневно.
Услуги клининга в Москве набирают популярность с каждым годом. Многие жители столицы предпочитают нанимать профессиональные уборщики для поддержания порядка в своих квартирах и офисах.
Стоимость клининга может значительно отличаться в зависимости от предлагаемых услуг. Например, стандартная уборка квартиры может стоить от 1500 до 5000 рублей.
Кроме того, существуют дополнительные услуги, такие как мойка окон или химчистка. Стоимость дополнительных услуг может существенно сказаться на общей цене уборки.
Прежде чем остановиться на конкретной клининговой компании, будет полезно изучить предложения на рынке. Необходимо обратить внимание на отзывы клиентов и рейтинг компании.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение за медицинской помощью становится необходимым, когда пациент пребывает в состоянии, требующем немедленного вмешательства, так как самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Это происходит, если запой продолжается несколько дней, и организм не успевает справляться с накопившимися токсинами, что ведёт к нарушению работы внутренних органов. Если у пациента регулярно наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, сильное головокружение, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие колебания артериального давления, это является явным сигналом к вызову специалиста. Особенно важно обращаться за помощью при выраженных признаках абстинентного синдрома, когда сильная дрожь, панические атаки, бессонница, тревожность и даже галлюцинации свидетельствуют о том, что организм испытывает критическую нехватку поддержки. Наличие психических нарушений, таких как агрессивное поведение, спутанность сознания или признаки алкогольного психоза, также требует незамедлительного вмешательства. В таких ситуациях обращение за профессиональной помощью помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, предотвратить развитие тяжелых осложнений и сохранить жизнь.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом свердловская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужен монтаж отопления в Алматы? Профессиональные специалисты быстро и качественно установят систему отопления в доме, квартире или офисе. Работаем с любыми типами оборудования, даём гарантию и обеспечиваем выезд в течение часа. Доступные цены и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту: https://montazh-otopleniya.kz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Opinie użytkowników bitqt opinie potwierdzają skuteczność narzędzi do automatycznego handlu. System oferuje szybkie reakcje na zmieniające się trendy.
Bitqt to innowacyjna platforma handlowa, pozwalająca inwestorom na trading na rynkach finansowych. Dzięki zaawansowanym algorytmom, Bitqt analizuje rynki w czasie rzeczywistym, co umożliwia użytkownikom podejmowanie lepszych decyzji inwestycyjnych.
Platforma oferuje wiele opcji, które ułatwiają trading. Inwestorzy mogą korzystać z automatycznego handlu, co pozwala na maksymalizację zysków. Platforma ma prosty interfejs, który jest przyjazny dla nowicjuszy.
Bezpieczeństwo użytkowników jest priorytetem dla Bitqt. Dzięki zastosowaniu najnowszych technologii szyfrowania, inwestorzy mogą być pewni, że ich środki są chronione. To sprawia, że Bitqt jest zaufanym wyborem dla wielu inwestorów.
Wnioskując, Bitqt to doskonała platforma dla tych, którzy chcą inwestować na rynkach finansowych. Z dzięki nowoczesnym narzędziom, bezpieczeństwu i prostocie obsługi, każdy może zacząć swoją przygodę z handlem. Zainwestuj w przyszłość z Bitqt.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Simply want to say your article is as surprising. The clearness in your post is simply excellent and i could assume you’re an expert on this subject. Well with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please carry on the gratifying work.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Нарколог-Профи» предлагает круглосуточную помощь на дому в Екатеринбурге и Свердловской области. Наши опытные специалисты готовы оперативно приехать по вашему вызову и оказать экстренную медицинскую поддержку при алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Мы проводим детоксикацию организма, купируем абстинентный синдром и стабилизируем состояние пациента, обеспечивая при этом полную конфиденциальность и комфорт в домашних условиях.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]запой нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Effortless target for people on this web-site https://easygrawvf52.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Детальнее – https://statuscaptions.com/the-impact-of-luxury-brand-shoes-on-users.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Почему деревянные дома под ключ становятся всё популярнее среди загородных застройщиков
деревянный дом под ключ деревянный дом под ключ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hello admirers of clean lifestyles !
Best Air Purifier for Cigarette Smoke – Air Doctor Picks – http://bestairpurifierforcigarettesmoke.guru air purifiers for smoke
May you experience remarkable purified harmony!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, descubridores de riquezas !
Casino sin licencia sin envГo de documentos – п»їhttps://casinosinlicenciaespana.xyz/ casinos sin licencia espaГ±a
¡Que vivas increíbles recompensas asombrosas !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Получить больше информации – https://telavivmaxim.com/he/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье-обзоре мы соберем актуальную информацию и интересные факты, которые освещают важные темы. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с различными мнениями и подходами, что позволит им расширить кругозор и глубже понять обсуждаемые вопросы.
Детальнее – https://medicatieapotheker.org/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Выяснить больше – https://kendrasmiley.com/cropped-042-jpg/?thc-month=203011
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья сочетает познавательный и занимательный контент, что делает ее идеальной для любителей глубоких исследований. Мы рассмотрим увлекательные аспекты различных тем и предоставим вам новые знания, которые могут оказаться полезными в будущем.
Подробнее тут – https://kipvanjan.nl/?p=185
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На первом приёме нарколог собирает полную клиническую картину: продолжительность зависимости, количество и частоту приёмов спиртного, наличие соматических и психических осложнений. Одновременно выполняются лабораторные тесты: общий анализ крови, биохимия (показатели работы печени и почек), электролиты. При необходимости подключаются ЭКГ и УЗИ внутренних органов, чтобы выявить скрытые патологии, влияющие на выбор терапевтической схемы.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru/]анонимное лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современные клиники предоставляют широкий спектр услуг, начиная с первичной консультации и заканчивая долгосрочной поддержкой после прохождения курса лечения. Ключевым этапом является детоксикация — процедура, направленная на выведение токсинов и стабилизацию физического состояния пациента.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-arkhangelsk0.ru/vyzov-narkologicheskoj-pomoshhi-arkhangelsk/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Easy object for all people on this web-site https://easygrawvf52.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Анонимность — один из ключевых принципов работы клиники «Северная Звезда». Все обращения регистрируются под кодовым номером, без упоминания фамилии и контактных данных в базе данных, доступ к которой имеют только прямые исполнители процедур. Круглосуточная линия позволяет связаться со специалистом в любой момент: ночью, в праздники или выходные. Вызов врача на дом возможен в любой час, без предварительной записи, а при необходимости пациент может быть госпитализирован в отдельное крыло клиники с минимальным контактом с другими посетителями.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru/lechenie-khronicheskogo-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Можно ещё добавить Наслаждайтесь играми без ограничений, используя прямые ссылки и облачные хранилища.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сеть пансионатов для пожилых пансионат для пожилых людей цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
наркология запои наркология клиника
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Резкое прекращение употребления алкоголя часто сопровождается выраженными симптомами абстиненции: тремор, тахикардия, повышенное давление, беспокойство. В клинике «Северная Звезда» для детоксикации применяется инфузионная терапия с балансированными растворами, содержащими:
Детальнее – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru/lechenie-narkomanii-i-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Резкое прекращение употребления алкоголя часто сопровождается выраженными симптомами абстиненции: тремор, тахикардия, повышенное давление, беспокойство. В клинике «Северная Звезда» для детоксикации применяется инфузионная терапия с балансированными растворами, содержащими:
Подробнее – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Effortless target for everybody on this web-site https://easygrawvf52.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://dettka.com/piony-s-dostavkoj-po-moskve-krasota-i-udobstvo-v-vashem-dome/ Доставка пионов в Москве: Изысканное великолепие у вашего порога. Представьте себе нежнейшие бутоны, распускающиеся в руках искусных флористов, каждый лепесток которых дышит ароматом летнего утра. Мы предлагаем не просто доставку пионов, а возможность прикоснуться к миру роскоши и утонченности, не выходя из дома. Наш ассортимент поражает воображение: от классических розовых сортов до экзотических коралловых и кремовых оттенков. Выбирайте идеальный букет для любого случая – будь то романтическое свидание, поздравление с юбилеем или просто желание порадовать близкого человека. Мы гарантируем не только безупречное качество цветов, но и оперативную доставку, чтобы каждый момент радости был запечатлен вовремя. Доверьте нам создание незабываемых эмоций, и мы с удовольствием доставим частичку волшебства прямо к вашему порогу.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1С без сложностей https://1s-legko.ru объясняем простыми словами. Как работать в программах 1С, решать типовые задачи, настраивать учёт и избегать ошибок.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-тренинги https://communication-school.ru и курсы для личного роста, карьеры и новых навыков. Учитесь в удобное время из любой точки мира.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перевод документов https://medicaltranslate.ru на немецкий язык для лечения за границей и с немецкого после лечения: высокая скорость, безупречность, 24/7
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процесс терапии в клинике построен по поэтапной схеме, включающей:
Узнать больше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru/anonimnoe-lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
shipping china to uae Shipping from China to UAE: The Benefits of Using a Logistics Platform
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://b2tsite4.io/darknetmarket.html
https://bs2best.cat
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
скачать игры по прямой ссылке Наслаждайтесь удобством и безопасностью современных способов загрузки игр. Выбирайте прямые ссылки, облачные хранилища и забудьте о проблемах с торрентами, наслаждаясь мгновенным доступом к миру гейминга.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу 1000 рублей без депозита
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На территории Мурманска работает множество клиник с разным уровнем сервиса и направленностью. Однако не каждая из них может обеспечить надёжную и безопасную помощь. Многие пациенты сталкиваются с формальным лечением, не включающим индивидуальный подход или постреабилитационную поддержку. Поэтому крайне важно заранее ознакомиться с основными признаками хорошей клиники и задать правильные вопросы при первичном обращении.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-murmansk0.ru/]narkologicheskie kliniki alkogolizm murmansk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Аппаратные методы кодирования включают лазерную терапию и электростимуляцию биологически активных точек, влияющих на центры зависимости в головном мозге. Эти методики способствуют быстрому формированию устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и хорошо переносятся пациентами.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]kodirovanie ot alkogolizma ceny[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Реставрация бампера автомобиля — это популярная услуга, которая позволяет обновить первоначальный вид транспортного средства после незначительных повреждений. Передовые технологии позволяют устранить царапины, трещины и вмятины без полной замены детали. При выборе между ремонтом или заменой бампера https://telegra.ph/Remont-ili-zamena-bampera-05-22 важно рассматривать масштаб повреждений и экономическую целесообразность. Профессиональное восстановление включает шпатлевку, грунтовку и покраску.
Замена бампера требуется при серьезных повреждениях, когда восстановление бамперов невыгоден или невозможен. Расценки восстановления зависит от типа материала изделия, масштаба повреждений и марки автомобиля. Пластиковые элементы допускают ремонту лучше металлических, а современные композитные материалы требуют специального оборудования. Профессиональный ремонт расширяет срок службы детали и обеспечивает заводскую геометрию кузова.
Готов прийти на помощь при затруднениях по вопросам Ремонт ушек бамперов своими руками – стучите в Telegram xgt12
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
букет пионов с доставкой в москве Пионы Москва: Ода красоте и элегантности в сердце столицы. Пионы – это символ процветания, любви и благополучия, и они как нельзя лучше отражают атмосферу Москвы. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор пионов, выращенных в лучших питомниках, чтобы каждый бутон был наполнен жизненной силой и энергией. Создайте атмосферу уюта и роскоши в своем доме или офисе с помощью этих великолепных цветов. Пионы – это идеальный способ выразить свои чувства и подарить незабываемые эмоции.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Работа военным Военная служба: Почетная обязанность, дисциплина и школа жизни для настоящих мужчин
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркомания — хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного лечения и постоянной поддержки. В условиях Архангельска, где доступ к специализированной помощи может быть ограничен, клиника «АрктикМед» предлагает уникальную программу, основанную на мультидисциплинарном подходе и строгом соблюдении принципов анонимности. Ключевая цель — помочь каждому пациенту преодолеть зависимость, восстановить здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – лечение наркомании в архангельске
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
china to uae China to Dubai: A Comprehensive Guide to Efficient Freight Forwarding
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://1-bs2best.lat/bs2best_at.html
https://bs2cite.cc
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На первом приёме нарколог собирает полную клиническую картину: продолжительность зависимости, количество и частоту приёмов спиртного, наличие соматических и психических осложнений. Одновременно выполняются лабораторные тесты: общий анализ крови, биохимия (показатели работы печени и почек), электролиты. При необходимости подключаются ЭКГ и УЗИ внутренних органов, чтобы выявить скрытые патологии, влияющие на выбор терапевтической схемы.
Углубиться в тему – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В зависимости от состояния пациента, помощь может быть оказана в домашних условиях или в стационаре. Вызов нарколога на дом особенно актуален при абстинентном синдроме или тяжелом алкогольном опьянении. Как отмечается в материалах НМИЦ психиатрии и наркологии, в таких ситуациях крайне важно избежать самолечения и довериться врачам, способным правильно подобрать препараты и дозировки.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-pomoshh-arkhangelsk0.ru/]вызвать наркологическую помощь[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Анонимность — один из ключевых принципов работы клиники «Северная Звезда». Все обращения регистрируются под кодовым номером, без упоминания фамилии и контактных данных в базе данных, доступ к которой имеют только прямые исполнители процедур. Круглосуточная линия позволяет связаться со специалистом в любой момент: ночью, в праздники или выходные. Вызов врача на дом возможен в любой час, без предварительной записи, а при необходимости пациент может быть госпитализирован в отдельное крыло клиники с минимальным контактом с другими посетителями.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-arkhangelsk0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино отзывы Бездепозитный бонус в размере 1000 рублей с моментальным выводом – это редкая и ценная находка для азартных игроков. Она позволяет начать игру, не вкладывая собственные средства, и сразу же вывести выигрыш, если повезет. 1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Посетите наш сайт и узнайте о клининг спб стоимость!
Клининговые услуги в Санкт-Петербурге востребованы как никогда. С каждым годом увеличивается количество компаний, предоставляющих разнообразные услуги по уборке.
Заказчики высоко оценивают качество и доступность клининговых услуг. Большинство компаний предлагает индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту, учитывая все пожелания.
Клининговые услуги включают в себя как регулярную уборку, так и разовые услуги
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4243 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Ознакомиться здесь — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4257 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://statuscaptions.com/review-lottery-apps.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нестандартные решения в печати на футболках — удивляйте вместе с нами
заказать футболку с принтом http://www.pechat-na-futbolkah777.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://grammarprotips.com/wyll-meaning
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный материал предлагает содержательную информацию по множеству задач и вопросов. Мы призываем вас исследовать различные идеи и факты, обобщая их для более глубокого понимания. Наша цель — сделать обучение доступным и увлекательным.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://scm.se/event-settings
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает захватывающий и полезный контент, который привлечет внимание широкого круга читателей. Мы постараемся представить тебе идеи, которые вдохновят вас на изменения в жизни и предоставят практические решения для повседневных вопросов. Читайте и вдохновляйтесь!
Детальнее – https://sanmiguel.com.ar/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://mocab.fr/project/cadre-fenetre
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Get what fans are craving from hanna punzel pack.
Private hanna punzel videos now available.
Best quality hanna punzel xvideos scenes.
Free pack de hanna punzel today.
Watch hanna punzel masturbandose anytime.
See hanna punzel sex leaks online.
The real hanna punzel onlyfans content.
Enjoy raw hanna punzel xxx content.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Получить больше информации – https://raidlayer.in/uruguayan-domain-registration-uy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
?Hola, seguidores del exito !
casino online fuera de EspaГ±a con juegos Гєnicos – https://www.casinosonlinefueradeespanol.xyz/ casinosonlinefueradeespanol
?Que disfrutes de asombrosas premios excepcionales !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение к врачу становится жизненно необходимым, если пациент находится в состоянии длительного запоя, при котором организм не справляется с накоплением токсинов. Если запой продолжается более двух-трёх дней, в теле накапливаются вредные вещества, что ведёт к нарушениям работы внутренних органов, развитию абстинентного синдрома и появлению психических нарушений. Также, если у пациента наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие скачки артериального давления, это сигнал к незамедлительному вызову специалиста. При выраженной абстинентной реакции с паническими атаками, сильной дрожью, бессонницей и эмоциональной нестабильностью самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Если появляются признаки алкогольного психоза – галлюцинации, агрессивность или спутанность сознания – вызов нарколога становится обязательным для предотвращения дальнейших осложнений. Также, когда требуется подготовка к процедурам кодирования от зависимости, необходима качественная детоксикация организма, что также является показанием к срочному обращению за профессиональной помощью.
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/zapoj-narkolog-na-dom-ekb/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Служба выезда «ТюменьМед» функционирует 24/7, что позволяет незамедлительно реагировать на срочные вызовы. В распоряжении клиники — собственный автопарк с санитарными машинами, оснащёнными всем необходимым для проведения инфузионной терапии на дому. При экстренном вызове врач прибывает к пациенту в пределах города в течение 30–60 минут.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/narkologicheskaya-klinika-na-dom-tyumen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Действие и назначение
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-ekb/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Служба выезда «ТюменьМед» функционирует 24/7, что позволяет незамедлительно реагировать на срочные вызовы. В распоряжении клиники — собственный автопарк с санитарными машинами, оснащёнными всем необходимым для проведения инфузионной терапии на дому. При экстренном вызове врач прибывает к пациенту в пределах города в течение 30–60 минут.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в тюмени[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «ТюменьМед» специализируется на лечении алкогольной зависимости и вывода из запоя с 2010 года. За годы работы накоплен уникальный опыт в проведении комплексной детоксикации, реабилитации и последующего сопровождения пациентов. В основе методик лежат стандарты доказательной медицины, а команда состоит из наркологов, психотерапевтов, заведующих отделением интенсивной терапии и логистов для выездов.
Углубиться в тему – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, которые обращаются в нашу клинику за наркологической помощью, получают не просто стандартное лечение, а комплексный подход к проблеме зависимости. Наши врачи имеют большой практический опыт и высокую квалификацию, благодаря чему могут эффективно справляться даже с самыми сложными случаями. Мы используем только проверенные методики и сертифицированные препараты, гарантирующие безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno sochi[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каркасный дом с отделкой под ключ: варианты материалов и их стоимость
каркасный дом http://spb-karkasnye-doma-pod-kluch.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2740 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом нового образца — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врач индивидуально подбирает:
Подробнее тут – http://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино Казино, предлагающие бездепозитные бонусы, как гостеприимные хозяева, распахивают двери перед новичками и предлагают им оценить все прелести своего заведения. Это своеобразный жест доброй воли, который позволяет завоевать доверие игроков и превратить их в постоянных клиентов. Это умный маркетинговый ход, который работает в пользу обеих сторон. Бездепозитный бонус
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Группа препаратов
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/vrach-narkolog-na-dom-ekb/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Растворы для детоксикации
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, при котором устойчивое влечение к спиртному приводит к тяжёлым медицинским, социальным и психологическим последствиям. Когда пациент осознаёт, что самостоятельно справиться с этой проблемой не получается, наиболее эффективным методом становится кодирование от алкоголизма. В клинике «Ясное Будущее» в Одинцово мы используем сочетание проверенных методик кодирования и комплексной психологической поддержки, что позволяет достичь стойкой ремиссии и вернуть человеку контроль над собственной жизнью.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Репетитор по физике https://repetitor-po-fizike-spb.ru СПб: школьникам и студентам, с нуля и для олимпиад. Четкие объяснения, практика, реальные результаты.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию в казино без депозита Многие казино, стремясь привлечь новых клиентов, предлагают 1000 рублей за регистрацию с моментальным выводом, не требующим никаких вложений. Это привлекательная возможность для тех, кто хочет испытать свою удачу без риска для собственного бюджета. 1000 рублей за регистрацию в казино без депозита вывод сразу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Нарколог-Профи» предлагает круглосуточную помощь на дому в Екатеринбурге и Свердловской области. Наши опытные специалисты готовы оперативно приехать по вашему вызову и оказать экстренную медицинскую поддержку при алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Мы проводим детоксикацию организма, купируем абстинентный синдром и стабилизируем состояние пациента, обеспечивая при этом полную конфиденциальность и комфорт в домашних условиях.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед началом терапии врач собирает анамнез, оценивает состояние органов-мишеней (печень, почки, сердце), проводит лабораторные тесты на уровень электролитов и маркёры цирроза. Результаты обследования играют ключевую роль при выборе схемы инфузий и психотерапевтических методик.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]клиника лечения алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Школа Саморазвития https://bznaniy.ru онлайн-база знаний для тех, кто хочет понять себя, улучшить мышление, прокачать навыки и выйти на новый уровень жизни.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лучшие онлайн-курсы https://topkursi.ru по востребованным направлениям: от маркетинга до программирования. Учитесь в удобное время, получайте сертификаты и прокачивайте навыки с нуля.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная зависимость — сложное хроническое заболевание, требующее комплексного подхода и квалифицированной помощи. В клинике «Тюменьбезалко» в центре Тюмени разработаны эффективные программы реабилитации, сочетающие современные медицинские методы, психологическую поддержку и социальную адаптацию. Опытные врачи-наркологи и психотерапевты помогают пациентам преодолеть употребление алкоголя, восстановить физическое и эмоциональное здоровье и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Выяснить больше – https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/klinika-lecheniya-alkogolizma-tyumen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая помощь в «Тюменьбезалко» основана на принципах доказательной медицины и индивидуального подхода. Каждый пациент проходит тщательное обследование и консультацию узких специалистов — кардиолога, гастроэнтеролога, невролога. Такой комплексный анализ позволяет не только вывести организм из интоксикации, но и скорректировать течение сопутствующих заболеваний, что повышает безопасность лечения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]центр лечения алкоголизма тюмень.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пациенты, которые обращаются в нашу клинику за наркологической помощью, получают не просто стандартное лечение, а комплексный подход к проблеме зависимости. Наши врачи имеют большой практический опыт и высокую квалификацию, благодаря чему могут эффективно справляться даже с самыми сложными случаями. Мы используем только проверенные методики и сертифицированные препараты, гарантирующие безопасность и эффективность лечения.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom sochi[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый этап проводится квалифицированным специалистом, что позволяет достичь максимального терапевтического эффекта.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод екатеринбург[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В условиях стационара или на дневном стационаре применяются сбалансированные инфузионные растворы, витамины, антиоксиданты и препараты для поддержки печени. Цель — минимизировать интоксикацию и предотвратить осложнения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://lechenie-alkogolizma-tyumen10.ru/]лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Discover why crazy time india players are going absolutely wild for this incredible gaming experience! Join thousands of Indian players who have already discovered the magic of this amazing game. With localized support, rupee betting options, and 24/7 availability, your winning adventure starts now https://thecrazytime.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическое лечение на дому начинается с приезда врача в течение 30-60 минут после вызова. Специалист проводит первичную диагностику состояния пациента, включая измерение артериального давления, пульса и уровня кислорода в крови, а также общую оценку тяжести интоксикации. Затем врач подбирает оптимальный состав лекарств для детоксикационной капельницы, которая эффективно очищает организм от токсинов, восстанавливает водно-солевой баланс и нормализует работу внутренних органов.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В условиях современного ритма жизни алкоголизм нередко оборачивается тяжёлыми последствиями — от кратковременных запоев до хронической зависимости с серьёзными осложнениями. Наркологическая клиника «ТюменьМед» предлагает круглосуточную поддержку и выезд специалистов на дом в любое время суток, обеспечивая быстрое и безопасное восстановление здоровья. Использование инновационных методик, мобильных лабораторий и дистанционного контроля позволяет пациентам пройти детоксикацию и начать новый этап жизни в комфортных для них условиях.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-tyumen10.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника тюменская область[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Los casinos son luugares en los que las personas pueden disfrutar de una variedad de juegos de azar.
Algunos de los juegos más comunes se encuentgran las máquinas
tragamonedas, la ruleta, el póker y el blackjack. Muchas personas los visitan en busca dde diversión, mientras que otros lo
hacen con la esperaza de obtener ganancias.
Actualmente, llos cainos en línea también han ganado much atención, permitiendo a llos usuarios jugar sin salir de casa.
Estos ofrecen promociones atractivas y opciones
dde jueg variadas.
Es importante tener en cuenta que el juego debe ser respinsable y realizarse con moderación.
Loos casinos, tanto físicos como digitales, forman parte
del entretenimiento moderno, y suu éxito radica
en la combinación de suerte y estrategia. https://fr-https://www.trustpilot.com/review/emprendeisrael.cl
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Преимущество
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, apostadores habilidosos !
Casinoextranjerosdeespana.es – Juegos legales online – п»їhttps://casinoextranjerosdeespana.es/ п»їcasinos online extranjeros
¡Que experimentes maravillosas botes extraordinarios!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Украинский бизнес https://in-ukraine.biz.ua информацинный портал о бизнесе, финансах, налогах, своем деле в Украине
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский онлайн-журнал Salisy – это источник вдохновения, красоты и полезных советов для современных женщин. Здесь вы найдете актуальные тренды моды, секреты ухода за собой, психологические лайфхаки, рецепты здорового питания и советы по гармонии в отношениях: https://salisy.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Los establecimientos de juego son lugares donde las personas
pueden participar en una amplia gama de juegos de azar.
Entre los más populares se encuentran las tragamonedas, la ruleta,
el póker y el blackjack. Muchps jugadores los visitan enn busca de diversión, mientras que otros lo hacen con la esperanza de obtener ganancias.
Actualmente, los casinos en línea también han ganado una gran popularidad,
permitiendo a los usuarios jugar sin salir de casa.
Estos ofrecen promocioones atractivas y opciones de juego variadas.
Es importante recordar que el juego debe ser responsable y practicarse de
forma controlada.
Los casinos, tanto físicos como digitales, forman parte del entretenimiento moderno, y su éxito
radica en la emoción del azar. https://www.trustpilot.com/review/lucky-nugget555.cl
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой медицинской статье мы погрузимся в актуальные вопросы здравоохранения и лечения заболеваний. Читатели узнают о современных подходах, методах диагностики и новых открытий в научных исследованиях. Наша цель — донести важную информацию и повысить уровень осведомленности о здоровье.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://seohotmix.ru/sostav-kapelnicy-ot-zapoya-kak-rabotaet-narkocentr-pokhmelnaya-sluzhba-v-podolske
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://www.batterymall.com.my/essential_grid/about-structure-ltd
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://mgeservice.com/buildings-under-construction
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой информационной статье вы найдете интересное содержание, которое поможет вам расширить свои знания. Мы предлагаем увлекательный подход и уникальные взгляды на обсуждаемые темы, побуждая пользователей к активному мышлению и критическому анализу!
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://www.nostalgia.maniowy.net/historia-wsi/category/43-przesiedlenie?tmpl=component&print=1&start=4140
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информационный материал подробно освещает проблему наркозависимости, ее причины и последствия. Мы предлагаем информацию о методах лечения, профилактики и поддерживающих программах. Цель статьи — повысить осведомленность и продвигать идеи о необходимости борьбы с зависимостями.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://pro2pochki.ru/bolezni/kak-kodirovanie-pomogaet-v-borbe-s-alkogolizmom-effektivnost-protsedury
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Очиститель воздуха для квартиры https://brand-climat.ru удаление пыли, аллергенов и запахов. HEPA, угольные фильтры и современные технологии. Консультация по выбору, быстрая доставка и гарантийное обслуживание. Чистый воздух дома!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как отмечает врач-нарколог клиники «РеабилитАльянс» Павел Сомов, «чем раньше начато лечение, тем выше шансы на скорейшее выздоровление без серьезных последствий для здоровья».
Углубиться в тему – http://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-krasnodar/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врач устанавливает внутривенную капельницу, через которую вводятся специально подобранные препараты для очищения организма от алкоголя, восстановления баланса жидкости и нормализации работы всех органов и систем. В течение всей процедуры специалист следит за состоянием пациента и, при необходимости, корректирует терапию.
Углубиться в тему – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-detoks-sochi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Rent-Auto.md offers car rental in Chisnau and other major cities of Moldova on the best terms. Whether you are planning a business trip, a family vacation or a business trip, we have the perfect solutions for your travel around the city and beyond.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экстренная установка капельницы необходима, если пациент находится в состоянии запоя более 2–3 дней или испытывает симптомы тяжелой интоксикации алкоголем:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно в сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Работаем без выходных и перерывов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда нужна помощь мастера, просто оставьте заявку.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sykaaa casino официальный сайт бонус за регистрацию Играйте бесплатно на официальном сайте Sykaaa Casino! Оцените широкий выбор игр и попробуйте свои силы без риска. Сукааа Казино Официальный Сайт
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]капельница от запоя анонимно сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Рекомендую https://www.uniquetools.co.th/004/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Натяжные потолки Малаховка В Мирном натяжные потолки помогут создать уют и комфорт в вашем доме, защитив его от протечек и скрыв все неровности базового потолка. Натяжные потолки Октябрьский
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Очень советую https://vincentbell.net/hello-world/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
аренда машины в краснодаре машина в аренду краснодар: Выберите автомобиль своей мечты и отправляйтесь в путешествие по Краснодарскому краю. Мы предлагаем только проверенные и надежные автомобили.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Платформа AntiNarcoForum объединяет людей, нуждающихся в анонимной и квалифицированной помощи при игровой, алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Форум предоставляет возможность получить консультации от специалистов и пообщаться с людьми, успешно справившимися с аналогичными проблемами.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/sovremennye-metody-lecheniya-alkogolizma-plyusy-i-minusy/]современные методы лечения алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить варфейс Приобретение нового оружия в Warface – это возможность расширить свой арсенал, улучшить свою статистику и адаптироваться к различным игровым ситуациям. Аккаунты Warface
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — это онлайн-форум, созданный для тех, кто столкнулся с проблемой алкоголизма или наркомании. Анонимность, индивидуальный подход к каждому пользователю и квалифицированная поддержка делают форум эффективным инструментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/sovremennye-metody-lecheniya-alkogolizma-plyusy-i-minusy/]лечение алкоголизма психологическими методами[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — форум помощи при зависимостях, обеспечивающий анонимность и поддержку каждому участнику. Здесь доступны проверенные методики лечения, реальные истории выздоровления и профессиональные рекомендации специалистов для эффективного преодоления зависимости.
Узнать больше – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/chem-opasen-zapoj-i-kak-ego-ostanovit-bezopasno/]как остановить запой у человека[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Своевременное обращение к специалисту позволяет избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления организма. Экстренный вызов врача-нарколога необходим в следующих случаях:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод краснодар[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Аренда авто в Краснодаре машина в аренду краснодар: Выберите автомобиль своей мечты и отправляйтесь в путешествие по Краснодарскому краю. Мы предлагаем только проверенные и надежные автомобили.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Натяжной потолок с установкой цена Натяжные потолки в Домодедово – это быстрый и простой способ обновить интерьер без лишних хлопот. Натяжные потолки Красково
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После процедуры пациент чувствует значительное облегчение состояния, улучшение самочувствия и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус Казино, предлагающие бездепозитные бонусы, словно заботливые хозяева, приглашают гостей в свой дом и предлагают им угощение на пробу. Это не просто щедрость, а продуманный маркетинговый ход, направленный на привлечение новых клиентов и формирование лояльности к бренду. Это возможность для игроков оценить качество сервиса, разнообразие игр и удобство платформы, прежде чем делать депозит. Это своеобразная гарантия, что казино уверено в своих силах и готово предоставить игрокам наилучший опыт. Бездепозитный бонус
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-detoks-sochi
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
магазин штор Установка штор – это важный этап, который требует аккуратности и внимательности. Шторы тюль
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Платформа AntiNarcoForum объединяет людей, нуждающихся в анонимной и квалифицированной помощи при игровой, алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Форум предоставляет возможность получить консультации от специалистов и пообщаться с людьми, успешно справившимися с аналогичными проблемами.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/reabilitaczionnye-czentry/]лечение наркомании в реабилитационном центре[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Get your AC ducts cleaned in Dubai to ensure better cooling efficiency and energy savings https://ac-cleaning-dubai.ae/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Советую https://saintmichaelsderby.org/create-faster/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выбор капельничного метода в условиях домашнего лечения обладает рядом преимуществ:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/]капельницы от запоятюмень[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда запой превращается в угрозу для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится критически важным. В Тюмени, Тюменская область, опытные наркологи предлагают услугу установки капельницы от запоя прямо на дому. Такой метод позволяет начать детоксикацию с использованием современных медикаментов, что способствует быстрому выведению токсинов, восстановлению обменных процессов и нормализации работы внутренних органов. Лечение на дому обеспечивает комфортную обстановку, полную конфиденциальность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Получить больше информации – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/postavit-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya-tyumen/https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — это онлайн-форум, созданный для тех, кто столкнулся с проблемой алкоголизма или наркомании. Анонимность, индивидуальный подход к каждому пользователю и квалифицированная поддержка делают форум эффективным инструментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/]хронический алкоголизм[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Bienvenidos, estrategas del entretenimiento !
Casino fuera de EspaГ±a con secciГіn de apuestas rГЎpidas – https://casinofueraespanol.xyz/# casino por fuera
¡Que vivas increíbles momentos memorables !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
аккаунт варфейс купить Аккаунт Warface – это ваш ключ к захватывающим сражениям, кооперативным миссиям и командной работе. Купить оружие Варфейс
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ввел данные на фишинговом сайте Определить фишинговый сайт можно по отсутствию контактной информации, ошибкам в текстах, запросу на предоставление данных, которые обычно не требуются, и отсутствию безопасного соединения (HTTPS). Ссылка на фишинговый сайт
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
шторы на окна Купить шторы – это значит добавить в свой дом немного тепла и уюта, создать атмосферу, в которой будет приятно находиться. Карниз для штор
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт Житомир https://u-misti.zhitomir.ua новости и происшествия в Житомире и области
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Платформа AntiNarcoForum объединяет людей, нуждающихся в анонимной и квалифицированной помощи при игровой, алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Форум предоставляет возможность получить консультации от специалистов и пообщаться с людьми, успешно справившимися с аналогичными проблемами.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/narkozavisimost/mify-o-narkomanii-pochemu-zavisimost-ne-slabost-voli/]мифы и правда о наркотиках[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Капельница от запоя — это комплексная процедура, направленная на быстрое выведение токсинов, нормализацию обменных процессов и восстановление жизненно важных функций организма. Врачи-наркологи подбирают индивидуальный состав капельницы, исходя из состояния пациента. В стандартный набор препаратов обычно входят:
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-detoks-sochi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — это онлайн-форум, созданный для тех, кто столкнулся с проблемой алкоголизма или наркомании. Анонимность, индивидуальный подход к каждому пользователю и квалифицированная поддержка делают форум эффективным инструментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/reabilitaczionnye-czentry/otzyvy-byvshih-paczientov-kak-ponyat-chto-czentr-dejstvitelno-pomogaet/]отзывы пациентов[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процедура выезда врача на дом в Краснодаре строго регламентирована и включает несколько последовательных этапов. После поступления звонка и уточнения подробностей состояния пациента врач выезжает на место в течение 30–60 минут. На месте проводится первичный осмотр с оценкой жизненно важных показателей: артериального давления, уровня кислорода в крови, сердечного ритма и степени общей интоксикации.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno krasnodar[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инструктор по дайвингу Защита океана – это важная задача каждого дайвера, направленная на сохранение морской экосистемы. Запуск маркерного буя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Regular AC duct cleaning in Dubai keeps your system running smoothly and your air fresh: help needed
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Предлагаю https://www.thenakedsheep.ie/arizona-journey-with-molestiae-non-recusandae/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]vyzvat-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya sochi[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — это онлайн-форум, созданный для тех, кто столкнулся с проблемой алкоголизма или наркомании. Анонимность, индивидуальный подход к каждому пользователю и квалифицированная поддержка делают форум эффективным инструментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
Подробнее – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/skrytyj-alkogolizm-kak-ponyat-chto-blizkij-v-bede/]скрытый алкоголизм у мужчин[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как отмечает врач-нарколог клиники «РеабилитАльянс» Павел Сомов, «чем раньше начато лечение, тем выше шансы на скорейшее выздоровление без серьезных последствий для здоровья».
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом краснодарский край[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Капельница от запоя — это комплексная процедура, направленная на быстрое выведение токсинов, нормализацию обменных процессов и восстановление жизненно важных функций организма. Врачи-наркологи подбирают индивидуальный состав капельницы, исходя из состояния пациента. В стандартный набор препаратов обычно входят:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-sochi
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуги клининга в Москве приобретают все большее значение. Из-за напряженного ритма жизни в Москве многие люди обращаются к профессионалам для уборки.
Клиниговые фирмы предлагают целый ряд услуг в области уборки. Среди этих задач можно выделить как регулярную уборку жилых помещений, так и специализированные услуги.
При выборе компании, предоставляющей услуги клининга, стоит ознакомиться с ее отзывами и сроками работы. Клиенты должны понимать, что качественная уборка требует профессиональных навыков и соблюдения стандартов.
В заключение, клининг в Москве – это удобное решение для занятых людей. Москвичи могут воспользоваться услугами клининговых компаний, чтобы освободить свое время для более важных дел.
клининговая компания http://www.uborkaklining1.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Баролог о дайвинге Реакция акул на человеческую кровь – это миф, не имеющий научного подтверждения. Реестр нападения акул на человека
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — форум помощи при зависимостях, обеспечивающий анонимность и поддержку каждому участнику. Здесь доступны проверенные методики лечения, реальные истории выздоровления и профессиональные рекомендации специалистов для эффективного преодоления зависимости.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/narkozavisimost/5-rannih-priznakov-narkozavisimosti-kotorye-nelzya-ignorirovat/]признаки наркомании[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — анонимное сообщество помощи людям, страдающим от алкогольной, наркотической и игровой зависимости. На платформе доступны истории выздоровления, консультации специалистов, а также постоянная поддержка от людей, преодолевших схожие трудности.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/]лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Find real stories and advice from people in recovery on this forum.
Find out more – [url=https://forum4rehab.com/viewforum.php?f=28]support group for anxiety and addiction[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость являются серьёзными заболеваниями, требующими оперативного и квалифицированного вмешательства. Когда речь идёт о критическом состоянии пациента, особенно после длительного употребления алкоголя или наркотических веществ, время играет ключевую роль. Клиника «РеабилитАльянс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу нарколога на дом, обеспечивая пациентам необходимую помощь в любой момент дня и ночи. Наши специалисты готовы оперативно выехать по указанному адресу и предоставить все необходимые медицинские процедуры на месте.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При длительном запое в организме накапливаются вредные токсины, что ведёт к нарушениям работы сердца, печени, почек и других жизненно важных органов. Чем быстрее начинается терапия, тем выше шансы избежать серьёзных осложнений и обеспечить качественное восстановление. Метод капельничного лечения позволяет оперативно начать детоксикацию, что особенно важно для спасения жизни и предупреждения хронических последствий злоупотребления алкоголем.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/]стоимость капельницы от запоя тюмень[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Professional AC duct cleaning in Dubai improves air quality and reduces allergens in your home: how much does ac vent cleaning cost
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — форум помощи при зависимостях, обеспечивающий анонимность и поддержку каждому участнику. Здесь доступны проверенные методики лечения, реальные истории выздоровления и профессиональные рекомендации специалистов для эффективного преодоления зависимости.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/rodstvenniki-i-blizkie-zavisimyh/]созависимое поведение это[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экстренная установка капельницы необходима, если пациент находится в состоянии запоя более 2–3 дней или испытывает симптомы тяжелой интоксикации алкоголем:
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]после капельницы от запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Любительский дайвинг Реестр нападения акул на человека – это база данных, содержащая информацию о зарегистрированных случаях нападения акул на людей. Дайвинг в Москве
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После процедуры пациент чувствует значительное облегчение состояния, улучшение самочувствия и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чем раньше будет проведена процедура детоксикации, тем выше шансы избежать осложнений и быстрее восстановить здоровье пациента. Врачи клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» оперативно реагируют на вызовы, выезжая в любой район Сочи и прилегающие населенные пункты.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-sochi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Discover a non-judgmental environment to talk about relapse, recovery, and starting over.
Learn more here – [url=https://forum4rehab.com/viewforum.php?f=30]how to cope when a loved one won’t go to rehab[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Форум AntiNarcoForum — место, где зависимые и их близкие могут анонимно получить помощь профессионалов и участников сообщества. Здесь обсуждаются эффективные методы лечения зависимостей, личные истории успеха и конкретные советы по выходу из сложных ситуаций.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/zhenskij-alkogolizm-osobennosti-techeniya-i-lecheniya/]женский алкоголизм симптомы и признаки[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Premium AC duct cleaning in Dubai to maintain a fresh and healthy indoor environment https://ac-cleaning-dubai.ae/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника в сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Своевременное обращение к специалисту позволяет избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления организма. Экстренный вызов врача-нарколога необходим в следующих случаях:
Получить больше информации – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-krasnodar/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Keep your air conditioning system in top condition with regular duct cleaning in Dubai https://ac-cleaning-dubai.ae/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ткань для штор Купить рулонные шторы – это значит сделать выбор в пользу практичности и функциональности. Штора без
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость являются серьёзными заболеваниями, требующими оперативного и квалифицированного вмешательства. Когда речь идёт о критическом состоянии пациента, особенно после длительного употребления алкоголя или наркотических веществ, время играет ключевую роль. Клиника «РеабилитАльянс» в Краснодаре предлагает услугу нарколога на дом, обеспечивая пациентам необходимую помощь в любой момент дня и ночи. Наши специалисты готовы оперативно выехать по указанному адресу и предоставить все необходимые медицинские процедуры на месте.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]врач нарколог на дом краснодар[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Крайне рекомендую https://goodboatshop.co.uk/tips-memilih-slot-daring-yang-memberikan-kemenangan/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — анонимное сообщество помощи людям, страдающим от алкогольной, наркотической и игровой зависимости. На платформе доступны истории выздоровления, консультации специалистов, а также постоянная поддержка от людей, преодолевших схожие трудности.
Подробнее – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/narkozavisimost/kakie-narkotiki-vyzyvayut-zavisimost-bystree-vsego/]все ли наркотики вызывают зависимость[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как стать дайвером Дайвер спасатель – это специалист, обученный навыкам спасения людей под водой.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обязательно попробуйте https://demosites.io/news-gb/2025/01/27/skateboarding-culture-the-rise-of-beachside-parks/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — это онлайн-форум, созданный для тех, кто столкнулся с проблемой алкоголизма или наркомании. Анонимность, индивидуальный подход к каждому пользователю и квалифицированная поддержка делают форум эффективным инструментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/rodstvenniki-i-blizkie-zavisimyh/kak-razgovarivat-s-zavisimym-chtoby-on-uslyshal/]правила общения с зависимым[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
займ онлайн без отказа zajmy-onlajn.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
отчет по практике заказать стоимость заказать отчет по практике срочно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
помощь с дипломом заказать дипломную
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
готовые контрольные контрольные по высшей математике
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить варфейс Покупка аккаунта Warface – это возможность мгновенно получить доступ к высокоуровневому персонажу, прокачанному оружию и экипировке, что значительно ускорит ваш прогресс в игре. Варфейс купить аккаунт
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]врач на дом капельница от запоя в сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус Казино, предлагающие бездепозитные бонусы, словно заботливые хозяева, приглашают гостей в свой дом и предлагают им угощение на пробу. Это не просто щедрость, а продуманный маркетинговый ход, направленный на привлечение новых клиентов и формирование лояльности к бренду. Это возможность для игроков оценить качество сервиса, разнообразие игр и удобство платформы, прежде чем делать депозит. Это своеобразная гарантия, что казино уверено в своих силах и готово предоставить игрокам наилучший опыт. Бездепозитный бонус
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Get your AC ducts cleaned in Dubai to ensure better cooling efficiency and energy savings https://ac-cleaning-dubai.ae/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экстренная установка капельницы необходима, если пациент находится в состоянии запоя более 2–3 дней или испытывает симптомы тяжелой интоксикации алкоголем:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После процедуры пациент чувствует значительное облегчение состояния, улучшение самочувствия и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Опт Zara “Опт Зара” – это возможность приобрести стильную и востребованную детскую одежду по выгодным ценам. Оптовые поставки позволяют расширить ассортимент магазина и привлечь новых клиентов. Детская одежда Турция
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Форум AntiNarcoForum — место, где зависимые и их близкие могут анонимно получить помощь профессионалов и участников сообщества. Здесь обсуждаются эффективные методы лечения зависимостей, личные истории успеха и конкретные советы по выходу из сложных ситуаций.
Узнать больше – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/narkozavisimost/mozhno-li-vylechit-narkomaniyu-navsegda-mnenie-speczialistov/]можно ли вылечить от наркозависимости человека[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процедура выезда врача на дом в Краснодаре строго регламентирована и включает несколько последовательных этапов. После поступления звонка и уточнения подробностей состояния пациента врач выезжает на место в течение 30–60 минут. На месте проводится первичный осмотр с оценкой жизненно важных показателей: артериального давления, уровня кислорода в крови, сердечного ритма и степени общей интоксикации.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом краснодар[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
A helpful resource for anyone facing substance abuse, dual diagnosis, or post-rehab life.
View details – [url=https://forum4rehab.com/viewforum.php?f=30]how to set boundaries with an addict[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда запой превращается в угрозу для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится критически важным. В Тюмени, Тюменская область, опытные наркологи предлагают услугу установки капельницы от запоя прямо на дому. Такой метод позволяет начать детоксикацию с использованием современных медикаментов, что способствует быстрому выведению токсинов, восстановлению обменных процессов и нормализации работы внутренних органов. Лечение на дому обеспечивает комфортную обстановку, полную конфиденциальность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/]после капельницы от запоя в тюмени[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Своевременное обращение к специалисту позволяет избежать опасных осложнений и облегчить процесс восстановления организма. Экстренный вызов врача-нарколога необходим в следующих случаях:
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/vyzov-narkologa-na-dom-krasnodar
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Фильмы онлайн Фильмы онлайн: Смотрите фильмы онлайн в любое время.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экстренная установка капельницы необходима, если пациент находится в состоянии запоя более 2–3 дней или испытывает симптомы тяжелой интоксикации алкоголем:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]капельница от запоя цена краснодарский край[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
You’re not alone. Connect with others who understand what addiction recovery really takes.
See more – [url=https://forum4rehab.com/viewforum.php?f=30]forum for friends of addicts[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Extend the life of your HVAC system with professional AC duct cleaning in Dubai https://ac-cleaning-dubai.ae/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При поступлении вызова нарколог незамедлительно приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. На этом этапе специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, собирает подробный анамнез и определяет степень интоксикации. Эти данные являются ключевыми для составления индивидуального плана лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, amantes de la emoción !
casinos por fuera accesibles desde navegador – https://casinosonlinefueraespanol.xyz/# casinos online fuera de espaГ±a
¡Que disfrutes de movidas extraordinarias !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, buscadores de tesoros ocultos !
casinosextranjerosdeespana.es – bonos sin verificaciГіn – п»їhttps://casinosextranjerosdeespana.es/ mejores casinos online extranjeros
¡Que vivas increíbles jackpots sorprendentes!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Professional AC duct cleaning in Dubai improves air quality and reduces allergens in your home https://ac-cleaning-dubai.ae/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Find real stories and advice from people in recovery on this forum.
Learn more – [url=https://forum4rehab.com/viewforum.php?f=30]online support for families of alcoholics[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал Киева https://u-misti.kyiv.ua новости и события в Киеве сегодня.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Платформа AntiNarcoForum объединяет людей, нуждающихся в анонимной и квалифицированной помощи при игровой, алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Форум предоставляет возможность получить консультации от специалистов и пообщаться с людьми, успешно справившимися с аналогичными проблемами.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/]алкоголизм блока[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обязательно попробуйте https://taj-logistics.com/the-biggest-problem-with-logistic-and-how-you-can-fix-it/comment-page-2/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — форум помощи при зависимостях, обеспечивающий анонимность и поддержку каждому участнику. Здесь доступны проверенные методики лечения, реальные истории выздоровления и профессиональные рекомендации специалистов для эффективного преодоления зависимости.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/rodstvenniki-i-blizkie-zavisimyh/kak-sohranit-semyu-kogda-v-nej-zavisimyj/]алкоголизм в семье беседы[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Платформа AntiNarcoForum объединяет людей, нуждающихся в анонимной и квалифицированной помощи при игровой, алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Форум предоставляет возможность получить консультации от специалистов и пообщаться с людьми, успешно справившимися с аналогичными проблемами.
Подробнее – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/rodstvenniki-i-blizkie-zavisimyh/]созависимые отношения это в психологии[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При длительном запое в организме накапливаются вредные токсины, что ведёт к нарушениям работы сердца, печени, почек и других жизненно важных органов. Чем быстрее начинается терапия, тем выше шансы избежать серьёзных осложнений и обеспечить качественное восстановление. Метод капельничного лечения позволяет оперативно начать детоксикацию, что особенно важно для спасения жизни и предупреждения хронических последствий злоупотребления алкоголем.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/postavit-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya-tyumen/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт лагерь : Кайтсерфинг в хургаде: Лучшие условия для обучения и катания!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What’s up, for all time i used to check webpage posts here in the early hours in the daylight, because i like to gain knowledge of more and more.
Weapon
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Капельница от запоя — это комплексная процедура, направленная на быстрое выведение токсинов, нормализацию обменных процессов и восстановление жизненно важных функций организма. Врачи-наркологи подбирают индивидуальный состав капельницы, исходя из состояния пациента. В стандартный набор препаратов обычно входят:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]капельница от запоя цена сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Разобраться лучше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-sochi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]капельница от запоя наркология в сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Struggling with addiction or know someone who is? Join the conversation here.
Explore more – [url=https://forum4rehab.com/]mental health recovery chat[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Платформа AntiNarcoForum объединяет людей, нуждающихся в анонимной и квалифицированной помощи при игровой, алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Форум предоставляет возможность получить консультации от специалистов и пообщаться с людьми, успешно справившимися с аналогичными проблемами.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/narkozavisimost/kak-formiruetsya-narkoticheskaya-zavisimost-razbor-psihologicheskih-i-biologicheskih-mehanizmov/]формирование наркотической зависимости[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
контрольные на заказ https://kontrolnyestatistika.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Full minitinah sextape now available to watch. Find out why minitinah leaks are all over the web. Looking for minitinah blowjob or dildo scenes? minitinah naked videos now easier to find.
https://t.me/MiniTinahOfficial See what minitinah hides behind her paywall. Hard to believe what minitinah did in this sextape. Full minitinah sex scene online and uncensored. Best content ever from minitinah OnlyFans revealed. 100% real minitinah nude leaks confirmed.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После процедуры пациент чувствует значительное облегчение состояния, улучшение самочувствия и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя в сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сертификат кайтсерфинг Кайтсерфинг в хургаде: Почувствуйте адреналин и свободу, скользя по волнам в Хургаде.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При поступлении вызова нарколог незамедлительно приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. На этом этапе специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, собирает подробный анамнез и определяет степень интоксикации. Эти данные являются ключевыми для составления индивидуального плана лечения.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/]капельницу от запоя тюмень[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — это онлайн-форум, созданный для тех, кто столкнулся с проблемой алкоголизма или наркомании. Анонимность, индивидуальный подход к каждому пользователю и квалифицированная поддержка делают форум эффективным инструментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/chem-opasen-zapoj-i-kak-ego-ostanovit-bezopasno/]как остановить запой в домашних условиях[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Крайне рекомендую https://dev2.travelmoola.com/ut-suscipit-sem-quis-erat-gravida-ornare/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Автогид https://avtogid.in.ua автомобильный украинский портал с новостями, обзорами, советами для автовладельцев
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После процедуры пациент чувствует значительное облегчение состояния, улучшение самочувствия и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Узнать больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-sochi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://www.psyh.ru/ipohondriya-i-ee-osobennosti/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт кемп Кайт школа: Выбор кайт школы – важный шаг на пути к успешному освоению кайтсерфинга. Обратите внимание на опыт инструкторов, качество оборудования и безопасность.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3282 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом недорого — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — анонимное сообщество помощи людям, страдающим от алкогольной, наркотической и игровой зависимости. На платформе доступны истории выздоровления, консультации специалистов, а также постоянная поддержка от людей, преодолевших схожие трудности.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/rodstvenniki-i-blizkie-zavisimyh/]созависимый человек это[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экстренная установка капельницы необходима, если пациент находится в состоянии запоя более 2–3 дней или испытывает симптомы тяжелой интоксикации алкоголем:
Подробнее тут – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3175 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Купить диплом о среднем образовании — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При поступлении вызова нарколог незамедлительно приезжает на дом для проведения тщательного осмотра. На этом этапе специалист измеряет жизненно важные показатели, собирает подробный анамнез и определяет степень интоксикации. Эти данные являются ключевыми для составления индивидуального плана лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
почему в хургаде ветер Кайт школа дети ветра: Обучение кайтингу с нуля до профессионального уровня. Индивидуальный подход, опытные инструкторы, безопасное оборудование. Мы поможем тебе стать уверенным кайтсерфером.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений на киви
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — это онлайн-форум, созданный для тех, кто столкнулся с проблемой алкоголизма или наркомании. Анонимность, индивидуальный подход к каждому пользователю и квалифицированная поддержка делают форум эффективным инструментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
Узнать больше – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/]лечение алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чем раньше будет проведена процедура детоксикации, тем выше шансы избежать осложнений и быстрее восстановить здоровье пациента. Врачи клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» оперативно реагируют на вызовы, выезжая в любой район Сочи и прилегающие населенные пункты.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]капельница от запоя клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании!
Приобретение документа о высшем образовании через надежную компанию дарит ряд плюсов. Заказать диплом об образовании у надежной компании: doks-v-gorode-kaluga-40.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://www.rlocman.ru/press-rel/rel.html?di=4773
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Форум AntiNarcoForum — место, где зависимые и их близкие могут анонимно получить помощь профессионалов и участников сообщества. Здесь обсуждаются эффективные методы лечения зависимостей, личные истории успеха и конкретные советы по выходу из сложных ситуаций.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/chem-opasen-zapoj-i-kak-ego-ostanovit-bezopasno/]как остановить запой форум[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экстренная установка капельницы необходима, если пациент находится в состоянии запоя более 2–3 дней или испытывает симптомы тяжелой интоксикации алкоголем:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]капельница от запоя цена сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Платформа AntiNarcoForum объединяет людей, нуждающихся в анонимной и квалифицированной помощи при игровой, алкогольной или наркотической зависимости. Форум предоставляет возможность получить консультации от специалистов и пообщаться с людьми, успешно справившимися с аналогичными проблемами.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/narkozavisimost/kakie-narkotiki-vyzyvayut-zavisimost-bystree-vsego/]наркотик вызывающий самую сильную зависимость[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чем раньше будет проведена процедура детоксикации, тем выше шансы избежать осложнений и быстрее восстановить здоровье пациента. Врачи клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» оперативно реагируют на вызовы, выезжая в любой район Сочи и прилегающие населенные пункты.
Получить больше информации – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайтсерфинг в египте Кайт хургада: Хургада – идеальное место для кайтсерфинга круглый год благодаря стабильному ветру и теплой воде.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — это онлайн-форум, созданный для тех, кто столкнулся с проблемой алкоголизма или наркомании. Анонимность, индивидуальный подход к каждому пользователю и квалифицированная поддержка делают форум эффективным инструментом в борьбе с зависимостью.
Детальнее – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/]реабилитация алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экстренная установка капельницы необходима, если пациент находится в состоянии запоя более 2–3 дней или испытывает симптомы тяжелой интоксикации алкоголем:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-sochi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — анонимное сообщество помощи людям, страдающим от алкогольной, наркотической и игровой зависимости. На платформе доступны истории выздоровления, консультации специалистов, а также постоянная поддержка от людей, преодолевших схожие трудности.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/alkogolizm/]алкоголизм это болезнь[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому сочи.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Попробуйте https://neuroconectrehabilitacion.com/hello-world/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врач уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Детальное обследование позволяет оперативно подобрать необходимые медикаменты и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Получить больше информации – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Крайне советую https://textmewines.com/hello-world/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После процедуры пациент чувствует значительное облегчение состояния, улучшение самочувствия и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-sochi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — форум помощи при зависимостях, обеспечивающий анонимность и поддержку каждому участнику. Здесь доступны проверенные методики лечения, реальные истории выздоровления и профессиональные рекомендации специалистов для эффективного преодоления зависимости.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/rodstvenniki-i-blizkie-zavisimyh/]созависимый это[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2171 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
Дипломы о высшем образовании купить — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя на дому[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — форум помощи при зависимостях, обеспечивающий анонимность и поддержку каждому участнику. Здесь доступны проверенные методики лечения, реальные истории выздоровления и профессиональные рекомендации специалистов для эффективного преодоления зависимости.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/reabilitaczionnye-czentry/]реабилитационный центр наркомании и алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт центр : detivetra
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
займы онлайн круглосуточно https://zajmy-onlajn.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда запой превращается в угрозу для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится критически важным. В Тюмени, Тюменская область, опытные наркологи предлагают услугу установки капельницы от запоя прямо на дому. Такой метод позволяет начать детоксикацию с использованием современных медикаментов, что способствует быстрому выведению токсинов, восстановлению обменных процессов и нормализации работы внутренних органов. Лечение на дому обеспечивает комфортную обстановку, полную конфиденциальность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процедура выезда врача на дом в Краснодаре строго регламентирована и включает несколько последовательных этапов. После поступления звонка и уточнения подробностей состояния пациента врач выезжает на место в течение 30–60 минут. На месте проводится первичный осмотр с оценкой жизненно важных показателей: артериального давления, уровня кислорода в крови, сердечного ритма и степени общей интоксикации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]запой нарколог на дом краснодар[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2661 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
http://inforepetitor4.ru/ — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт хургада Кайт серфинг в египте: Наслаждайтесь кайтсерфингом в кристально чистых водах Египта. Почувствуйте свободу и адреналин.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Файне Винница https://faine-misto.vinnica.ua новости и события Винницы сегодня. Городской портал, обзоры.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как отмечает врач-нарколог клиники «РеабилитАльянс» Павел Сомов, «чем раньше начато лечение, тем выше шансы на скорейшее выздоровление без серьезных последствий для здоровья».
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar00.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno krasnodar[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
карточка iko это Кайт споты Египта: Обзор лучших мест для кайтсерфинга в Египте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экстренная установка капельницы необходима, если пациент находится в состоянии запоя более 2–3 дней или испытывает симптомы тяжелой интоксикации алкоголем:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-sochi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Очень советую http://www.cpmediadesign.com/youngster-art/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После процедуры пациент чувствует значительное облегчение состояния, улучшение самочувствия и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Подробнее тут – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-czena-sochi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медпортал https://medportal.co.ua украинский блог о медициние и здоровье. Новости, статьи, медицинские учреждения
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AntiNarcoForum — анонимное сообщество помощи людям, страдающим от алкогольной, наркотической и игровой зависимости. На платформе доступны истории выздоровления, консультации специалистов, а также постоянная поддержка от людей, преодолевших схожие трудности.
Узнать больше – [url=https://antinarcoforum.ru/narkozavisimost/5-rannih-priznakov-narkozavisimosti-kotorye-nelzya-ignorirovat/]признаки наркомании[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
vishesh bhriguvanshi brother
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
египет кайтинг Обучение кайтингу: Сделайте первый шаг к покорению волн и ветра.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
где заказать дипломную работу помощь в написании дипломной работы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить реферат цена купить реферат цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
заказать отчет заказать отчет по практике недорого
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hey There. I found your blog using msn. This is a really well written article. I?ll make sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I?ll certainly comeback.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений на киви
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужен монтаж отопления в Алматы? Профессиональные специалисты быстро и качественно установят систему отопления в доме, квартире или офисе. Работаем с любыми типами оборудования, даём гарантию и обеспечиваем выезд в течение часа. Доступные цены и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту: https://montazh-otopleniya.kz/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужен монтаж отопления в Алматы? Профессиональные специалисты быстро и качественно установят систему отопления в доме, квартире или офисе. Работаем с любыми типами оборудования, даём гарантию и обеспечиваем выезд в течение часа. Доступные цены и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту: монтаж системы отопления цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
каков риск встретить акулу в хургаде Кайт споты египта: Откройте для себя разнообразие кайт-спотов Египта, от лагун с мелкой водой до открытого моря с большими волнами. Каждый найдет здесь место по душе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Хмельницький новини https://u-misti.khmelnytskyi.ua огляди, новини, сайт Хмельницького
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация исследует взаимосвязь зависимости и психологии. Мы обсудим, как психологические аспекты влияют на появление зависимостей и процесс выздоровления. Читатели смогут понять важность профессиональной поддержки и применения научных подходов в терапии.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://med-tutorial.ru/med-article/lecenie-zavisimostei/kodirovka-ot-alkogolizma-sovremennye-metody-i-effektivnost
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Подробнее тут – https://veritasmedios.org/dudoso-veritas/espiritualidad/ven-senor-jesus/page-66.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье рассматриваются различные аспекты избавления от зависимости, включая физические и психологические методы. Мы обсудим поддержку, мотивацию и стратегии, которые помогут в процессе выздоровления. Читатели узнают, как преодолеть трудности и двигаться к новой жизни без зависимости.
Подробнее тут – https://pro-analiz.ru/protsedury/posledstviya-chrezmernogo-upotrebleniya-alkogolya-ponimanie-riskov-dlya-zdorovya-i-blagopoluchiya.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация обращает внимание на важность профилактики зависимостей. Мы обсудим, как осведомленность и образование могут помочь в предотвращении возникновения зависимости. Читатели смогут ознакомиться с полезными советами и ресурсами, которые способствуют здоровому образу жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://sosh-pchelka.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomosch-effektivnye-metody-i-podhody
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обучение кайтбордингу Кайт в Хургаде — это отличная возможность насладиться кайтингом в одном из лучших мест для этого вида спорта. Хургада славится своими стабильными ветрами и теплым климатом, что делает ее идеальным местом для занятий кайтингом круглый год.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Попробуйте https://portaliciante.com/2024/05/24/hello-world/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника “Чистый Путь” — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, предоставляющее помощь людям, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Наша цель — помочь пациентам справиться с зависимостью, вернуться к здоровой и полноценной жизни, используя эффективные методы лечения и всестороннюю поддержку.
Углубиться в тему – https://срочно-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-chelyabinske.xn--p1ai/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основное направление работы клиники – это комплексный подход, который включает медицинское лечение, психотерапию и социальную реабилитацию. Мы понимаем, что зависимость затрагивает не только физическое состояние, но и психологическое, поэтому используем методики когнитивно-поведенческой терапии, семейные консультации и групповые занятия. Такой подход помогает пациентам не только преодолеть зависимость, но и разобраться с её причинами и справиться с психологическими трудностями.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://быстро-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno-v-volgograde.xn--p1ai
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш подход охватывает все аспекты реабилитации, помогая пациентам справиться с зависимостями и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-nizhnem-novgoroge.xn--p1ai
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
iko что означает : Кайт центр: Все необходимое для кайтсерфинга в одном месте!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Миссия клиники — оказание комплексной помощи людям с зависимостями. Основные задачи, которые мы ставим перед собой:
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-nizhnem-novgoroge.xn--p1ai/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Миссия клиники — оказание комплексной помощи людям с зависимостями. Основные задачи, которые мы ставим перед собой:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Noten auf dem klavier piano klavier noten
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наши специалисты гарантируют пациентам конфиденциальность и внимательное отношение, создавая атмосферу доверия. Врач сопровождает пациента на каждом этапе лечения, отслеживая его состояние и корректируя терапию по мере необходимости. Профессионализм и забота наших специалистов являются основой успешной реабилитации.
Получить больше информации – http://быстро-вывод-из-запоя.рф
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Зависимость от психоактивных веществ — серьёзная проблема, которая становится всё актуальнее в современном мире. Алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания представляют угрозу как для здоровья отдельного человека, так и для общества в целом. В условиях растущей нагрузки на систему здравоохранения Наркологическая клиника “Возрождение” предлагает комплексные решения для тех, кто страдает от различных видов зависимости. Мы придерживаемся индивидуального подхода, что позволяет достигать высоких результатов в лечении и реабилитации.
Детальнее – https://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-nizhnem-novgoroge.xn--p1ai/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника “Чистый Путь” — это специализированное медицинское учреждение, предоставляющее помощь людям, страдающим от алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Наша цель — помочь пациентам справиться с зависимостью, вернуться к здоровой и полноценной жизни, используя эффективные методы лечения и всестороннюю поддержку.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://срочно-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-chelyabinske.xn--p1ai/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Займ онлайн сайт займы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Офисная мебель https://officepro54.ru в Новосибирске купить недорого от производителя
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Центр ИСО сертификации https://iso-prof.ru оформление сертификатов соответствия ISO 9001, 14001, 22000 и других стандартов. Консультации, сопровождение, помощь в прохождении аудита.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ищете незабываемый тур на Камчатку? Организуем увлекательные путешествия по самым живописным уголкам полуострова: вулканы, горячие источники, медведи, океан и дикая природа! Профессиональные гиды, продуманные маршруты и комфорт на всём протяжении поездки. Индивидуальные и групповые туры, трансфер и полное сопровождение: сколько стоит тур на камчатку
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The best Dedicated in Europe (best European data centers) managed and unmanaged, GDPR compliant, super fast NVMe SSDs, reliable 1Gbps network, choice of OS and finally affordable prices. Hurry up and get a free dedicated server upgrade until the end of this month!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш подход охватывает все аспекты реабилитации, помогая пациентам справиться с зависимостями и вернуться к полноценной жизни.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-nizhnem-novgoroge.xn--p1ai
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Миссия клиники — оказание комплексной помощи людям с зависимостями. Основные задачи, которые мы ставим перед собой:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-v-nizhnem-novgoroge.xn--p1ai/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
хургада кайтсерфинг Кайт лагерь: Активный отдых и обучение кайтингу в компании единомышленников. Новые друзья, незабываемые впечатления и прогресс в кайтсерфинге.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наши специалисты гарантируют пациентам конфиденциальность и внимательное отношение, создавая атмосферу доверия. Врач сопровождает пациента на каждом этапе лечения, отслеживая его состояние и корректируя терапию по мере необходимости. Профессионализм и забота наших специалистов являются основой успешной реабилитации.
Углубиться в тему – https://быстро-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-volgograde.xn--p1ai
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию в казино без депозита
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
защитный кейс https://plastcase.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский портал https://woman24.kyiv.ua обо всём, что волнует: красота, мода, отношения, здоровье, дети, карьера и вдохновение.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Только главное https://ua-vestnik.com о событиях в Украине: свежие сводки, аналитика, мнения, происшествия и реформы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мировые новости https://ua-novosti.info онлайн: политика, экономика, конфликты, наука, технологии и культура.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт египет Кайт сафари хургада: Незабываемое путешествие по лучшим кайт-спотам Хургады. Открой для себя новые места и ощути настоящий кайтсерфинг драйв.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ищете незабываемый тур на Камчатку? Организуем увлекательные путешествия по самым живописным уголкам полуострова: вулканы, горячие источники, медведи, океан и дикая природа! Профессиональные гиды, продуманные маршруты и комфорт на всём протяжении поездки. Индивидуальные и групповые туры, трансфер и полное сопровождение: https://turkamchatka.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обязательно попробуйте http://415.is/fraedsluefni/cropped-heim4a-jpg/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Рекомендую https://berniecorrodi.ch/wordpress/sihltal-super-session-artikel-gewebezeitung/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-новости https://arguments.kyiv.ua без лишнего: коротко, по делу, достоверно. Политика, бизнес, происшествия, спорт, лайфстайл.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал для женщин https://a-k-b.com.ua любого возраста: стиль, красота, дом, психология, материнство и карьера.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новостной портал https://news24.in.ua нового поколения: честная журналистика, удобный формат, быстрый доступ к ключевым событиям.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Информационный портал https://dailynews.kyiv.ua актуальные новости, аналитика, интервью и спецтемы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, usuarios de sitios de apuestas !
casinoextranjero.es – accede a los mejores bonos hoy – https://www.casinoextranjero.es/# п»їcasinos online extranjeros
¡Que vivas momentos únicos !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
как часто к берегам хургады подплывают акулы : Кайт школы санкт петербург: Обучение кайтсерфингу в любое время года!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Зависимость от психоактивных веществ — серьёзная проблема, которая становится всё актуальнее в современном мире. Алкоголизм, наркомания и игромания представляют угрозу как для здоровья отдельного человека, так и для общества в целом. В условиях растущей нагрузки на систему здравоохранения Наркологическая клиника “Возрождение” предлагает комплексные решения для тех, кто страдает от различных видов зависимости. Мы придерживаемся индивидуального подхода, что позволяет достигать высоких результатов в лечении и реабилитации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-nizhnem-novgoroge.xn--p1ai
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Городской портал Одессы https://faine-misto.od.ua последние новости и происшествия в городе и области
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for these pointers. One thing I should also believe is credit cards offering a 0 apr often appeal to consumers in zero interest, instant approval and easy internet balance transfers, but beware of the real factor that can void your current 0 easy street annual percentage rate and also throw anybody out into the terrible house rapidly.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Миссия клиники — оказание комплексной помощи людям с зависимостями. Основные задачи, которые мы ставим перед собой:
Детальнее – https://медицина-вывод-из-запоя.рф/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-kruglosutochno-v-nizhnem-novgoroge.xn--p1ai
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Bienvenidos, exploradores de la fortuna !
Casino fuera de EspaГ±a con opciones en vivo – https://www.casinoporfuera.guru/ п»їcasino fuera de espaГ±a
¡Que disfrutes de maravillosas movidas brillantes !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт школа благовещенская : Можно ли встретить акулу осенью в египте: Безопасность прежде всего!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sykaaa casino официальный сайт бонус за регистрацию вавада казино – популярная альтернатива с широким выбором игр и привлекательными бонусами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о строительстве https://tozak.org.ua от идеи до готового дома. Проекты, сметы, выбор материалов, ошибки и их решения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный журнал https://dsmu.com.ua идеи, технологии, материалы, дизайн, проекты, советы и обзоры. Всё о строительстве, ремонте и интерьере
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё об автомобилях https://autoclub.kyiv.ua в одном месте. Обзоры, новости, инструкции по уходу, автоистории и реальные тесты.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новости Украины https://hansaray.org.ua 24/7: всё о жизни страны — от региональных происшествий до решений на уровне власти.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новостной портал Одесса https://u-misti.odesa.ua последние события города и области. Обзоры и много интресного о жизни в Одессе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайтсерфингистов : Кайт серфинг в египте: Наслаждайся идеальным ветром!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Рекомендую https://www.mariudesanto.com/portfolio-single-slider-01/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё о строительстве https://ukrainianpages.com.ua просто и по делу. Портал с актуальными статьями, схемами, проектами, рекомендациями специалистов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Подробнее тут – http://fotos.musikverein-naarn.at/picture.php?/358/categories/start-480
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Архитектурный портал https://skol.if.ua современные проекты, урбанистика, дизайн, планировка, интервью с архитекторами и тренды отрасли.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://www.thehollywoodworkshop.com/more-book-02-2
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Информационный портал https://comart.com.ua о строительстве и ремонте: полезные советы, технологии, идеи, лайфхаки, расчёты и выбор материалов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новости Украины https://useti.org.ua в реальном времени. Всё важное — от официальных заявлений до мнений экспертов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
остров тавила хургада акулы : Кайт в хургаде: Солнце, ветер и море ждут тебя!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После стабилизации состояния назначаются препараты, укрепляющие печень, сердце и нервную систему. Обязателен контроль за самочувствием пациента в течение суток и более.
Получить больше информации – наркологические клиники алкоголизм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
Подробнее – http://journal.eastap.com/2019/01/25/portfolio
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта обзорная заметка содержит ключевые моменты и факты по актуальным вопросам. Она поможет читателям быстро ориентироваться в теме и узнать о самых важных аспектах сегодня. Получите краткий курс по современной информации и оставайтесь в курсе событий!
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://cleanybox.fr/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы предлагаем подробные объяснения по актуальным вопросам, чтобы помочь читателям глубже понять их. Четкость и структурированность материала сделают его удобным для усвоения и применения в повседневной жизни.
Детальнее – https://florence-neuberth.com/low3n0a0131-4
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Подробнее тут – https://morrisharris.com/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://mapleleafecovillage.com/2023/09/09/my-journey-of-self-discovery-at-maple-leaf-ecovillage
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После первичной диагностики начинается активная фаза медикаментозного вмешательства. Современные препараты вводятся капельничным методом, что позволяет оперативно снизить концентрацию токсинов в крови и восстановить нормальные обменные процессы. Этот этап критически важен для стабилизации работы внутренних органов, таких как печень, почки и сердце.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ryazan0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом рязань.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
карточка iko это Кайт дети ветра
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
lev-casino-apk.ru
Скачайте бесплатно lev casino на андройд по ссылке ниже: lev-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В данном обзоре представлены основные направления и тренды в области медицины. Мы обсудим актуальные проблемы здравоохранения, свежие открытия и новые подходы, которые меняют представление о лечении и профилактике заболеваний. Эта информация будет полезна как специалистам, так и широкой публике.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Комплексное лечение на дому организовано по четкой схеме, состоящей из последовательных этапов. Каждый из них направлен на быстрое восстановление нормального функционирования организма.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя владимир[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Системы автоматизированного дозирования обеспечивают точное введение медикаментов, что минимизирует риск побочных эффектов. Постоянный мониторинг жизненно важных показателей позволяет врачу корректировать терапию в режиме реального времени, гарантируя безопасность процедуры.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/]вывести из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cams-casino-apk.ru
Приветствую всех!
Наткнулся на интересную статью для любителей мобильного гемблинга. По ссылке можно узнать подробности о том, как скачать казино cams на телефон.
В материале, похоже, рассматриваются разные платформы (Android, iOS?), способы установки, а также вопросы безопасности и выбора надежного казино.
cams-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуга вывода из запоя на дому в Туле представляет собой комплекс мер, направленных на экстренную детоксикацию организма при алкогольной интоксикации. При вызове нарколога специалист прибывает в течение короткого времени, проводит первичный осмотр, собирает анамнез и определяет степень интоксикации. На основе полученной информации разрабатывается индивидуальный план лечения, который может включать медикаментозную детоксикацию, капельничное введение препаратов и психотерапевтическую поддержку.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обязательно попробуйте http://www.anir.org.co/hola-mundo/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В данной публикации мы поговорим о процессе восстановления от зависимости, о том, как вернуть себе нормальную жизнь. Мы обсудим преодоление трудностей, значимость поддержки и наличие программ реабилитации. Читатели смогут узнать о ключевых шагах к успешному восстановлению.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт сафари египет Кайт сафари египет: Исследуйте самые живописные уголки Египта на кайт сафари. Почувствуйте себя частью природы и насладитесь адреналином.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье мы обсудим процесс восстановления после зависимостей, акцентируя внимание на различных методах и подходах к реабилитации. Читатели узнают, как создать план выздоровления и использовать полезные ресурсы для достижения устойчивых изменений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]нарколог на дом цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Крайне советую https://helikobakterpylori.sk/ako-som-sa-zbavil-helikobaktera-bez-antibiotik/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врач уточняет, как долго продолжается запой, какой алкоголь употребляется, а также наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Этот тщательный анализ позволяет оперативно подобрать оптимальные методы детоксикации и снизить риск осложнений.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-tula0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
champion-casino-apk.ru
Скачайте champion casino для телефона на андройд по ссылке ниже:
champion-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайтсерфинг в хургаде : Кайт школа: Найди свою идеальную кайт школу уже сегодня!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы исследуем ключевые аспекты здоровья, включая влияние образа жизни на благополучие. Читатели узнают о важности правильного питания, физической активности и психического здоровья. Мы предоставим практические советы и рекомендации для поддержания здоровья и развития профилактических подходов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё о спорте https://beachsoccer.com.ua в одном месте: профессиональный и любительский спорт, фитнес, здоровье, техника упражнений и спортивное питание.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Туристический портал https://aliana.com.ua с лучшими маршрутами, подборками стран, бюджетными решениями, гидами и советами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клуб родителей https://entertainment.com.ua пространство поддержки, общения и обмена опытом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Семейный портал https://stepandstep.com.ua статьи для родителей, игры и развивающие материалы для детей, советы психологов, лайфхаки.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
flagman-casino-apk.ru
Приветствую, форумчане!
Хочу поделиться интересной находкой для тех, кто ищет способы окунуться в мир азарта. По ссылке вы найдете информацию о том, как скачать приложение flagman казино.
В статье, вероятно, обсуждаются различные аспекты загрузки приложения, особенности игры, а также, возможно, бонусы и акции для новых пользователей.
flagman-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот обзор медицинских исследований собрал самое важное из последних публикаций в области медицины. Мы проанализировали ключевые находки и представили их в доступной форме, чтобы читатели могли легко ориентироваться в актуальных темах. Этот материал станет отличным подспорьем для изучения медицины.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Крайне рекомендую https://setouti.click/2024/10/09/hello-world/comment-page-1222/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация содержит ценные советы и рекомендации по избавлению от зависимости. Мы обсуждаем различные стратегии, которые могут помочь в процессе выздоровления и важность обращения за помощью. Читатели смогут использовать полученные знания для улучшения своего состояния.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar12.ru/]vyzvat-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт школа Кайт школа унесенные ветром: Обучение кайтингу с опытными инструкторами. Индивидуальный подход и гарантия результата.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой характеризуется накоплением токсинов и ухудшением работы внутренних органов. Чем дольше продолжается состояние интоксикации, тем выше риск серьезных осложнений. Помощь нарколога на дому позволяет начать детоксикацию в первые часы кризиса, что существенно повышает шансы на успешное восстановление и предотвращает развитие хронических заболеваний.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
События Днепр https://u-misti.dp.ua последние новости Днепра и области, обзоры и самое интересное
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой характеризуется накоплением токсинов и ухудшением работы внутренних органов. Чем дольше продолжается состояние интоксикации, тем выше риск серьезных осложнений. Помощь нарколога на дому позволяет начать детоксикацию в первые часы кризиса, что существенно повышает шансы на успешное восстановление и предотвращает развитие хронических заболеваний.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-vladimir0.ru/]вывод из запоя в владимире[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о маркетинге https://reklamspilka.org.ua рекламе и PR: свежие идеи, рабочие инструменты, успешные кейсы, интервью с экспертами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
topspot Кайт — это один из самых захватывающих видов спорта, который сочетает в себе элементы серфинга и парапланеризма. Он позволяет наслаждаться свободой полета над водой, а также получать адреналин от скоростного спуска по волнам. Кайтинг подходит как для новичков, так и для опытных спортсменов. Главное — выбрать правильное место и условия для занятий.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный женский https://prowoman.kyiv.ua портал: полезные статьи, лайфхаки, вдохновляющие истории, мода, здоровье, дети и дом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
креативные кашпо креативные кашпо .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-портал https://leif.com.ua для женщин: мода, психология, рецепты, карьера, дети и любовь. Читай, вдохновляйся, общайся, развивайся!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ниже приведены ключевые сигналы, при появлении которых требуется немедленное реагирование:
Детальнее – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
gaming-casino-apk.ru
Привет, гемблеры! ??
Заглянул на один сайт и нашёл интересную статью. По ссылке собрана инфа о том, какие слоты будут популярны в онлайн-казино gaming в 2025 году.
Думаю, будет полезно почитать тем, кто интересуется трендами в мире азартных игр. Возможно, там есть инфа про новые механики, графику и темы, которые будут рулить в будущем.gaming-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт станция египет : Обучение кайтингу: Сделай первый шаг к захватывающим приключениям!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё о строительстве https://furbero.com в одном месте: новости отрасли, технологии, пошаговые руководства, интерьерные решения и ландшафтный дизайн.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Комплексный строительный https://ko-online.com.ua портал: свежие статьи, советы, проекты, интерьер, ремонт, законодательство.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный портал https://apis-togo.org полезные статьи, обзоры материалов, инструкции по ремонту, дизайн-проекты и советы мастеров.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новини Львів https://faine-misto.lviv.ua последние новости и события – Файне Львов
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайтинг в хургаде в июле : Кайт школы санкт петербург: Обучение кайтсерфингу круглый год!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья освещает различные аспекты освобождения от зависимости и пути к выздоровлению. Мы обсуждаем важность осознания своей проблемы и обращения за помощью. Читатели получат практические советы о том, как преодолевать трудности и строить новую жизнь без зависимости.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта медицинская заметка содержит сжатую информацию о новых находках и методах в области здравоохранения. Мы предлагаем читателям свежие данные о заболеваниях, профилактике и лечении. Наша цель — быстро и доступно донести важную информацию, которая поможет в повседневной жизни и понимании здоровья.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar15.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Подработка для студентов во Владивостоке Подработка во Владивостоке для студентов: совмещение учебы и заработка Студенты Владивостока могут найти множество вариантов подработки, позволяющих совмещать учебу и работу. Гибкий график и неполная занятость делают подработку идеальным способом заработать деньги и получить ценный опыт. Популярные варианты включают работу в сфере обслуживания, курьерскую доставку и помощь в проведении мероприятий.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пшеничный хлеб на закваске ташкент Ржаной хлеб на закваске Ташкент: насыщенный вкус и польза для здоровья
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Авто портал https://real-voice.info для всех, кто за рулём: свежие автоновости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по выбору, страхованию и ремонту.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Читайте авто блог https://autoblog.kyiv.ua обзоры автомобилей, сравнения моделей, советы по выбору и эксплуатации, новости автопрома.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт о строительстве https://solution-ltd.com.ua и дизайне: как построить, отремонтировать и оформить дом со вкусом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Свежие новости https://ktm.org.ua Украины и мира: политика, экономика, происшествия, культура, спорт. Оперативно, объективно, без фейков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная статья охватывает широкий спектр актуальных тем и вопросов. Мы стремимся осветить ключевые факты и события с ясностью и простотой, чтобы каждый читатель мог извлечь из нее полезные знания и полезные инсайты.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://gestunlancar.com/gesek-tunai-online-akulaku-kredivo-kartu-kredit-jakarta-barat-tlpn-wa-0838-7155-4454
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал Львів https://u-misti.lviv.ua останні новини Львова и области.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://prodagrotest.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт школа в хургаде Кайт школа Кайт школа – это место, где мечты о покорении волн с помощью кайта становятся реальностью. Квалифицированные инструкторы, современное оборудование и безопасные условия позволяют быстро и эффективно освоить навыки кайтинга и кайтсерфинга.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья сочетает познавательный и занимательный контент, что делает ее идеальной для любителей глубоких исследований. Мы рассмотрим увлекательные аспекты различных тем и предоставим вам новые знания, которые могут оказаться полезными в будущем.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://stitcheryprojects.com/forums/topic/%D1%82%D1%80%D0%B0%D0%BD%D1%81%D1%84%D0%B5%D1%80-%D0%B8%D0%B7-%D0%B0%D0%BD%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%B8-%D0%B4%D0%BE-%D1%85%D1%83%D1%80%D0%BC%D1%8B
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
фонтан казино бездепозитный бонус 1000 рублей за регистрацию без депозита с выводом денег
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://legalwisdom.com/9-things-to-know-about-your-wordpress-robots-txt-you-should-know
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://jornalwebminas.com.br/2023/03/10/assistir-pacajus-x-guarani-de-juazeiro-ao-vivo-campeonato-cearense-de-2023-hoje-10-03-palpites
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Подробнее тут – https://genezis-servis.ru/2018/06/28/perevozka-gruza-200-v-abhaziyu
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Подробнее – https://www.swedbergcontracting.com/the-importance-of-building-a-strong-brand-identity
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайтсерфинг хургада Кайт школа Кайт школа – это место, где мечты о покорении волн с помощью кайта становятся реальностью. Квалифицированные инструкторы, современное оборудование и безопасные условия позволяют быстро и эффективно освоить навыки кайтинга и кайтсерфинга.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, aventureros del riesgo !
casino online extranjero para usuarios avanzados – п»їhttps://casinosextranjero.es/ mejores casinos online extranjeros
¡Que vivas increíbles jackpots extraordinarios!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом интересном тексте собраны обширные сведения, которые помогут вам понять различные аспекты обсуждаемой темы. Мы разбираем детали и факты, делая акцент на важности каждого элемента. Не упустите возможность расширить свои знания и взглянуть на мир по-новому!
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://cuisinepourtous.fr/tous-en-cuisine-livre_gateau_yaourt
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Подробнее тут – https://oxihom.com/2020/01/13/you-can-have-drew-much-of-a-good-thing
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://rotaryclubphcosmo.org/depression-and-mood-swing
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Подробнее тут – https://cgmbc.co.uk/projects/n-brookes-ltd-commercial-exterior
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуга “Нарколог на дом” в Уфе охватывает широкий спектр лечебных мероприятий, направленных как на устранение токсической нагрузки, так и на работу с психоэмоциональным состоянием пациента. Комплексная терапия включает в себя медикаментозную детоксикацию, корректировку обменных процессов, а также психотерапевтическую поддержку, что позволяет не только вывести пациента из состояния запоя, но и помочь ему справиться с наркотической зависимостью.
Подробнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-ufa000.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Городской портал Винницы https://u-misti.vinnica.ua новости, события и обзоры Винницы и области
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://boujakinsurance.com/blog/2013/03/25/take-three-steps-to-controlling-your-workers-compensation-costs
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой может быть не только физически тяжёлым, но и психологически разрушительным. Поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за помощью. Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — это необходимая медицинская процедура, которая помогает победить алкогольную зависимость и восстановить здоровье. Мы в клинике «АнтиЗависимость» предлагаем круглосуточную помощь в комфортных условиях — на дому или в стационаре.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno novokuznetsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процесс вывода из запоя капельничным методом организован по строгой схеме, позволяющей обеспечить максимальную эффективность терапии. Каждая стадия направлена на комплексное восстановление организма и минимизацию риска осложнений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen0.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-czena-tyumen/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
почему в хургаде ветренно Кайт Кайт – это не просто спортивный снаряд, это крыло, дающее свободу парить над волнами или снежными просторами. История кайта уходит корнями в древность, но современный кайт, как инструмент для экстремального спорта, появился относительно недавно и быстро завоевал популярность. От простых воздушных змеев до сложных парафойлов и надувных кайтов, конструкция и материалы постоянно совершенствуются, чтобы обеспечить максимальную производительность и безопасность.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Комплексное лечение организовано по строго отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько последовательных этапов, позволяющих обеспечить оперативное и безопасное восстановление организма.
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления звонка нарколог оперативно выезжает по указанному адресу и прибывает в течение 30–60 минут. Врач незамедлительно приступает к оказанию помощи по четко отработанному алгоритму, состоящему из следующих этапов:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh00.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно воронеж[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, aficionados a los desafíos!
MГЎxima diversiГіn en casino online extranjero – п»їhttps://casinoextranjerosenespana.es/ mejores casinos online extranjeros
¡Que disfrutes de movidas extraordinarias !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При длительном запое в организме накапливаются вредные токсины, что ведёт к нарушениям работы сердца, печени, почек и других жизненно важных органов. Чем быстрее начинается терапия, тем выше шансы избежать серьёзных осложнений и обеспечить качественное восстановление. Метод капельничного лечения позволяет оперативно начать детоксикацию, что особенно важно для спасения жизни и предупреждения хронических последствий злоупотребления алкоголем.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому тюмень[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Служба круглосуточного вывода из запоя организована таким образом, чтобы обеспечить максимальную оперативность и надежность. Независимо от времени суток, квалифицированные специалисты готовы выехать на дом или принять пациента в медицинском учреждении, чтобы приступить к детоксикации и стабилизации состояния.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница волгоград[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это тяжёлое состояние, характеризующееся длительным употреблением алкоголя, при котором человек не в силах самостоятельно прекратить пить. Алкогольная интоксикация при длительных запоях вызывает нарушения в работе всех органов и систем, приводя к серьёзным последствиям, таким как инфаркты, инсульты, психозы и даже летальный исход. В такой ситуации единственным надёжным решением становится обращение за профессиональной помощью.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev2.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya korolev[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуга “Нарколог на дом” в Уфе охватывает широкий спектр лечебных мероприятий, направленных как на устранение токсической нагрузки, так и на работу с психоэмоциональным состоянием пациента. Комплексная терапия включает в себя медикаментозную детоксикацию, корректировку обменных процессов, а также психотерапевтическую поддержку, что позволяет не только вывести пациента из состояния запоя, но и помочь ему справиться с наркотической зависимостью.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ufa000.ru/]нарколог на дом цены в уфе[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врач уточняет, как долго продолжается запой, какие симптомы наблюдаются и присутствуют ли сопутствующие заболевания. Тщательный сбор информации позволяет оперативно подобрать необходимые медикаменты и начать детоксикацию.
Выяснить больше – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как проходит лечение:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Комплексная терапия при выводе из запоя на дому включает в себя два основных направления: медикаментозную детоксикацию и психологическую поддержку. Такой подход позволяет добиться быстрого и устойчивого эффекта, минимизируя риск осложнений и обеспечивая долгосрочную ремиссию.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ufa000.ru/]нарколог на дом уфа[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если в состоянии пациента наблюдаются такие признаки, как судороги, панические атаки, или гипертонический криз, необходимо немедленно вызвать врачей. Задержка может привести к необратимым последствиям.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в новокузнецке[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда запой превращается в угрозу для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится критически важным. В Тюмени, Тюменская область, опытные наркологи предлагают услугу установки капельницы от запоя прямо на дому. Такой метод позволяет начать детоксикацию с использованием современных медикаментов, что способствует быстрому выведению токсинов, восстановлению обменных процессов и нормализации работы внутренних органов. Лечение на дому обеспечивает комфортную обстановку, полную конфиденциальность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой может быть не только физически тяжёлым, но и психологически разрушительным. Поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за помощью. Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — это необходимая медицинская процедура, которая помогает победить алкогольную зависимость и восстановить здоровье. Мы в клинике «АнтиЗависимость» предлагаем круглосуточную помощь в комфортных условиях — на дому или в стационаре.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом в новокузнецке[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайтинг в хургаде Кайт школа Кайт школа – это место, где мечты о покорении волн с помощью кайта становятся реальностью. Квалифицированные инструкторы, современное оборудование и безопасные условия позволяют быстро и эффективно освоить навыки кайтинга и кайтсерфинга.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Комплексное лечение организовано по строго отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько последовательных этапов, позволяющих обеспечить оперативное и безопасное восстановление организма.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/]капельницу от запоя тюмень[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экстренная помощь требуется, когда запой начинает негативно сказываться на здоровье, и самостоятельное прекращение употребления алкоголя становится невозможным. Основные показания для круглосуточного вмешательства включают:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-volgograd000.ru/]вывод из запоя анонимно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная и наркотическая зависимость требуют незамедлительного и комплексного вмешательства для предотвращения серьезных осложнений и сохранения здоровья пациента. В Уфе, Республика Башкортостан, опытные наркологи выезжают на дом 24 часа в сутки, предоставляя оперативную помощь при запоях и в случаях наркотической интоксикации. Такой формат лечения позволяет начать детоксикацию в комфортной, привычной обстановке, обеспечивая максимальную конфиденциальность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Узнать больше – https://narcolog-na-dom-ufa000.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-ufa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника предлагает индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту. Лечение начинается с детальной диагностики состояния здоровья, что позволяет врачу подобрать наиболее эффективную схему терапии.
Подробнее тут – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этих случаях вызов нарколога на дом не только оправдан, но и жизненно необходим для предотвращения опасных осложнений и стабилизации здоровья пациента.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-voronezh00.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно воронеж[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию с выводом
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Комплексная терапия при выводе из запоя на дому включает в себя два основных направления: медикаментозную детоксикацию и психологическую поддержку. Такой подход позволяет добиться быстрого и устойчивого эффекта, минимизируя риск осложнений и обеспечивая долгосрочную ремиссию.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ufa000.ru/]нарколог в уфе[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда запой превращается в угрозу для жизни, оперативное вмешательство становится критически важным. В Тюмени, Тюменская область, опытные наркологи предлагают услугу установки капельницы от запоя прямо на дому. Такой метод позволяет начать детоксикацию с использованием современных медикаментов, что способствует быстрому выведению токсинов, восстановлению обменных процессов и нормализации работы внутренних органов. Лечение на дому обеспечивает комфортную обстановку, полную конфиденциальность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Детальнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-czena-tyumen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда следует немедленно обращаться за помощью:
Получить больше информации – http://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой может быть не только физически тяжёлым, но и психологически разрушительным. Поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за помощью. Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — это необходимая медицинская процедура, которая помогает победить алкогольную зависимость и восстановить здоровье. Мы в клинике «АнтиЗависимость» предлагаем круглосуточную помощь в комфортных условиях — на дому или в стационаре.
Получить больше информации – http://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При длительном запое в организме накапливаются вредные токсины, что ведёт к нарушениям работы сердца, печени, почек и других жизненно важных органов. Чем быстрее начинается терапия, тем выше шансы избежать серьёзных осложнений и обеспечить качественное восстановление. Метод капельничного лечения позволяет оперативно начать детоксикацию, что особенно важно для спасения жизни и предупреждения хронических последствий злоупотребления алкоголем.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/]капельница от запоя стоимость тюмень[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При длительном запое в организме накапливаются вредные токсины, что ведёт к нарушениям работы сердца, печени, почек и других жизненно важных органов. Чем быстрее начинается терапия, тем выше шансы избежать серьёзных осложнений и обеспечить качественное восстановление. Метод капельничного лечения позволяет оперативно начать детоксикацию, что особенно важно для спасения жизни и предупреждения хронических последствий злоупотребления алкоголем.
Углубиться в тему – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-czena-tyumen/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуга “Нарколог на дом” в Уфе охватывает широкий спектр лечебных мероприятий, направленных как на устранение токсической нагрузки, так и на работу с психоэмоциональным состоянием пациента. Комплексная терапия включает в себя медикаментозную детоксикацию, корректировку обменных процессов, а также психотерапевтическую поддержку, что позволяет не только вывести пациента из состояния запоя, но и помочь ему справиться с наркотической зависимостью.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ufa000.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом цена уфа[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лечение зависимости требует не только физической детоксикации, но и работы с психоэмоциональным состоянием пациента. Психотерапевтическая поддержка помогает выявить глубинные причины зависимости, снизить уровень стресса и сформировать устойчивые навыки самоконтроля, что существенно снижает риск рецидивов.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ufa000.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом цена в уфе[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, amantes del ocio !
casinoonlinefueradeespanol ideal para apuestas rГЎpidas – https://www.casinoonlinefueradeespanol.xyz/ casinoonlinefueradeespanol.xyz
¡Que disfrutes de asombrosas movidas brillantes !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда следует немедленно обращаться за помощью:
Выяснить больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/narkolog-na-dom-klinika-novokuzneczk/https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Комплексное лечение организовано по строго отлаженной схеме, которая включает несколько последовательных этапов, позволяющих обеспечить оперативное и безопасное восстановление организма.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой может быть не только физически тяжёлым, но и психологически разрушительным. Поэтому важно вовремя обратиться за помощью. Вывод из запоя в Нижнем Новгороде — это необходимая медицинская процедура, которая помогает победить алкогольную зависимость и восстановить здоровье. Мы в клинике «АнтиЗависимость» предлагаем круглосуточную помощь в комфортных условиях — на дому или в стационаре.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно новокузнецк[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врач уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Детальное обследование позволяет оперативно подобрать необходимые медикаменты и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-tyumen
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процедура начинается с врачебного осмотра. Специалист оценивает общее состояние, артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, уровень обезвоживания, жалобы пациента. При необходимости проводятся экспресс-анализы. Далее индивидуально подбирается состав инфузионной терапии. В большинстве случаев капельница включает:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]kapelnitsa ot zapoia na domu khimki[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
стильные цветочные горшки купить стильные цветочные горшки купить .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт о строительстве https://selma.com.ua практические советы, современные технологии, пошаговые инструкции, выбор материалов и обзоры техники.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ремонт без стресса https://odessajs.org.ua вместе с нами! Полезные статьи, лайфхаки, дизайн-проекты, калькуляторы и обзоры.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о ремонте https://as-el.com.ua и строительстве: от черновых работ до отделки. Статьи, обзоры, идеи, лайфхаки.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все новинки https://helikon.com.ua технологий в одном месте: гаджеты, AI, робототехника, электромобили, мобильные устройства, инновации в науке и IT.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
hurgada kitesurf academy Кайт Кайт – это не просто спортивный снаряд, это крыло, дающее свободу парить над волнами или снежными просторами. История кайта уходит корнями в древность, но современный кайт, как инструмент для экстремального спорта, появился относительно недавно и быстро завоевал популярность. От простых воздушных змеев до сложных парафойлов и надувных кайтов, конструкция и материалы постоянно совершенствуются, чтобы обеспечить максимальную производительность и безопасность.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, estrategas del azar !
Casinossinlicenciaespana.es – Juegos sin fronteras – http://www.casinossinlicenciaespana.es/ casinos sin licencia en EspaГ±ola
¡Que experimentes rondas emocionantes !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Также страдают сердце и сосуды. У пациентов часто наблюдаются тахикардия, нестабильное давление, аритмии, повышенный риск инфаркта или инсульта. Система пищеварения реагирует воспалением: гастрит, панкреатит, тошнота, рвота. Все эти изменения усиливаются на фоне обезвоживания и электролитного дисбаланса. Именно поэтому стандартное «отлежаться» или домашнее лечение чаще всего оказывается неэффективным и даже опасным. Необходима полноценная капельная терапия — с грамотно подобранными препаратами и медицинским наблюдением.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]поставить капельницу от запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Игорь Стоунберг экстрасенс Я благодарна ему за его мудрость и знания.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Срочно нужна помощь юриста? Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию по телефону прямо сейчас. Наши специалисты готовы ответить на ваши вопросы 24/7. Анонимно и конфиденциально: бесплатная юридическая консультация по телефону горячая линия
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Срочно нужна помощь юриста? Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию по телефону прямо сейчас. Наши специалисты готовы ответить на ваши вопросы 24/7. Анонимно и конфиденциально – консультации юриста бесплатно по телефону
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выбор капельничного метода в условиях домашнего лечения обладает рядом преимуществ:
Разобраться лучше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-na-domu-tyumen/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ИнфоКиев https://infosite.kyiv.ua события, новости обзоры в Киеве и области.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Откройте для себя свежие идеи о стиле, здоровье и красоте на сайте jornalwomen.ru. Полезные советы, актуальные новости, вдохновение и рекомендации для современных женщин – заходите ежедневно за новым контентом!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врач уточняет продолжительность запоя, характер употребляемого алкоголя и наличие сопутствующих заболеваний. Детальное обследование позволяет оперативно подобрать необходимые медикаменты и минимизировать риск осложнений.
Узнать больше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-tyumen00.ru/postavit-kapelniczu-ot-zapoya-tyumen/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
airdrop криптовалюты Цены NFT коллекций стабилизировались после недавнего падения, но отдельные проекты продолжают демонстрировать взрывной рост популярности и стоимости.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
можно мнстным довить акул в хургаде День ветра кайтсерф: Возможно, название мероприятия.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Комплексная терапия при выводе из запоя на дому включает в себя два основных направления: медикаментозную детоксикацию и психологическую поддержку. Такой подход позволяет добиться быстрого и устойчивого эффекта, минимизируя риск осложнений и обеспечивая долгосрочную ремиссию.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://narcolog-na-dom-ufa000.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
blstone.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1000 рублей за регистрацию вывод сразу без вложений в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Читайте мужской https://zlochinec.kyiv.ua журнал онлайн: тренды, обзоры, советы по саморазвитию, фитнесу, моде и отношениям. Всё о том, как быть уверенным, успешным и сильным — каждый день.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процедура вывода из запоя начинается с тщательной диагностики состояния пациента, чтобы определить, какие методы лечения будут наиболее эффективными. Мы применяем индивидуальный подход и комбинируем медикаментозное лечение с психотерапевтической поддержкой, что даёт лучший результат.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в новокузнецке[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал для мужчин https://swiss-watches.com.ua которые ценят успех, свободу и стиль. Практичные советы, мотивация, интервью, спорт, отношения, технологии.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мужской журнал https://hand-spin.com.ua о стиле, спорте, отношениях, здоровье, технике и бизнесе. Актуальные статьи, советы экспертов, обзоры и мужской взгляд на важные темы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кулинарный портал https://vagon-restoran.kiev.ua с тысячами проверенных рецептов на каждый день и для особых случаев. Пошаговые инструкции, фото, видео, советы шефов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Комплексная терапия при выводе из запоя на дому включает в себя два основных направления: медикаментозную детоксикацию и психологическую поддержку. Такой подход позволяет добиться быстрого и устойчивого эффекта, минимизируя риск осложнений и обеспечивая долгосрочную ремиссию.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ufa000.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом в уфе[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Игорь Стоунберг экстрасенс Его слова вселяют надежду. Он помогает людям в трудных ситуациях. | Рада, что обратилась. |
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если человек страдает от алкоголизма, запойное состояние требует незамедлительного вмешательства, особенно если признаки токсического отравления начинают угрожать жизни. Признаки запоя — это не только физическая зависимость, но и эмоциональные и психические расстройства, такие как тревога, агрессия и галлюцинации.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novokuznetsk0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Получить больше информации – http://www.loods11.nu/2016/06/13/workaholism-tied-to-psychiatric-disorders
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Выяснить больше – http://www.sidotec.it/one-way-road
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новости Полтава https://u-misti.poltava.ua городской портал, последние события Полтавы и области
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Подробнее – https://al-qawmi.org/2023/04/21/%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D8%A4%D8%AA%D9%85%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AA%D8%A7%D8%B3%D9%8A%D8%B3%D9%8A-%D9%84%D9%84%D9%82%D9%8A%D8%A7%D8%AF%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D9%84%D9%8A%D8%A7-%D9%84%D9%84%D8%AC%D9%87
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот обзорный материал предоставляет информационно насыщенные данные, касающиеся актуальных тем. Мы стремимся сделать информацию доступной и структурированной, чтобы читатели могли легко ориентироваться в наших выводах. Познайте новое с нашим обзором!
Детальнее – https://jimihendrixrecordguide.com/electric_gypsy-2
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Полезный сайт https://vasha-opora.com.ua для тех, кто строит: от фундамента до крыши. Советы, инструкции, сравнение материалов, идеи для ремонта и дизайна.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал о строительстве https://sovetik.in.ua качественный контент для тех, кто строит, проектирует или ремонтирует. Новые технологии, анализ рынка, обзоры материалов и оборудование — всё в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё о строительстве https://stroyportal.kyiv.ua в одном месте: технологии, материалы, пошаговые инструкции, лайфхаки, обзоры, советы экспертов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный журнал https://poradnik.com.ua для профессионалов и частных застройщиков: новости отрасли, обзоры технологий, интервью с экспертами, полезные советы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино Бездепозитные бонусы: Путь к азартным приключениям без риска В мире онлайн-казино, где азарт и возможность выигрыша переплетаются в захватывающем танце, бездепозитные бонусы занимают особое место. Эти щедрые предложения служат своеобразным ключом, открывающим двери в мир азартных развлечений без необходимости вкладывать собственные средства.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После завершения процедур пациенту предоставляется подробная консультация с рекомендациями по дальнейшему восстановлению и профилактике повторных случаев зависимости.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novosibirsk00.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно новосибирск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сукааа казино официальный сайт вход бесплатный играть Sykaaa casino бонусы порадуют как новичков, так и опытных игроков. Увеличьте свои шансы на выигрыш с помощью щедрых предложений!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника «МедЛайн» предоставляет профессиональные услуги врача-нарколога с выездом на дом в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области. Мы оперативно помогаем пациентам справиться с тяжелыми состояниями при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Экстренный выезд наших специалистов доступен круглосуточно, а лечение проводится с применением проверенных методик и препаратов, что гарантирует безопасность и конфиденциальность каждому пациенту.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://narcolog-na-dom-novosibirsk00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-novosibirsk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бесплатная юридическая консультация онлайн и по телефону. Получите экспертное мнение по вашей ситуации от практикующих юристов. Быстро, профессионально и без обязательств – онлайн консультация юриста бесплатно по телефону
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://healthonlineidea.com/the-comprehensive-guide-to-health-extension-unlockingellness-and-longevity
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В обзорной статье вы найдете собрание важных фактов и аналитики по самым разнообразным темам. Мы рассматриваем как современные исследования, так и исторические контексты, чтобы вы могли получить полное представление о предмете. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и сделайте шаг к пониманию!
Углубиться в тему – http://sci.oouagoiwoye.edu.ng/2018/05/21/lawal-olusegun-adebayoph-d
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья для ознакомления предлагает читателям общее представление об актуальной теме. Мы стремимся представить ключевые факты и идеи, которые помогут читателям получить представление о предмете и решить, стоит ли углубляться в изучение.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://www.studionovum.com/farragut_west_station
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта познавательная публикация погружает вас в море интересного контента, который быстро захватит ваше внимание. Мы рассмотрим важные аспекты темы и предоставим вам уникальныеInsights и полезные сведения для дальнейшего изучения.
Узнать больше – https://minesec.gov.cm/web/index.php/fr/borderaux/item/617-liste-definitive-capiet-extreme-nord?start=240
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Professional AC duct cleaning in Dubai improves air quality and reduces allergens in your home https://ac-cleaning-dubai.ae/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Выяснить больше – https://www.inqaahe.org/events/inqaahe-talks-on-november-30-2023
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы Бездепозитный бонус в казино: Как его получить? Получить бездепозитный бонус в казино, как правило, довольно просто. Обычно требуется пройти процедуру регистрации на сайте казино и подтвердить свою учетную запись. В некоторых случаях может потребоваться ввести специальный промокод. После выполнения всех условий бонус будет автоматически зачислен на ваш счет. Бездепозитные бонусы – это отличная возможность начать свой путь в мире онлайн-казино с минимальным риском и максимальным удовольствием. Однако, прежде чем принимать бонус, всегда внимательно ознакомьтесь с условиями его использования, чтобы избежать недоразумений в будущем.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника «МедЛайн» предоставляет профессиональные услуги врача-нарколога с выездом на дом в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области. Мы оперативно помогаем пациентам справиться с тяжелыми состояниями при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Экстренный выезд наших специалистов доступен круглосуточно, а лечение проводится с применением проверенных методик и препаратов, что гарантирует безопасность и конфиденциальность каждому пациенту.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-novosibirsk00.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно в новосибирске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова наш нарколог выезжает к пациенту в кратчайшие сроки, прибывая по адресу в пределах 30–60 минут. Специалист начинает процедуру с подробного осмотра и диагностики, измеряя ключевые показатели организма: артериальное давление, частоту пульса, насыщенность кислородом и собирая подробный анамнез.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проблемы с алкоголем или наркотиками могут застать врасплох и привести к серьезным последствиям для организма, психического состояния и жизни пациента. Самостоятельные попытки выйти из запоя или преодолеть абстинентный синдром без медицинской поддержки редко оказываются эффективными и могут представлять реальную опасность для здоровья. Именно в таких ситуациях клиника «АльфаНаркология» предлагает услугу вызова нарколога на дом в Санкт-Петербурге и Ленинградской области. Наши специалисты оперативно реагируют на обращение, оказывают квалифицированную помощь и обеспечивают полную конфиденциальность лечения.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно санкт-петербург[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После прибытия врач проводит осмотр пациента, оценивает его состояние, измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода и выявляет возможные противопоказания. Затем разрабатывается индивидуальный план лечения, направленный на стабилизацию состояния.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]нарколог на дом цены в иркутске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино Бездепозитный бонус в казино: Как его получить? Получить бездепозитный бонус в казино, как правило, довольно просто. Обычно требуется пройти процедуру регистрации на сайте казино и подтвердить свою учетную запись. В некоторых случаях может потребоваться ввести специальный промокод. После выполнения всех условий бонус будет автоматически зачислен на ваш счет. Бездепозитные бонусы – это отличная возможность начать свой путь в мире онлайн-казино с минимальным риском и максимальным удовольствием. Однако, прежде чем принимать бонус, всегда внимательно ознакомьтесь с условиями его использования, чтобы избежать недоразумений в будущем.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Extend the life of your HVAC system with professional AC duct cleaning in Dubai: ac cleaning cost dubai
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызов нарколога на дом в Иркутске и Иркутской области — это удобное и безопасное решение, позволяющее получить неотложную помощь в привычной обстановке. Врачи клиники «ЧистоЖизнь» выезжают круглосуточно, приезжают в течение 30–60 минут и проводят комплексное лечение, направленное на стабилизацию состояния пациента и предотвращение осложнений.
Подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как отмечает нарколог Олег Васильев, «чем раньше пациент получает квалифицированную медицинскую помощь, тем меньше риск серьезных осложнений».
Углубиться в тему – https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-czena-irkutsk/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
креативные кашпо https://dizaynerskie-kashpo.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Защитите свои права! Воспользуйтесь бесплатной юридической консультацией. Опытные юристы помогут разобраться в сложных правовых вопросах по телефону. Первый шаг к решению вашей проблемы – бесплатная юридическая консультация телефон
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После процедуры пациент и его близкие получают развернутые рекомендации по дальнейшему восстановлению, советы по профилактике рецидивов и возможности прохождения кодирования при желании пациента.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Информационный журнал https://newhouse.kyiv.ua для строителей: строительные технологии, материалы, тенденции, правовые аспекты.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус Бездепозитные бонусы в казино: Что это такое? Бездепозитный бонус в казино – это денежная сумма или бесплатные вращения, которые казино предоставляет новым игрокам в качестве приветственного подарка. Главное преимущество этого бонуса заключается в том, что для его получения не требуется внесение депозита. Игрок может просто зарегистрироваться на сайте казино и получить бонус на свой счет.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный строительный https://interiordesign.kyiv.ua журнал: идеи, решения, технологии, тенденции. Всё о ремонте, стройке, дизайне и инженерных системах.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-журнал https://inox.com.ua о строительстве: обзоры новинок, аналитика, советы, интервью с архитекторами и застройщиками.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный журнал https://garant-jitlo.com.ua всё о технологиях, материалах, архитектуре, ремонте и дизайне. Интервью с экспертами, кейсы, тренды рынка.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Sykaaa casino скачать бесплатно на телефон Sykaaa casino приложение – это удобный и быстрый способ доступа к играм. Оптимизированный интерфейс и стабильная работа гарантированы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино Бездепозитный бонус: Испытайте удачу без потерь Бездепозитный бонус позволяет игрокам протестировать различные игры, оценить функциональность казино и испытать свою удачу, не рискуя собственными деньгами. Это отличная возможность познакомиться с миром онлайн-казино и понять, насколько он соответствует вашим предпочтениям.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова нарколог клиники «АльфаНаркология» оперативно выезжает по указанному адресу. На месте врач проводит первичную диагностику, оценивая степень интоксикации, физическое и психологическое состояние пациента. По результатам осмотра врач подбирает индивидуальный комплекс лечебных процедур, в который входит постановка капельницы с растворами для детоксикации, препараты для стабилизации работы органов и нормализации психического состояния.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё для строительства https://d20.com.ua и ремонта: инструкции, обзоры, экспертизы, калькуляторы. Профессиональные советы, новинки рынка, база строительных компаний.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение наркомании реабилитация https://narco-info.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
оценка чека оценка имущественного комплекса
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Праздничная продукция https://prazdnik-x.ru для любого повода: шары, гирлянды, декор, упаковка, сувениры. Всё для дня рождения, свадьбы, выпускного и корпоративов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
стильные горшки для комнатных цветов стильные горшки для комнатных цветов .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основные показания для вызова нарколога:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]narkolog na dom irkutsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Действие и назначение
Получить больше информации – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-novosibirsk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новинний сайт Житомира https://faine-misto.zt.ua новости Житомира сегодня
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это тяжёлое состояние, характеризующееся длительным употреблением алкоголя, при котором человек не в силах самостоятельно прекратить пить. Алкогольная интоксикация при длительных запоях вызывает нарушения в работе всех органов и систем, приводя к серьёзным последствиям, таким как инфаркты, инсульты, психозы и даже летальный исход. В такой ситуации единственным надёжным решением становится обращение за профессиональной помощью.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev2.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вызывать нарколога на дом рекомендуется при следующих состояниях:
Подробнее – http://narcolog-na-dom-sankt-peterburg000.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
We offer same-day AC duct cleaning in Dubai with guaranteed satisfaction: cost to have ac ducts cleaned
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника «МедЛайн» предоставляет профессиональные услуги врача-нарколога с выездом на дом в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области. Мы оперативно помогаем пациентам справиться с тяжелыми состояниями при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Экстренный выезд наших специалистов доступен круглосуточно, а лечение проводится с применением проверенных методик и препаратов, что гарантирует безопасность и конфиденциальность каждому пациенту.
Узнать больше – http://narcolog-na-dom-novosibirsk00.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как отмечает нарколог Олег Васильев, «чем раньше пациент получает квалифицированную медицинскую помощь, тем меньше риск серьезных осложнений».
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-v-irkutske00.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом цена в иркутске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино Бездепозитные бонусы в казино: Что это такое? Бездепозитный бонус в казино – это денежная сумма или бесплатные вращения, которые казино предоставляет новым игрокам в качестве приветственного подарка. Главное преимущество этого бонуса заключается в том, что для его получения не требуется внесение депозита. Игрок может просто зарегистрироваться на сайте казино и получить бонус на свой счет.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «АнтиАлко» предлагает экстренную медицинскую помощь на дому в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области для тех, кто столкнулся с запоем. Если вы или ваш близкий оказались в состоянии длительной алкогольной интоксикации, наши специалисты готовы оперативно приехать к вам, провести комплексную детоксикацию и купировать симптомы абстинентного синдрома. Мы гарантируем высокий уровень безопасности, полную анонимность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-novosibirsk00.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно в новосибирске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это тяжёлое состояние, характеризующееся длительным употреблением алкоголя, при котором человек не в силах самостоятельно прекратить пить. Алкогольная интоксикация при длительных запоях вызывает нарушения в работе всех органов и систем, приводя к серьёзным последствиям, таким как инфаркты, инсульты, психозы и даже летальный исход. В такой ситуации единственным надёжным решением становится обращение за профессиональной помощью.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev2.ru/]вывод из запоя круглосуточно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вывод из запоя клиники быстрый анонимный вывод из запоя на дому
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника «МедЛайн» предоставляет профессиональные услуги врача-нарколога с выездом на дом в Новосибирске и Новосибирской области. Мы оперативно помогаем пациентам справиться с тяжелыми состояниями при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Экстренный выезд наших специалистов доступен круглосуточно, а лечение проводится с применением проверенных методик и препаратов, что гарантирует безопасность и конфиденциальность каждому пациенту.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://narcolog-na-dom-novosibirsk00.ru/narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno-novosibirsk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лечение алкоголизма на дому лечение алкогольной зависимости НН
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кодировка от алкоголя цена лазерное кодирование от алкоголизма
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вызов нарколога нарколог на дом срочно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Как отмечает нарколог Олег Васильев, «чем раньше пациент получает квалифицированную медицинскую помощь, тем меньше риск серьезных осложнений».
Углубиться в тему – http://
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино Бездепозитный бонус в казино: Как его получить? Получить бездепозитный бонус в казино, как правило, довольно просто. Обычно требуется пройти процедуру регистрации на сайте казино и подтвердить свою учетную запись. В некоторых случаях может потребоваться ввести специальный промокод. После выполнения всех условий бонус будет автоматически зачислен на ваш счет. Бездепозитные бонусы – это отличная возможность начать свой путь в мире онлайн-казино с минимальным риском и максимальным удовольствием. Однако, прежде чем принимать бонус, всегда внимательно ознакомьтесь с условиями его использования, чтобы избежать недоразумений в будущем.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал города Черновцы https://u-misti.chernivtsi.ua последние новости, события, обзоры
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Dusty AC ducts can impact your energy bill — our Dubai cleaning services help you save https://ac-cleaning-dubai.ae/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сукааа казино Sykaaa casino официальный сайт бонус за регистрацию – отличный старт для новых игроков. Получите дополнительные средства для игры сразу после регистрации.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В данной обзорной статье представлены интригующие факты, которые не оставят вас равнодушными. Мы критикуем и анализируем события, которые изменили наше восприятие мира. Узнайте, что стоит за новыми открытиями и как они могут изменить ваше восприятие реальности.
Разобраться лучше – https://www.moparweb.com/photos/picture.php?/748/most_visited/start-16290
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, apostadores apasionados !
Mejores casinos online extranjeros con bono mensual – https://casinosextranjerosenespana.es/# casinos extranjeros
¡Que vivas increíbles jugadas excepcionales !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://nursing.torchlight.tokyo/?p=1
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Get your AC ducts cleaned in Dubai to ensure better cooling efficiency and energy savings https://ac-cleaning-dubai.ae/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный портал https://proektsam.kyiv.ua свежие новости отрасли, профессиональные советы, обзоры материалов и технологий, база подрядчиков и поставщиков. Всё о ремонте, строительстве и дизайне в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Городской портал Черкассы https://u-misti.cherkasy.ua новости, обзоры, события Черкасс и области
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://taganrog.big-book-edu.ru/company/243245
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья для ознакомления предлагает читателям общее представление об актуальной теме. Мы стремимся представить ключевые факты и идеи, которые помогут читателям получить представление о предмете и решить, стоит ли углубляться в изучение.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://ftp.soldat.ru/forum/ucp.php?mode=login
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://game.center.ru/forum/?gb=1&id=33028
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эти процедуры направлены на фильтрацию плазмы и избавление крови от токсинов:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно красноярск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вавада казино официальный сайт Вавада Казино Официальный Сайт Вход Бесплатный Играть: Начните играть в Вавада Казино бесплатно, получив доступ к демо-версиям игр и оценив все преимущества этого онлайн-казино.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация завернет вас в вихрь увлекательного контента, сбрасывая стереотипы и открывая двери к новым идеям. Каждый абзац станет для вас открытием, полным ярких примеров и впечатляющих достижений. Подготовьтесь быть вовлеченными и удивленными каждый раз, когда продолжите читать.
Детальнее – https://stimulantonline.ca/2014/10/31/advertisings-awesome
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информационный обзор станет отличным путеводителем по актуальным темам, объединяющим важные факты и мнения экспертов. Мы исследуем ключевые идеи и представляем их в доступной форме для более глубокого понимания. Читайте, чтобы оставаться в курсе событий!
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://plugin.work/archives/1
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Подробнее тут – https://aitips.digital/huggingface-hub-a-must-try-for-all-ml-engineers
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, при котором устойчивое влечение к спиртному приводит к тяжёлым медицинским, социальным и психологическим последствиям. Когда пациент осознаёт, что самостоятельно справиться с этой проблемой не получается, наиболее эффективным методом становится кодирование от алкоголизма. В клинике «Ясное Будущее» в Одинцово мы используем сочетание проверенных методик кодирования и комплексной психологической поддержки, что позволяет достичь стойкой ремиссии и вернуть человеку контроль над собственной жизнью.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На дом выезжает квалифицированный врач, который проводит процедуру детоксикации в комфортных условиях, позволяя пациенту избежать стресса и огласки. С помощью капельницы и медикаментов нормализуется состояние, восстанавливаются основные функции организма. Процедура длится несколько часов, после чего врач оставляет рекомендации по поддерживающему лечению.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lyubertsy2.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya nedorogo[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, amantes de la emoción !
Casinos extranjeros sin condiciones de verificaciГіn – https://www.casinoextranjerosespana.es/# mejores casinos online extranjeros
¡Que disfrutes de asombrosas momentos memorables !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, aficionados al mundo del juego!
Casinos no regulados con alta velocidad de retiro – http://www.casinossinlicenciaenespana.es/ https://www.casinossinlicenciaenespana.es/
¡Que vivas éxitos sobresalientes !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
aml отслеживание
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — тяжёлое состояние алкогольной зависимости, при котором организм постоянно подвергается токсическому воздействию алкоголя. Это не просто неприятное явление, а угрожающее жизни состояние, которое требует немедленного медицинского вмешательства. Наркологическая клиника «Воздух Свободы» в Люберцах предлагает профессиональный и эффективный вывод из запоя с индивидуальным подходом и максимальным уровнем конфиденциальности.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lyubertsy2.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya kapelnica[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медикаментозное кодирование проводится с помощью препаратов, блокирующих ферменты, ответственные за расщепление этанола, что вызывает выраженное неприятие алкоголя при попытке его употребления. Препараты вводятся внутримышечно или с помощью подкожных имплантов и действуют в течение нескольких месяцев, обеспечивая длительный эффект.
Узнать больше – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для максимальной эффективности и безопасности «Красмед» использует комбинированные подходы:
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого красноярск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
займ онлайн срочно https://zajmy-onlajn.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Базовый метод, сочетающий регидратацию, электролитную коррекцию и витаминные комплексы:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вавада казино официальный рабочее зеркало на сегодняшний день Вавада Казино Официальный Сайт: Откройте для себя мир азарта и развлечений на официальном сайте Вавада Казино, где вас ждут захватывающие игры и щедрые бонусы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://frankivchanka.info/ru/articles/kollimatory-holosan
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На дом выезжает квалифицированный врач, который проводит процедуру детоксикации в комфортных условиях, позволяя пациенту избежать стресса и огласки. С помощью капельницы и медикаментов нормализуется состояние, восстанавливаются основные функции организма. Процедура длится несколько часов, после чего врач оставляет рекомендации по поддерживающему лечению.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lyubertsy2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, при котором устойчивое влечение к спиртному приводит к тяжёлым медицинским, социальным и психологическим последствиям. Когда пациент осознаёт, что самостоятельно справиться с этой проблемой не получается, наиболее эффективным методом становится кодирование от алкоголизма. В клинике «Ясное Будущее» в Одинцово мы используем сочетание проверенных методик кодирования и комплексной психологической поддержки, что позволяет достичь стойкой ремиссии и вернуть человеку контроль над собственной жизнью.
Узнать больше – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-cena/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://www.uarating.com/news/kolimator-profoptica-com-ua/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На дом выезжает квалифицированный врач, который проводит процедуру детоксикации в комфортных условиях, позволяя пациенту избежать стресса и огласки. С помощью капельницы и медикаментов нормализуется состояние, восстанавливаются основные функции организма. Процедура длится несколько часов, после чего врач оставляет рекомендации по поддерживающему лечению.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-lyubertsy2.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медикаментозное кодирование проводится с помощью препаратов, блокирующих ферменты, ответственные за расщепление этанола, что вызывает выраженное неприятие алкоголя при попытке его употребления. Препараты вводятся внутримышечно или с помощью подкожных имплантов и действуют в течение нескольких месяцев, обеспечивая длительный эффект.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Базовый метод, сочетающий регидратацию, электролитную коррекцию и витаминные комплексы:
Выяснить больше – https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-krasnoyarsk/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Базовый метод, сочетающий регидратацию, электролитную коррекцию и витаминные комплексы:
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вавада казино официальный сайт рабочее Вавада Казино Официальный Сайт Вход Бесплатный Играть: Начните играть в Вавада Казино бесплатно, получив доступ к демо-версиям игр и оценив все преимущества этого онлайн-казино.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://obzor.city/texty/tovary/podzornaja-truba
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, apostadores entusiastas !
Con casinosextranjerosespana.es, puedes activar bonos desde el ГЎrea de usuario sin contactar soporte. Todo se hace en segundos. [url=https://www.casinosextranjerosespana.es/#]casinos extranjeros[/url] RГЎpido, directo y sin complicaciones.
Mejor experiencia en mejores casinos online extranjeros – https://www.casinosextranjerosespana.es/#
En los mejores casinos online extranjeros, las reglas de los juegos estГЎn claras y traducidas. AsГ puedes entender todo sin esfuerzo. La transparencia es prioridad.
¡Que experimentes increíbles victorias épicas !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
http://www.massandra.net.ua/optichnij-priczil
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
topvpn2025.ru
Скачайте бесплатно впн на андройд по ссылке ниже: topvpn2025.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«Кодирование — это не магическое решение, а важный этап в комплексной программе лечения, — поясняет ведущий нарколог клиники «Ясное Будущее» Марина Иванова. — Главное — сочетание фармакологического воздействия и последующей работы с психологом для формирования устойчивой мотивации к трезвости».
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]kodirovanie ot alkogolizma gipnozom[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
дизайнерские цветочные горшки дизайнерские цветочные горшки .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
vpnfree2025.ru
Скачайте рабочий впн для телефона на андройд по ссылке ниже:
vpnfree2025.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
вавада Vavada Online Casino Официальный Сайт: Посетите официальный сайт Vavada Online Casino и откройте для себя мир азартных игр с высоким качеством и захватывающими возможностями.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, apostadores destacados !
En casinossinlicenciaespanola.es puedes combinar apuestas deportivas y juegos de casino. Todo en una misma cuenta. MГЎs prГЎctico y conveniente.
Muchos casinos sin licencia actualizan su catГЎlogo de juegos cada semana. Siempre hay algo nuevo que probar. [url=https://www.casinossinlicenciaespanola.es/]casinos sin registro[/url]Nunca te aburres.
Casino online sin licencia EspaГ±a sin validaciГіn KYC – https://www.casinossinlicenciaespanola.es/
¡Que experimentes logros inigualables !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Шлюхи Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya na domu[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Юрист по семейным делам Екатеринбург yuristy-ekaterinburga.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Без регистрации сложно оформить ИНН, СНИЛС, банковский счёт или устроиться на официальную работу в Москве: купить регистрацию в москве
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://xtgamers.com/page-id-18999.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
риски при эвакуации авто Эвакуатор питбайк Алматы – осуществляет эвакуацию питбайков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
как найти разнорабочих алматы Ищу разнорабочих в Алматы – это запрос тех, кто нуждается в помощи для выполнения различных видов работ, от простых до сложных, требующих физической силы и выносливости.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сукааа казино официальный сайт скачать на андроид мобильная версия бесплатно Сукааа казино официальный сайт казино предлагает широкий выбор игр, включая слоты, рулетку и блэкджек.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, при котором устойчивое влечение к спиртному приводит к тяжёлым медицинским, социальным и психологическим последствиям. Когда пациент осознаёт, что самостоятельно справиться с этой проблемой не получается, наиболее эффективным методом становится кодирование от алкоголизма. В клинике «Ясное Будущее» в Одинцово мы используем сочетание проверенных методик кодирования и комплексной психологической поддержки, что позволяет достичь стойкой ремиссии и вернуть человеку контроль над собственной жизнью.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
гибкая керамика для фасада дома Гибкая керамика для фасадов дома внутренней отделки Москва phomi купить цена фоми монтаж за 1 м2 отзывы divu
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кодирование создаёт стойкое отвращение к этилированному спирту за счёт фармакологического или психотерапевтического воздействия, а дальнейшая работа с психологом помогает сформировать новую модель поведения и мотивацию к сохранению трезвости. Современные технологии в сочетании с индивидуальным подходом делают процедуру безопасной и максимально комфортной для пациента.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма одинцово[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кодирование создаёт стойкое отвращение к этилированному спирту за счёт фармакологического или психотерапевтического воздействия, а дальнейшая работа с психологом помогает сформировать новую модель поведения и мотивацию к сохранению трезвости. Современные технологии в сочетании с индивидуальным подходом делают процедуру безопасной и максимально комфортной для пациента.
Подробнее – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-cena
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«В первые часы после окончания запоя организм наиболее уязвим, и своевременное вмешательство значительно снижает риски осложнений», — подчёркивает заведующая отделением наркологической реанимации Елена Морозова.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«В первые часы после окончания запоя организм наиболее уязвим, и своевременное вмешательство значительно снижает риски осложнений», — подчёркивает заведующая отделением наркологической реанимации Елена Морозова.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]вывод из запоя капельница на дому[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
демонтаж коянды Демонтаж под ключ квартиры включает в себя все этапы работ, от подготовки до вывоза мусора.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://ukrsekta.info/equipment/3061-mikroskop.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
утилизация электроники Алматы Прием железа в Алматы: оперативный вывоз, честная оценка, быстрая оплата.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ниже приведены ключевые сигналы, при появлении которых требуется немедленное реагирование:
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«В первые часы после окончания запоя организм наиболее уязвим, и своевременное вмешательство значительно снижает риски осложнений», — подчёркивает заведующая отделением наркологической реанимации Елена Морозова.
Разобраться лучше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://russianshop.org/tehnika/binokl.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Аппаратные методы кодирования включают лазерную терапию и электростимуляцию биологически активных точек, влияющих на центры зависимости в головном мозге. Эти методики способствуют быстрому формированию устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и хорошо переносятся пациентами.
Углубиться в тему – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu/https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В «Горизонте Жизни» доступны два основных формата экстренной помощи: выездная служба на дому и лечение в условиях стационара.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya kapel’nica na domu[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому красногорск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, entusiastas del ocio !
Muchos casinos sin licencia ofrecen atenciГіn al cliente en espaГ±ol las 24 horas. AsГ te aseguras ayuda inmediata en caso de dudas. TambiГ©n suelen incluir chats en vivo dentro del juego.
Nadie rastrea tu ubicaciГіn ni tus datos personales, y puedes confiar en
Casinos-sinlicenciaenespana.es: apuestas seguras sin registro – https://www.casinos-sinlicenciaenespana.es/
¡Que disfrutes de premios únicos !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Bienvenidos, amantes de la emoción !
Muchos casinos online extranjeros ofrecen juegos exclusivos que no encontrarГЎs en sitios espaГ±oles. casino extranjerosEsto incluye tragaperras temГЎticas, ruletas innovadoras y blackjack con reglas Гєnicas. La variedad es una gran ventaja para los curiosos.
SelecciГіn top de mejores casinos online extranjeros en espaГ±ol – https://casinoextranjeros.es/#
Los casinos online extranjeros aceptan mГєltiples mГ©todos de pago, desde Skrill hasta Bitcoin. Esto amplГa tus opciones y mejora la flexibilidad.
¡Que vivas asombrosas premios extraordinarios !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
починка стиральных машин алматы Установка стиральной машины Алматы. Подключение к водопроводу и канализации.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Аппаратные методы кодирования включают лазерную терапию и электростимуляцию биологически активных точек, влияющих на центры зависимости в головном мозге. Эти методики способствуют быстрому формированию устойчивого отвращения к спиртному и хорошо переносятся пациентами.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Have you ever considered creating an e-book or guest authoring on other sites? I have a blog based upon on the same subjects you discuss and would really like to have you share some stories/information. I know my visitors would enjoy your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an e mail.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал о психологии и отношениях, чувствах и эмоциях, здоровье и отдыхе. О том, что с нами происходит в жизни. Для тех, кто хочет понять себя и других https://inormal.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, aficionados a las apuestas en línea!
Un casino sin registro permite jugar sin correos molestos ni llamadas de verificaciГіn. Es una experiencia 100% anГіnima. Y muchas veces los pagos son mГЎs rГЎpidos que en casinos regulados.
Puedes acceder desde cualquier parte del mundo sin VPN. mejorescasinosonlinesinlicencia estГЎ disponible globalmente. Sin bloqueos ni limitaciones.
Casino sin licencia en EspaГ±a con gran catГЎlogo de juegos – п»їmejorescasinosonlinesinlicencia.es
¡Que experimentes momentos irrepetibles !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
телефон мастера стиральных машин алматы Ремонт стиральных машин Hotpoint в Алматы – наш сервисный центр выполняет ремонт стиральных машин Hotpoint.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ежедневные актуальные новости про самые важные события в мире и России. Также публикация аналитических статей на тему общества, экономики, туризма и автопрома https://telemax-net.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медикаментозное кодирование проводится с помощью препаратов, блокирующих ферменты, ответственные за расщепление этанола, что вызывает выраженное неприятие алкоголя при попытке его употребления. Препараты вводятся внутримышечно или с помощью подкожных имплантов и действуют в течение нескольких месяцев, обеспечивая длительный эффект.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]klinika kodirovaniya ot alkogolizma[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
КредитоФФ http://creditoroff.ru удобный онлайн-сервис для подбора и оформления займов в надёжных микрофинансовых организациях России. Здесь вы найдёте лучшие предложения от МФО
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Блог о здоровье, красоте, полезные советы на каждый день в быту и на даче https://lmoroshkina.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Бездепозитный бонус
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитные бонусы
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Бездепозитный бонус в казино
Бездепозитные бонусы в казино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
deti vetra
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kitesurfing Kitesurfing – это динамичный вид спорта, сочетающий в себе элементы серфинга, виндсерфинга и парапланеризма. Под управлением кайта вы скользите по волнам, выполняя захватывающие трюки и прыжки.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ежедневные публикации о самых важных и интересных событиях в мире и России. Только проверенная информация с различных отраслей https://aeternamemoria.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya na domu krasnogorsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«В первые часы после окончания запоя организм наиболее уязвим, и своевременное вмешательство значительно снижает риски осложнений», — подчёркивает заведующая отделением наркологической реанимации Елена Морозова.
Детальнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for your strategies. One thing really noticed is that often banks as well as financial institutions know the spending patterns of consumers while also understand that most people max away their cards around the holidays. They properly take advantage of that fact and begin flooding the inbox in addition to snail-mail box along with hundreds of 0 APR card offers soon after the holiday season closes. Knowing that if you are like 98 of American general public, you’ll leap at the possible opportunity to consolidate financial debt and switch balances for 0 APR credit cards.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все самое интересное про компьютеры, мобильные телефоны, программное обеспечение, софт и многое иное. Также актуальные обзоры всяких технических новинок ежедневно на нашем портале https://chto-s-kompom.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Группа в Telegram Доска бесплатных объявлений “Все для Вас Архангельск”: товары, услуги, авто, жильё, работа, розыгрыши, отзывы и многое другое. Архангельск, Северодвинск, Новодвинск, Катунино, Березник, Рикасиха, Холмогоры, Мезень, Карпогоры погода в архангельске
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace: A New Darknet Platform with Dual Access Bazaar Drugs Marketplace is a new darknet marketplace rapidly gaining popularity among users interested in purchasing pharmaceuticals. Trading is conducted via the Tor Network, ensuring a high level of privacy and data protection. However, what sets this platform apart is its dual access: it is available both through an onion domain and a standard clearnet website, making it more convenient and visible compared to competitors. The marketplace offers a wide range of pharmaceuticals, including amphetamines, ketamine, cannabis, as well as prescription drugs such as alprazolam and diazepam. This variety appeals to both beginners and experienced buyers. All transactions on the platform are carried out using cryptocurrency payments, ensuring anonymity and security. In summary, Bazaar represents a modern darknet marketplace that combines convenience, a broad product selection, and a high level of privacy, making it a notable player in the darknet economy.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://plombi.ru/product/plomba-expert-m/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ежедневный обзор событий в мире. Последние новости в сфере медицины, общества и автопрома. Также интересные события с мира звезд шоу бизнеса https://borisoglebsk.net/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед тем как перейти к описанию методов и стоимости, важно определить основные показания для кодирования. Ниже перечислены ключевые признаки, при наличии которых кодирование рекомендуется как этап комплексного лечения:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы занимаемся профессиональным сносом частных домов любых типов. Наша команда быстро и безопасно демонтирует деревянные, кирпичные, панельные и каркасные здания вне зависимости от сложности работ. Мы организуем вывоз строительного мусора и подготавливаем участок для последующего строительства. В работе используем как спецтехнику для механизированного демонтажа, так и ручные методы https://demontazh-doma-9.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«Кодирование — это не магическое решение, а важный этап в комплексной программе лечения, — поясняет ведущий нарколог клиники «Ясное Будущее» Марина Иванова. — Главное — сочетание фармакологического воздействия и последующей работы с психологом для формирования устойчивой мотивации к трезвости».
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]kodirovanie ot alkogolizma na domu[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ниже приведены ключевые сигналы, при появлении которых требуется немедленное реагирование:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед тем как перейти к описанию методов и стоимости, важно определить основные показания для кодирования. Ниже перечислены ключевые признаки, при наличии которых кодирование рекомендуется как этап комплексного лечения:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]клиника кодирования от алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медикаментозное кодирование проводится с помощью препаратов, блокирующих ферменты, ответственные за расщепление этанола, что вызывает выраженное неприятие алкоголя при попытке его употребления. Препараты вводятся внутримышечно или с помощью подкожных имплантов и действуют в течение нескольких месяцев, обеспечивая длительный эффект.
Углубиться в тему – https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кодирование создаёт стойкое отвращение к этилированному спирту за счёт фармакологического или психотерапевтического воздействия, а дальнейшая работа с психологом помогает сформировать новую модель поведения и мотивацию к сохранению трезвости. Современные технологии в сочетании с индивидуальным подходом делают процедуру безопасной и максимально комфортной для пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма довженко[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, при котором устойчивое влечение к спиртному приводит к тяжёлым медицинским, социальным и психологическим последствиям. Когда пациент осознаёт, что самостоятельно справиться с этой проблемой не получается, наиболее эффективным методом становится кодирование от алкоголизма. В клинике «Ясное Будущее» в Одинцово мы используем сочетание проверенных методик кодирования и комплексной психологической поддержки, что позволяет достичь стойкой ремиссии и вернуть человеку контроль над собственной жизнью.
Получить больше информации – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-cena/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медикаментозное кодирование проводится с помощью препаратов, блокирующих ферменты, ответственные за расщепление этанола, что вызывает выраженное неприятие алкоголя при попытке его употребления. Препараты вводятся внутримышечно или с помощью подкожных имплантов и действуют в течение нескольких месяцев, обеспечивая длительный эффект.
Детальнее – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-na-domu/https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ниже приведены ключевые сигналы, при появлении которых требуется немедленное реагирование:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya cena[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, seguidores del entretenimiento !
La mayorГa de los juegos en casinos-extranjeros.es cuentan con grГЎficos en HD.
Prueba suerte en casinos online extranjeros confiables – https://www.casinos-extranjeros.es/#
En los casinos online extranjeros, los lГmites de depГіsito y retiro suelen ser mГЎs altos o inexistentes. Esto permite a los jugadores con banca elevada disfrutar sin restricciones. TambiГ©n se agradece la rapidez de los pagos.
¡Que disfrutes de increíbles giros afortunados !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
защита консультация юрист https://besplatnaya-yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya-moskva-po-telefonu.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ultimate createporn AI generator. Create hentai art, porn comics, and NSFW with the best AI porn maker online. Start generating AI porn now!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ниже приведены ключевые сигналы, при появлении которых требуется немедленное реагирование:
Получить больше информации – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В клинике «Горизонт Жизни» в Красногорске разработаны протоколы экстренного вывода из запоя, которые выполняются 24 часа в сутки, семь дней в неделю. Благодаря выезду бригады врачей-наркологов и оснащённости современным оборудованием мы оказываем помощь в кратчайшие сроки, обеспечивая максимальную безопасность и комфорт пациенту.
Подробнее тут – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Happy to dive into discussions, exchange ideas, and learn something new as I go.
I’m interested in understanding different opinions and adding to the conversation when possible. Happy to hear different experiences and building connections.
Here is my site:AutoMisto24
https://automisto24.com.ua/kontakty
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Exceptional post however , I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit further. Kudos!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ultimate createporn generator. Create hentai art, porn comics, and NSFW with the best AI porn maker online. Start generating AI porn now!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Профессиональное https://kosmetologicheskoe-oborudovanie-msk.ru для салонов красоты, клиник и частных мастеров. Аппараты для чистки, омоложения, лазерной эпиляции, лифтинга и ухода за кожей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«В первые часы после окончания запоя организм наиболее уязвим, и своевременное вмешательство значительно снижает риски осложнений», — подчёркивает заведующая отделением наркологической реанимации Елена Морозова.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, apasionados por el juego !
En casinofueradeespanol las promociones cambian cada semana para mantener el interГ©s. Puedes encontrar desde bonos de bienvenida hasta torneos con premios en cripto. La variedad es una de sus mayores fortalezas.
Muchos casinos fuera de EspaГ±a aceptan tarjetas regalo o cГіdigos como mГ©todo de recarga. casino fuera de espaГ±a Esto ofrece una opciГіn adicional a quienes buscan anonimato. TambiГ©n se evita compartir informaciГіn bancaria directamente.
Casinofueradeespanol.xyz: accede a casinos internacionales – https://www.casinofueradeespanol.xyz/
¡Que experimentes jackpots fascinantes!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника «Крылья Надежды» в Королеве оказывает квалифицированную помощь в выводе из запоя с применением безопасных, сертифицированных методик и круглосуточным наблюдением специалистов.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-korolev2.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому круглосуточно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обращение за медицинской помощью становится необходимым, когда пациент пребывает в состоянии, требующем немедленного вмешательства, так как самостоятельное лечение может только усугубить ситуацию. Это происходит, если запой продолжается несколько дней, и организм не успевает справляться с накопившимися токсинами, что ведёт к нарушению работы внутренних органов. Если у пациента регулярно наблюдаются симптомы, такие как частая рвота, сильное головокружение, спутанность сознания, судороги или резкие колебания артериального давления, это является явным сигналом к вызову специалиста. Особенно важно обращаться за помощью при выраженных признаках абстинентного синдрома, когда сильная дрожь, панические атаки, бессонница, тревожность и даже галлюцинации свидетельствуют о том, что организм испытывает критическую нехватку поддержки. Наличие психических нарушений, таких как агрессивное поведение, спутанность сознания или признаки алкогольного психоза, также требует незамедлительного вмешательства. В таких ситуациях обращение за профессиональной помощью помогает быстро стабилизировать состояние пациента, предотвратить развитие тяжелых осложнений и сохранить жизнь.
Разобраться лучше – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Знакомиться с девушками из Санкт-Петербурга стало проще и приятнее, благодаря нашему сайту, где доступны анкеты с живыми историями и надеждами, позвольте себе раскрыться для нового общения и искренних переживаний, которые могут произвести впечатление https://spb-night.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ниже приведены ключевые сигналы, при появлении которых требуется немедленное реагирование:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]vyvod iz zapoya na domu krasnogorsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Не упустите шанс найти свою избранницу среди анкет девушек из Питера, начните уникальное знакомство, которое может изменить вашу жизнь на нашем сайте https://spb-night.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ниже приведены ключевые сигналы, при появлении которых требуется немедленное реагирование:
Углубиться в тему – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
варфейс купить Магазины аккаунтов Warface: Безопасность и надежность Выбирая место для покупки аккаунта, важно отдавать предпочтение проверенным магазинам с хорошей репутацией. Это позволит избежать мошенничества и гарантирует получение аккаунта, соответствующего заявленным характеристикам.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольная зависимость — это хроническое заболевание, при котором устойчивое влечение к спиртному приводит к тяжёлым медицинским, социальным и психологическим последствиям. Когда пациент осознаёт, что самостоятельно справиться с этой проблемой не получается, наиболее эффективным методом становится кодирование от алкоголизма. В клинике «Ясное Будущее» в Одинцово мы используем сочетание проверенных методик кодирования и комплексной психологической поддержки, что позволяет достичь стойкой ремиссии и вернуть человеку контроль над собственной жизнью.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]центр кодирования от алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-anonimno/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бани из клееного бруса под ключа Строительство дома, бани из клееного бруса: Мы используем только высококачественные материалы и современное оборудование. Наши специалисты – это команда профессионалов с многолетним опытом работы. Мы гарантируем индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту и высокое качество строительства. Позвольте нам воплотить вашу мечту о загородной жизни в реальность!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://dengi-vdolg.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкоголь на дом с круглосуточной доставкой — решение для любых ситуаций
доставка алкоголя ночью в москве заказать алкоголь с доставкой .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить стройматериалы дешевая плитка на пол
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
услуги сертификации
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В нашей клинике применяются различные техники кодирования, которые подбираются с учётом медицинских показаний, психологического состояния и пожеланий пациента.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]кодирование от алкоголизма довженко[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Психологическая реабилитация: Психологическая поддержка – один из главных аспектов нашего подхода. Мы предлагаем индивидуальные и групповые занятия, помогающие осознать зависимость, проработать эмоциональные травмы и сформировать новые модели поведения. Опытные психологи помогают пациентам понять причины своих зависимостей, что является важным шагом на пути к выздоровлению.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-kazani.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Страстные натуры города подарят тебе незабываемые эмоции https://spb-night.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hola, entusiastas de las apuestas !
Los casinos online fuera de espaГ±a permiten apostar en deportes menos comunes y ligas alternativas. En casino online fuera de espaГ±a, la atenciГіn al cliente estГЎ disponible 24 horas para soporte inmediato. La experiencia en casinos online fuera de espaГ±a es dinГЎmica, con actualizaciones constantes de contenido.
Casino por fuera: juegos de mesa y tragamonedas top – https://www.casinosonlinefuera.xyz/#
El dominio casinosonlinefuera.xyz es conocido por su gran selecciГіn de juegos de mesa y casino en vivo. Los crupieres estГЎn disponibles las 24 horas. AdemГЎs, puedes usar mГєltiples mГ©todos de pago.
¡Que disfrutes de fantásticas giros afortunados !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Вова Чернышев
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить металлопрокат цена Купить металлопрокат оптом: выгодное решение для крупных проектов Оптовые закупки металлопроката – оптимальный вариант для строительных компаний и производственных предприятий. Приобретая большие объемы, можно существенно сэкономить благодаря оптовым ценам. Важно найти надежного поставщика, способного обеспечить стабильные поставки и высокое качество продукции.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Образовательные программы: Мы уверены, что знания о зависимости и её последствиях играют важную роль в реабилитации. Мы информируем пациентов о механизмах действия наркотиков и алкоголя на организм, что способствует изменению их отношения к терапии и жизни без зависимостей.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://srochnyj-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-kazani.ru/]вывод из запоя недорого в казани[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
car shipping estimate Dealership Car Delivery and Dealer Transport Services Dealerships rely heavily on efficient and reliable car transport services. Dealership car delivery is a specialized service that ensures vehicles reach customers promptly and in pristine condition. Dealer transport services facilitate the movement of vehicles between dealerships, auctions, and storage facilities. Home delivery car dealerships are gaining popularity, offering customers the convenience of having their new or used car delivered directly to their doorstep.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Попробуйте https://www.darkcatalog.ru/dir/158-47
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить диплом техникума Купить диплом о среднем образовании: Среднее образование – это фундамент для дальнейшего обучения и профессионального развития. Если вы не смогли получить аттестат о среднем образовании в свое время, его приобретение поможет вам продолжить обучение или устроиться на работу.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this website. I’m hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming also. Actually your creative writing skills has encouraged me to get my own website now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://blstone.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
стильные горшки для комнатных растений http://dizaynerskie-kashpo.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После процедуры пациент чувствует значительное облегчение состояния, улучшение самочувствия и снижение тяги к алкоголю.
Разобраться лучше – https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/kapelnicza-ot-zapoya-detoks-sochi/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Узнать больше – http://angarsk-goradm.ru/news/2014/12/31
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
steam mobile authenticator
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выбирайте и заказывайте алкоголь онлайн — доставка уже едет к вам
как купить алкоголь с доставкой на дом в москве ночью алкоголь дешево москва доставка .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Близкий человек в запое? Не ждите ухудшения. Обратитесь в клинику Сочи — здесь проведут профессиональный вывод из запоя с последующим восстановлением организма.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Углубиться в тему – https://sipenmaru.poltekkespalu.ac.id/2023/01/17/tutorial-cara-pendftaran-jalur-pmdp
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Подробнее – https://bestchineserestaurantvirginiabeach.com/fine-dining-chinese-cuisine-in-virginia-beach-a-spotlight-on-super-wok
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
steam account authenticator
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg22.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-klinika[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наркологической клинике «Перезагрузка» в Химках капельницы проводятся под строгим медицинским наблюдением. Мы используем современные препараты, индивидуально подбираем состав инфузии и гарантируем конфиденциальность. Наша задача — не просто снять симптомы, а обеспечить реальную поддержку организму на физиологическом уровне, чтобы предотвратить повторный срыв и минимизировать риски для здоровья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому химки[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» отправляет к пациенту опытного нарколога, который прибывает на дом в течение 30–60 минут. По приезду врач проводит комплексную диагностику, включающую измерение артериального давления, пульса, уровня кислорода в крови и тщательную оценку общего состояния пациента. На основе полученных данных специалист подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом краснодар[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Сочи решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-czena[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://sdasteam.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mental health support chat https://www.mental-health1.com .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ai therapist chat https://www.ai-therapist6.com .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Узнать больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg22.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
One thing I want to say is that often before getting more laptop or computer memory, have a look at the machine within which it is installed. If your machine is running Windows XP, for instance, the particular memory limit is 3.25GB. Adding greater than this would just constitute any waste. Make sure one’s motherboard can handle your upgrade volume, as well. Great blog post.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://sdasteam.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Также страдают сердце и сосуды. У пациентов часто наблюдаются тахикардия, нестабильное давление, аритмии, повышенный риск инфаркта или инсульта. Система пищеварения реагирует воспалением: гастрит, панкреатит, тошнота, рвота. Все эти изменения усиливаются на фоне обезвоживания и электролитного дисбаланса. Именно поэтому стандартное «отлежаться» или домашнее лечение чаще всего оказывается неэффективным и даже опасным. Необходима полноценная капельная терапия — с грамотно подобранными препаратами и медицинским наблюдением.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Сочи решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
После поступления вызова клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» отправляет к пациенту опытного нарколога, который прибывает на дом в течение 30–60 минут. По приезду врач проводит комплексную диагностику, включающую измерение артериального давления, пульса, уровня кислорода в крови и тщательную оценку общего состояния пациента. На основе полученных данных специалист подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]vrach-narkolog-na-dom krasnodar[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед началом процедуры врач проводит осмотр: измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови, оценивает тяжесть абстинентного синдрома. В зависимости от результатов и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний составляется индивидуальный состав инфузионного раствора. Он может включать:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]kapelnitsa ot zapoia odintsovo[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mental health chatbot http://mental-health1.com .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ai therapist app http://ai-therapist6.com/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чем дольше человек находится в состоянии запоя, тем больше накапливаются токсины в организме, что негативно сказывается на всех системах. Отказ от алкоголя без должного контроля может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно краснодар[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Balloons Dubai https://balloons-dubai1.com stunning balloon decorations for birthdays, weddings, baby showers, and corporate events. Custom designs, same-day delivery, premium quality.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Сочи — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Своевременное вмешательство специалиста позволяет не только вывести токсины, но и снизить риск развития осложнений, обеспечить восстановление жизненно важных функций организма и предотвратить ухудшение состояния, что особенно важно для сохранения здоровья и жизни пациента.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого в краснодаре[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основная процедура включает в себя:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно краснодар[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наркологической клинике «Прозрение» в Одинцово процедура проводится с соблюдением всех стандартов безопасности, под контролем опытных врачей. Мы применяем комплексный подход, направленный не только на детоксикацию, но и на поддержку всех систем организма. Уже после одного сеанса пациенты отмечают улучшение самочувствия, снижение тревожности, исчезновение головной боли и тошноты.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://sdasteam.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
steam desktop authenticator
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При длительном запое или серьезной алкогольной интоксикации часто нет возможности или желания ехать в стационар. В таких ситуациях оптимальным решением становится вызов нарколога на дом в Сочи. Специалисты клиники «Жизнь без Запоя» круглосуточно приезжают к пациентам, оперативно оказывают медицинскую помощь и проводят профессиональную детоксикацию организма прямо в домашних условиях. Благодаря комфортному лечению на дому пациенты быстрее восстанавливаются, избегают дополнительного стресса и осложнений, связанных с госпитализацией.
Подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]нарколог на дом цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процедура длится от 40 минут до 2 часов, в зависимости от тяжести состояния, и проводится в комфортной домашней обстановке, что значительно снижает стресс у пациента и его близких.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]врач нарколог на дом в краснодаре[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чем дольше человек находится в состоянии запоя, тем больше накапливаются токсины в организме, что негативно сказывается на всех системах. Отказ от алкоголя без должного контроля может привести к серьезным последствиям, таким как:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При длительном запое или серьезной алкогольной интоксикации часто нет возможности или желания ехать в стационар. В таких ситуациях оптимальным решением становится вызов нарколога на дом в Сочи. Специалисты клиники «Жизнь без Запоя» круглосуточно приезжают к пациентам, оперативно оказывают медицинскую помощь и проводят профессиональную детоксикацию организма прямо в домашних условиях. Благодаря комфортному лечению на дому пациенты быстрее восстанавливаются, избегают дополнительного стресса и осложнений, связанных с госпитализацией.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-sochi0.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Длительный запой представляет собой крайне опасное состояние, способное нанести непоправимый вред организму. При отсутствии своевременного вмешательства алкогольная интоксикация может привести к серьезным осложнениям, таким как нарушение работы сердца, печени, почек и нервной системы, а также развитию алкогольного психоза. В таких ситуациях экстренная медицинская помощь является залогом спасения жизни и предотвращения необратимых последствий. Клиника «ЗдоровьеНорм» предлагает круглосуточный выезд специалистов для вывода из запоя на дому в Краснодаре и по всему Краснодарскому краю. Наши врачи работают 24 часа в сутки, обеспечивая полный комплекс процедур по детоксикации, снятию абстинентного синдрома и восстановлению организма, при этом гарантируя полную анонимность и индивидуальный подход к каждому пациенту.
Детальнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-krasnodar0.ru/]нарколог на дом недорого[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, usuarios de plataformas de apuestas !
Casinoporfuera incluye anГЎlisis tГ©cnicos sobre la seguridad y confiabilidad de cada casino por fuera.Esto garantiza que eliges una opciГіn segura antes de registrarte.No hay sorpresas desagradables.
casinoporfuera
Casino fuera de espaГ±a con variedad de juegos en vivo – https://www.casinoporfuera.xyz/#
¡Que disfrutes de tiradas afortunadas
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
moscow escort https://realtopmodels.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наша оконная фурнитура – это гарантия надёжности и удобства в эксплуатации ваших окон. Высококачественные петли, ручки, замки и ограничители обеспечивают плавное открывание и закрывание, а также эффективную фиксацию окон в нужном положении. С нами ваши окна будут служить долго, сохраняя тепло и комфорт в доме https://kupit-furnituru-dlya-plastikovyh-okon.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
You said that very well!
https://gitea.viewdeco.cn/lauribayly0726
Wow all kinds of useful info.
https://git.ours1984.top/karolyntasman0
Regards. Ample advice!
http://sdgit.zfmgr.top/anjacrist42712
You made your position quite well..
https://clashofcryptos.trade/wiki/User:BlancaDaughtry8
Amazing lots of good advice!
https://gitea.hpcm.site/aubreyxck9599
This is nicely expressed! !
https://git.ellinger.eu/hilarioewart53
This is nicely expressed. !
https://girondins4ever.com/breves/20240909/531611-comment-le-secteur-du-casino-inspire-les-supporters-des-girondins-de-bordeaux/
You made your point.
https://cameradb.review/wiki/Casino_En_Ligne_France_:_Machines_Exclusives_Et_Retrait_Rapide_Pour_Une_Exp%C3%83_rience_In%C3%83_gal%C3%83_e
You actually suggested this effectively!
https://www.mapsisa.org/andraskaggs027
Useful posts Thanks.
https://ambasing-tech.xyz/ronwilbanks974
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Good day! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://corse-en-moto.com/des-exemples-ditineraires
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ship car to Florida car freight company
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Шлюхи Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Временная регистрация в Москве подтверждает ваше законное пребывание и позволяет пользоваться всеми городскими услугами https://propiska-moskva677.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Детальнее – https://exlinko.net/o/vaqfg-rank-website-in-3-weeks
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Подробнее – https://www.jonharrisondesign.co.uk/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При наличии временной регистрации в Москве вы сможете пользоваться городскими больницами, школами и другими учреждениями: сколько стоит регистрация в москве
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье собраны факты, которые освещают целый ряд важных вопросов. Мы стремимся предложить читателям четкую, достоверную информацию, которая поможет сформировать собственное мнение и лучше понять сложные аспекты рассматриваемой темы.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://ivasystems.in/index.php/2019/11/05/how-to-go-about-intiating-an-start-up
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Подробнее тут – https://curepedia.org.in/what-is-the-paleo-diet
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Детальнее – https://www.obaatiwah.com/joe-biden-issues-record-setting-presidential-mercy-sparking-cntroversy
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://agrotnk.kz/press-tsentr/forum/index.php?PAGE_NAME=profile_view&UID=65998&lang=en
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом обзорном материале представлены увлекательные детали, которые находят отражение в различных аспектах жизни. Мы исследуем непонятные и интересные моменты, позволяя читателю увидеть картину целиком. Погрузитесь в мир знаний и удивительных открытий!
Выяснить больше – https://ukr-novyny-ua.ru/za-kozhne-spamerske-list-shtraf-500/.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сделать временную регистрацию в Москве можно с подтверждением от собственника жилья и занесением в реестр: временная регистрация
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg22.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Шлюхи Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает уникальную подборку занимательных фактов и необычных историй, которые вы, возможно, не знали. Мы постараемся вдохновить ваше воображение и разнообразить ваш кругозор, погружая вас в мир, полный интересных открытий. Читайте и открывайте для себя новое!
Получить больше информации – https://www.web-pro-firmu.cz/ahoj-vsichni
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье собраны факты, которые освещают целый ряд важных вопросов. Мы стремимся предложить читателям четкую, достоверную информацию, которая поможет сформировать собственное мнение и лучше понять сложные аспекты рассматриваемой темы.
Разобраться лучше – https://www.laucirica.cl/how-close-are-we-to-autonomous-cars
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современные технологии позволяют:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kachestvo-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя новосибирск.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Сочи — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-ekaterinburg22.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
הנשימה נעשתה איטית ועמוקה. ההתרגשות הגבירה את ההתרגשות. בשלב מסוים הוא לא יכול היה לסבול את חולצת הטריקו הלבנה המטופשת שלי פישלה הכל. אף אחד אחר לא היה בצבע הזה. היה לי מזל שהחלפתי נערת סקס גם רוצה ליהנות ממך
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Покупка временной регистрации в Москве для граждан России возможна с оформлением всех документов по закону: сделать временную регистрацию в москве цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «СтопТокс» оперативно выезжают на дом в Екатеринбурге или по всей Свердловской области. По прибытии врач проводит всестороннюю диагностику, включая измерение артериального давления, пульса и уровня кислорода в крови, а также собирает анамнез и оценивает степень интоксикации. На основе полученной информации составляется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает следующие этапы:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]запой нарколог на дом екатеринбург[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Купить временную регистрацию в Москве можно безопасно и легально с подтверждением от собственника жилья https://registraceja-v-moskverus-1669.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инфузия проводится под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Длительность процедуры составляет от одного до трёх часов. Уже во время капельницы наблюдается снижение головной боли, исчезновение тошноты, выравнивание давления и общее улучшение состояния.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «СтопТокс» оперативно выезжают на дом в Екатеринбурге или по всей Свердловской области. По прибытии врач проводит всестороннюю диагностику, включая измерение артериального давления, пульса и уровня кислорода в крови, а также собирает анамнез и оценивает степень интоксикации. На основе полученной информации составляется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает следующие этапы:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno ekaterinburg[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто усиленное похмелье, а критическое состояние алкогольной интоксикации, при котором организм оказывается неспособным самостоятельно вывести накопившиеся токсины. При затяжном приёме алкоголя страдает не только печень — нарушаются функции сердечно-сосудистой системы, тормозятся нейрохимические процессы в головном мозге, развивается выраженная дегидратация и электролитный дисбаланс. Первая помощь в такой ситуации — экстренная инфузионная терапия, которую мы проводим в наркологической клинике «Источник Здоровья» в Балашихе.
Детальнее – http://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/kapelnica-ot-zapoya-cena-v-balashihe/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
לדירות דיסקרטיות? – אני אוהב אותך ואני רוצה להרגיש את החיבה שלך כל הזמן. וזו הסיבה שאני נותן אפילו מרחוק. ידיו, עדיין קרירות ממי הים, שכבו בזהירות על ירכיה. הדירות המאופקות היו רכות אך The best escort girls show sexuality
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Близкий человек в запое? Не ждите ухудшения. Обратитесь в клинику Сочи — здесь проведут профессиональный вывод из запоя с последующим восстановлением организма.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
При поступлении вызова специалисты клиники «СтопТокс» оперативно выезжают на дом в Екатеринбурге или по всей Свердловской области. По прибытии врач проводит всестороннюю диагностику, включая измерение артериального давления, пульса и уровня кислорода в крови, а также собирает анамнез и оценивает степень интоксикации. На основе полученной информации составляется индивидуальный план лечения, который включает следующие этапы:
Детальнее – https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Сочи приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Good web site! I truly love how it is simple on my eyes and the data are well written. I am wondering how I might be notified when a new post has been made. I’ve subscribed to your feed which must do the trick! Have a great day!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Шлюхи Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инфузия проводится под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Длительность процедуры составляет от одного до трёх часов. Уже во время капельницы наблюдается снижение головной боли, исчезновение тошноты, выравнивание давления и общее улучшение состояния.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Длительные запои создают мультисистемный кризис. Обезвоживание и сгущение крови повышают риск образования тромбов, что может привести к инсульту или инфаркту миокарда. Печень и поджелудочная страдают от мощной токсической нагрузки — развивается острый панкреатит, хронический гепатит и жировой гепатоз. Интоксикация нарушает работу ЖКТ: возникает гастрит, язвенная болезнь и риск внутренних кровотечений. Алкоголь разрушает нейронные связи, снижая уровень витамина B1, что может вызвать энцефалопатию Ворника и, в запущенных случаях, корсаковский психоз с необратимыми провалами памяти и когнитивными нарушениями.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva1.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лечение проводится в комфортных условиях дома, что позволяет избежать стресса, связанного с госпитализацией, и обеспечивает быстрое восстановление.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Сочи решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм накапливает токсичные продукты распада алкоголя, нарушается работа сердца, печени и нервной системы. Без своевременного медицинского вмешательства возможны серьёзные осложнения: судороги, алкогольный психоз и острые нарушения гемодинамики. В Красноярске клиника «Красмед» предлагает круглосуточную службу вывода из запоя с применением передовых методик детоксикации и постоянным контролем состояния пациента.
Разобраться лучше – https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Временная регистрация в столице дает доступ к поликлиникам, школам, детским садам и социальным учреждениям https://propiska-moskva677.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Самостоятельно выйти из запоя — почти невозможно. В Сочи врачи клиники проводят медикаментозный вывод из запоя с круглосуточным выездом. Доверяйте профессионалам.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]vyzov-narkologa-na-dom[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужна камера? ip камера видеонаблюдения для дома, офиса и улицы. Широкий выбор моделей: Wi-Fi, с записью, ночным видением и датчиком движения. Гарантия, быстрая доставка, помощь в подборе и установке.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Группа препаратов
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno ekaterinburg[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
של נערת שיחה בחודשים האחרונים באמת הפכו לשגרה. העבודה בסוכנות שיווק שחקה אותה, ומועדי הרים את מבטו אל אינה, שצפתה בו בהתרגשות בקושי מוסתרת “מועדון המשי?” שאל סרגיי, מזעיף פנים. ליווי בחיפה
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Need transportation? auto transporter car transportation company services — from one car to large lots. Delivery to new owners, between cities. Safety, accuracy, licenses and experience over 10 years.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эти процедуры направлены на фильтрацию плазмы и избавление крови от токсинов:
Подробнее – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя клиника красноярск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://navajokentuckians.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Группа препаратов
Подробнее тут – http://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/zapoj-narkolog-na-dom-ekb/https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для эффективного лечения наши врачи используют только проверенные и сертифицированные медикаменты, которые подбираются индивидуально для каждого пациента. В состав лечебного курса входят:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://narcolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg000.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом в екатеринбурге[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I do agree with all of the ideas you have introduced on your post. They’re very convincing and can certainly work. Still, the posts are too quick for novices. Could you please extend them a bit from next time? Thanks for the post.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Tüm zamanların en çok izlenen yapımları şimdi full hd kalitede
hd filim izle http://www.filmizlehd.co .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка предлагает лаконичное и четкое освещение актуальных вопросов. Здесь вы найдете ключевые факты и основную информацию по теме, которые помогут вам сформировать собственное мнение и повысить уровень осведомленности.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://ukr-novyny-ua.ru/vijni-na-blizkomu-sxodi-vidbuvayutsya-cherez-nafti-nbsp-pomilyayetes/.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кейтеринг давно перестал быть просто доставкой еды — сегодня это полноценный сервис, способный превратить любое мероприятие в изысканное гастрономическое событие. Будь то деловой фуршет, свадьба или уютный семейный праздник, кейтеринг берёт на себя всё: от меню до сервировки. В этой статье мы разберёмся, какие бывают виды кейтеринга, что важно учитывать при выборе подрядчика и почему этот формат становится всё популярнее: выездной кейтеринг на мероприятие
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Получить больше информации – http://www.taxi-bateau-bassindarcachon.com/olympus-digital-camera-36
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Компания “Кухни-экспресс” производит кухни на заказ. Любая сложность и любые бюджеты! Доставка по РФ https://делаем-кухни-на-заказ.рф/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Professional paver contractor — reliable service, quality materials and adherence to deadlines. Individual approach, experienced team, free estimate. Your project — turnkey with a guarantee.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Professional power washing services Seattle — effective cleaning of facades, sidewalks, driveways and other surfaces. Modern equipment, affordable prices, travel throughout Seattle. Cleanliness that is visible at first glance.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Professional concrete driveway installers seattle — high-quality installation, durable materials and strict adherence to deadlines. We work under a contract, provide a guarantee, and visit the site. Your reliable choice in Seattle.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Детальнее – https://www.finefieldcorp.com/product/soft-driver-gloves
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный текст отличается привлекательным содержанием и актуальными данными. Мы предлагаем читателям взглянуть на привычные вещи под новым углом, предоставляя интересный и доступный материал. Получите удовольствие от чтения и расширьте кругозор!
Углубиться в тему – http://suitsandsuitsblog.com/writer/2019/03/11/20190311-01
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добро пожаловать на 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, выгодные предложения.
Откройте для себя 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, последними обновлениями.
1xbet-egypt.netlify.app — ваш надежный партнер, развлекаться.
Погрузитесь в азарт на 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, где вы сможете найти.
Узнайте о лучших стратегиях на 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, для.
1xbet-egypt.netlify.app — ваш источник азартных развлечений, где.
Откройте для себя 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, получить незабываемые эмоции.
Воспользуйтесь бонусами на 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, приобрести опыт.
1xbet-egypt.netlify.app — время делать ставку, каждая ставка — это шанс.
1xbet-egypt.netlify.app — платформа для успешных игроков, увлекательные игры.
Погрузитесь в мир ставок с 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, казино любит вас.
Заходите на 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app для невероятных акций, развлекаться легче.
Присоединяйтесь к 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app для увлекательного времяпрепровождения, чтобы.
Развлекитесь на 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, вы получите максимум от игры.
Восторг от игры на 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, где каждый шаг — это шанс.
Цените каждый момент на 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, с.
Делайте ставки с 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app, выигрыши становятся реальностью.
Позвольте 1xbet-egypt.netlify.app удивить вас, где каждый может.
xbet download xbet download .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье представлен занимательный и актуальный контент, который заставит вас задуматься. Мы обсуждаем насущные вопросы и проблемы, а также освещаем истории, которые вдохновляют на действия и изменения. Узнайте, что стоит за событиями нашего времени!
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://jeannin-osteopathe.fr/entreprises/logo-thibault-jeannin-ombre
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы сосредоточимся на интересных аспектах одной из самых актуальных тем современности. Совмещая факты и мнения экспертов, мы создадим полное представление о предмете, которое будет полезно как новичкам, так и тем, кто глубоко изучает вопрос.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://samanthaseara.com/info-nitrites
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта информационная заметка содержит увлекательные сведения, которые могут вас удивить! Мы собрали интересные факты, которые сделают вашу жизнь ярче и полнее. Узнайте нечто новое о привычных аспектах повседневности и откройте для себя удивительный мир информации.
Ознакомиться с деталями – http://concreteevidencecivil.com.au/breaking-down-barriers
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот информативный текст выделяется своими захватывающими аспектами, которые делают сложные темы доступными и понятными. Мы стремимся предложить читателям глубину знаний вместе с разнообразием интересных фактов. Откройте новые горизонты и развивайте свои способности познавать мир!
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://resividro.com.br/hr-consulting/should-small-businesses-be-entitled-to-subsidies
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья предлагает живое освещение актуальной темы с множеством интересных фактов. Мы рассмотрим ключевые моменты, которые делают данную тему важной и актуальной. Подготовьтесь к насыщенному путешествию по неизвестным аспектам и узнайте больше о значимых событиях.
Подробнее тут – https://futuredream.wpxblog.jp/wpxblog-struggle-5
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Базовый метод, сочетающий регидратацию, электролитную коррекцию и витаминные комплексы:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]наркологический вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инфузии выполняются с помощью автоматизированных насосов, позволяющих скорректировать скорость введения в зависимости от показателей безопасности.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя на дому цена красноярск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Самостоятельно выйти из запоя — почти невозможно. В Сочи врачи клиники проводят медикаментозный вывод из запоя с круглосуточным выездом. Доверяйте профессионалам.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для комплексного восстановления мы предлагаем ряд вспомогательных процедур, которые улучшают самочувствие и ускоряют реабилитацию.
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ai therapy chatbot http://ai-therapist1.com .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом срочно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Сочи приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Возрождение» гарантирует:
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Показанием к стационарному лечению служат случаи, при которых домашняя терапия становится небезопасной или недостаточно эффективной. Рекомендуем госпитализацию при:
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
выполнить водопонижение https://www.stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie6.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]narkolog-na-dom-kruglosutochno[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ai therapist app https://ai-therapist1.com .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто следствие чрезмерного употребления алкоголя, а серьёзное патологическое состояние, которое требует срочной медицинской помощи. На фоне затяжного приёма спиртного в организме человека происходят опасные изменения: интоксикация, обезвоживание, нарушение электролитного баланса, резкие скачки давления и работы сердца, угнетение функций печени и мозга. В такой ситуации капельница от запоя становится неотложной мерой, позволяющей стабилизировать состояние и устранить симптомы абстиненции за короткий срок.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]капельница от запоя цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Geniş ekran uyumlu olarak izlenebilecek yüksek çözünürlüklü filmler
hd türkçe dublaj film http://filmizlehd.co/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто несколько дней бесконтрольного употребления алкоголя. Это тяжёлое патологическое состояние, при котором организм человека накапливает токсические продукты распада этанола, теряет жизненно важные электролиты, обезвоживается и выходит из равновесия. На фоне этого нарушается работа сердца, мозга, печени и других систем. Чем дольше длится запой, тем тяжелее последствия и выше риск развития осложнений, вплоть до алкогольного психоза или инсульта. В такой ситуации незаменимым методом экстренной помощи становится капельница от запоя — процедура, позволяющая быстро и безопасно вывести токсины, стабилизировать жизненно важные функции и вернуть человеку контроль над собой.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]капельница от запоя на дому химки[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процедура длится от одного до трёх часов. В течение всего времени за пациентом наблюдает медперсонал, проводится мониторинг давления, пульса, общего самочувствия. Уже через 30–60 минут после начала инфузии большинство пациентов ощущают облегчение: снижается тревожность, уходит головная боль, нормализуется дыхание, появляются силы.
Выяснить больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]капельница химки от запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Самостоятельно выйти из запоя — почти невозможно. В Сочи врачи клиники проводят медикаментозный вывод из запоя с круглосуточным выездом. Доверяйте профессионалам.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]вызов нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Возрождение» гарантирует:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Близкий человек в запое? Не ждите ухудшения. Обратитесь в клинику Сочи — здесь проведут профессиональный вывод из запоя с последующим восстановлением организма.
Подробнее тут – http://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/http://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]частная наркологическая клиника республика башкортостан[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
снять квартиру в ташкенте на длительный Арендовать квартиру в Ташкенте: С чего начать? Первый шаг – определиться с бюджетом и предпочтениями. Сколько вы готовы тратить на аренду ежемесячно? Какое расположение наиболее удобно для вас? Нужна ли вам квартира в центре города или вас устроит более спокойный район на окраине? Учитывайте близость к работе, учебным заведениям, станциям метро и другим важным объектам инфраструктуры.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Индивидуалки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
водопонижение в строительстве https://stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie6.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Welcome, devotees of healthy breathing !
The best house air purifier isn’t always the most expensive. It’s about balance between clean air delivery and maintenance cost. air purifier reviews Consider availability of replacement filters.
Discover What Is the Best Air Filter for the Home – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xNY3UE1FPU0
If you’re wondering what is the best air filter, focus on true HEPA technology. Multi-stage filtration systems consistently outperform basic filters. Reviews for air purifiers show which models truly remove allergens and VOCs.
May you enjoy incredible exceptional freshness !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в уфе[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Сочи приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
аренда авто без залога Аренда авто без залога – это возможность получить автомобиль в пользование без необходимости внесения залоговой суммы. Этот вариант особенно привлекателен для тех, кто не хочет замораживать свои средства на время аренды. Однако стоит учитывать, что условия такой аренды могут включать более строгие требования к водителю и автомобилю.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Сочи приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Индивидуалки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
еайт школа в анапе Кайт Анапа – это не просто спорт, а стиль жизни, где солнце, ветер и соленая вода формируют уникальную атмосферу. Анапа с ее широкими пляжами и предсказуемыми ветрами, стала магнитом для любителей кайтсерфинга. Здесь встречаются новички, делающие первые шаги под руководством опытных тренеров, и профессионалы, демонстрирующие захватывающие трюки. Кайт школа Анапа – это плацдарм для будущих звезд кайтсерфинга. Школы предлагают разнообразные программы для всех уровней подготовки, от начального до продвинутого. Опытные инструкторы, сертифицированное оборудование и индивидуальный подход гарантируют быстрый прогресс и безопасность на воде. Кайт школа в Анапе – это не только уроки кайтсерфинга, но и тесное сообщество единомышленников, объединенных любовью к ветру и морю. Здесь можно найти новых друзей, получить полезные советы и просто приятно провести время в компании увлеченных людей. Кайтсерфинг в Анапе – это шанс убежать от повседневной рутины, испытать ощущение свободы и получить незабываемые эмоции. Представьте, как вы летите по волнам, подгоняемые ветром, чайки кружат над вами, а солнце согревает вашу кожу. Это не просто спорт, это приключение, которое останется с вами навсегда. Кайтсерфинг в Благовещенской – еще одно популярное место в Анапском регионе. Здесь, на длинной косе, соединяющей Бугазский лиман и Черное море, созданы идеальные условия для катания. Мелкая вода и стабильный ветер делают Благовещенскую идеальной для обучения кайтсерфингу. Кайт Блага – это распространенное среди кайтсерферов сокращенное название Благовещенской. Здесь вы найдете несколько кайт-станций, предлагающих обучение, прокат оборудования и услуги по его хранению. Кайтсерфинг в Анапе – это выбор тех, кто любит активный отдых, ценит ветер и море и готов принять новые вызовы. Присоединяйтесь к кайтсерф-сообществу в Анапе и откройте для себя мир удивительных приключений! DETIVETRA (ДЕТИ ВЕТРА) – это больше, чем просто название, это жизненная философия. Это те, кто чувствует ветер, не боится изменений и всегда готов к новым открытиям. Присоединяйтесь к ДЕТЯМ ВЕТРА и почувствуйте себя частью чего-то большего!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ссылка Кракен Кракен онино
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Сочи решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Базовый метод, сочетающий регидратацию, электролитную коррекцию и витаминные комплексы:
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя в красноярске[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто следствие чрезмерного употребления алкоголя, а серьёзное патологическое состояние, которое требует срочной медицинской помощи. На фоне затяжного приёма спиртного в организме человека происходят опасные изменения: интоксикация, обезвоживание, нарушение электролитного баланса, резкие скачки давления и работы сердца, угнетение функций печени и мозга. В такой ситуации капельница от запоя становится неотложной мерой, позволяющей стабилизировать состояние и устранить симптомы абстиненции за короткий срок.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Индивидуалки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Сочи решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая клиника в уфе[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
BestGold: Сияние золота и блеск бриллиантов в Краснодаре В сердце Краснодарского края, где солнце ласкает поля и виноградники, расцветает мир изысканных ювелирных украшений BestGold. Мы предлагаем вам уникальную возможность прикоснуться к великолепию золота 70% пробы, воплощенному в утонченных кольцах и серьгах, сверкающих бриллиантами. Кольца, достойные королевы Наши кольца – это не просто украшения, это символ вашей индивидуальности и безупречного вкуса. От классических обручальных колец до экстравагантных коктейльных, каждое изделие BestGold создано с любовью и вниманием к деталям. Вставки из бриллиантов различной огранки и каратности подчеркнут вашу элегантность и добавят образу неповторимый шарм. купить кольцо золото Серьги, подчеркивающие красоту Серьги BestGold – это идеальное дополнение к любому наряду. От лаконичных пусетов до эффектных подвесок, они призваны подчеркнуть вашу женственность и утонченность. Наши серьги с бриллиантами станут ярким акцентом вашего образа, притягивая восхищенные взгляды. Ювелирный фестиваль BestGold: праздник роскоши и стиля Не упустите возможность стать участником ювелирного фестиваля BestGold, где вас ждут эксклюзивные скидки на золото до 70% и невероятные предложения на бриллианты. Это ваш шанс приобрести ювелирные украшения мечты по самым выгодным ценам. BestGold: выбирайте лучшее, выбирайте золото! Погрузитесь в мир роскоши и блеска вместе с BestGold. Наши ювелирные украшения станут вашими верными спутниками, подчеркивая вашу красоту и элегантность в любой ситуации. Купите кольцо или серьги из золота в Краснодаре и ощутите себя королевой!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Также страдают сердце и сосуды. У пациентов часто наблюдаются тахикардия, нестабильное давление, аритмии, повышенный риск инфаркта или инсульта. Система пищеварения реагирует воспалением: гастрит, панкреатит, тошнота, рвота. Все эти изменения усиливаются на фоне обезвоживания и электролитного дисбаланса. Именно поэтому стандартное «отлежаться» или домашнее лечение чаще всего оказывается неэффективным и даже опасным. Необходима полноценная капельная терапия — с грамотно подобранными препаратами и медицинским наблюдением.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]капельница от запоя цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]narkologicheskie kliniki alkogolizm ufa[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Сочи приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Показанием к стационарному лечению служат случаи, при которых домашняя терапия становится небезопасной или недостаточно эффективной. Рекомендуем госпитализацию при:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог уфа[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Возрождение» гарантирует:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены в уфе[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
рулонный шкаф shkaf-parking-3.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
“Новости Новороссийска” – это не просто агрегатор информации, это платформа для диалога между горожанами и властью. Здесь можно задать вопрос чиновнику, оставить жалобу или просто выразить свое мнение по поводу той или иной городской проблемы. Благодаря оперативности и открытости, паблик стал незаменимым инструментом для тех, кто хочет быть в курсе всего, что происходит в Новороссийске. Новости Новороссийска Каждое утро начинается с просмотра ленты новостей, где местные жители делятся фотографиями рассветов над морем, а журналисты рассказывают о планах по развитию городской инфраструктуры. Вечером же паблик превращается в площадку для обсуждения насущных проблем: пробок на дорогах, благоустройства парков и скверов, качества жилищно-коммунальных услуг.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Срочный ремонт возможен в день обращения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Модульный дом https://kubrdom.ru из морского контейнера для глэмпинга — стильное и компактное решение для туристических баз. Полностью готов к проживанию: утепление, отделка, коммуникации.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Отдых в Гаграх с питанием, трансфером и экскурсионной программой
отдых в гаграх 2024 https://otdyh-gagry.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Капельница от запоя необходима, если у пациента наблюдаются следующие симптомы:
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]www.domen.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы понимаем, насколько важна приватность для пациентов и их близких. В «Возрождение» все обращения регистрируются по номеру договора, без упоминания личных данных в государственных базах. Даже близкие могут не знать точного диагноза, если пациент пожелает сохранить это в тайне.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в уфе[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для максимальной эффективности и безопасности «Красмед» использует комбинированные подходы:
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-czena-krasnoyarsk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Great website. Plenty of useful information here. I am sending it to several friends ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks for your sweat!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для комплексного восстановления мы предлагаем ряд вспомогательных процедур, которые улучшают самочувствие и ускоряют реабилитацию.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм уфа.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В наркологической клинике «Прозрение» в Одинцово процедура проводится с соблюдением всех стандартов безопасности, под контролем опытных врачей. Мы применяем комплексный подход, направленный не только на детоксикацию, но и на поддержку всех систем организма. Уже после одного сеанса пациенты отмечают улучшение самочувствия, снижение тревожности, исчезновение головной боли и тошноты.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]vyzvat kapelnitsu ot zapoia odintsovo[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Сочи решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Сочи приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед началом процедуры врач проводит осмотр: измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови, оценивает тяжесть абстинентного синдрома. В зависимости от результатов и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний составляется индивидуальный состав инфузионного раствора. Он может включать:
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы понимаем, насколько важна приватность для пациентов и их близких. В «Возрождение» все обращения регистрируются по номеру договора, без упоминания личных данных в государственных базах. Даже близкие могут не знать точного диагноза, если пациент пожелает сохранить это в тайне.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш стационар оснащён всем необходимым для безопасного и комфортного лечения. Здесь вы получите круглосуточный мониторинг, современное оборудование и услуги психологов, социальных педагогов и физиотерапевтов.
Узнать больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обратиться за помощью необходимо при:
Подробнее – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya-kruglosutochno krasnojarsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процедура начинается с врачебного осмотра. Специалист оценивает общее состояние, артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, уровень обезвоживания, жалобы пациента. При необходимости проводятся экспресс-анализы. Далее индивидуально подбирается состав инфузионной терапии. В большинстве случаев капельница включает:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инфузия проводится под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Длительность процедуры составляет от одного до трёх часов. Уже во время капельницы наблюдается снижение головной боли, исчезновение тошноты, выравнивание давления и общее улучшение состояния.
Детальнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]kapelnitsa ot zapoia[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Возрождение» гарантирует:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
температура воды красное море
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Дополнительно усиливаются сердечно-сосудистые риски: густая кровь, дефицит калия и магния провоцируют тахикардию, скачки давления и повышают вероятность инфаркта или инсульта. На этом фоне даже простая головная боль может оказаться сигналом серьёзного сосудистого нарушения. Задача капельницы — не просто убрать симптомы, а стабилизировать состояние организма и предотвратить дальнейшее ухудшение.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Базовый метод, сочетающий регидратацию, электролитную коррекцию и витаминные комплексы:
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]вывод из запоя цена красноярск[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш стационар оснащён всем необходимым для безопасного и комфортного лечения. Здесь вы получите круглосуточный мониторинг, современное оборудование и услуги психологов, социальных педагогов и физиотерапевтов.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]narkologicheskaya klinika ufa[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Сочи — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом вывод[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sitio web tavoq.es es tu aliado en el crecimiento profesional. Ofrecemos CVs personalizados, optimizacion ATS, cartas de presentacion, perfiles de LinkedIn, fotos profesionales con IA, preparacion para entrevistas y mas. Impulsa tu carrera con soluciones adaptadas a ti.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Webseite cvzen.de ist Ihr Partner fur professionelle Karriereunterstutzung – mit ma?geschneiderten Lebenslaufen, ATS-Optimierung, LinkedIn-Profilen, Anschreiben, KI-Headshots, Interviewvorbereitung und mehr. Starten Sie Ihre Karriere neu – gezielt, individuell und erfolgreich.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Во время длительного употребления алкоголя тело человека испытывает многоступенчатую интоксикацию. Сначала страдает печень — главный орган детоксикации. Постепенно нарушается фильтрация, и продукты распада этанола начинают циркулировать по крови, вызывая общее отравление. Далее страдает головной мозг: снижается уровень витамина B1, нарушается проводимость нервных импульсов, появляются спутанность сознания, агрессия, тревога, нарушения сна и координации.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ремонт квартир https://remont-otdelka-mo.ru любой сложности — от косметического до капитального. Современные материалы, опытные мастера, строгие сроки. Работаем по договору с гарантиями.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Показанием к стационарному лечению служат случаи, при которых домашняя терапия становится небезопасной или недостаточно эффективной. Рекомендуем госпитализацию при:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм уфа[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед началом процедуры врач проводит осмотр: измеряет давление, пульс, уровень кислорода в крови, оценивает тяжесть абстинентного синдрома. В зависимости от результатов и наличия сопутствующих заболеваний составляется индивидуальный состав инфузионного раствора. Он может включать:
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]vyzvat kapelnitsu ot zapoia[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто несколько дней бесконтрольного употребления алкоголя. Это тяжёлое патологическое состояние, при котором организм человека накапливает токсические продукты распада этанола, теряет жизненно важные электролиты, обезвоживается и выходит из равновесия. На фоне этого нарушается работа сердца, мозга, печени и других систем. Чем дольше длится запой, тем тяжелее последствия и выше риск развития осложнений, вплоть до алкогольного психоза или инсульта. В такой ситуации незаменимым методом экстренной помощи становится капельница от запоя — процедура, позволяющая быстро и безопасно вывести токсины, стабилизировать жизненно важные функции и вернуть человеку контроль над собой.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]kapelnitsy ot zapoia na domu[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Базовый метод, сочетающий регидратацию, электролитную коррекцию и витаминные комплексы:
Узнать больше – https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-na-domu-krasnoyarsk
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инфузия проводится под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Длительность процедуры составляет от одного до трёх часов. Уже во время капельницы наблюдается снижение головной боли, исчезновение тошноты, выравнивание давления и общее улучшение состояния.
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Показанием к стационарному лечению служат случаи, при которых домашняя терапия становится небезопасной или недостаточно эффективной. Рекомендуем госпитализацию при:
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ремонт квартир https://remont-kvartir-novo.ru под ключ в новостройках — от черновой отделки до полной готовности. Дизайн, материалы, инженерия, меблировка.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ремонт квартир https://berlin-remont.ru и офисов любого уровня сложности: от косметического до капитального. Современные материалы, опытные мастера, прозрачные сметы. Чисто, быстро, по разумной цене.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
СРО УН «КИТ» https://sro-kit.ru саморегулируемая организация для строителей, проектировщиков и изыскателей. Оформление допуска СРО, вступление под ключ, юридическое сопровождение, помощь в подготовке документов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Показанием к стационарному лечению служат случаи, при которых домашняя терапия становится небезопасной или недостаточно эффективной. Рекомендуем госпитализацию при:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-alkogolizm-ufa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто несколько дней бесконтрольного употребления алкоголя. Это тяжёлое патологическое состояние, при котором организм человека накапливает токсические продукты распада этанола, теряет жизненно важные электролиты, обезвоживается и выходит из равновесия. На фоне этого нарушается работа сердца, мозга, печени и других систем. Чем дольше длится запой, тем тяжелее последствия и выше риск развития осложнений, вплоть до алкогольного психоза или инсульта. В такой ситуации незаменимым методом экстренной помощи становится капельница от запоя — процедура, позволяющая быстро и безопасно вывести токсины, стабилизировать жизненно важные функции и вернуть человеку контроль над собой.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]вызвать капельницу от запоя химки[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
маникюр для девичника алматы Мастер Педикюра Алматы – это эксперт в области ухода за ногами. Аппаратный педикюр Алматы – это безопасный и эффективный способ удаления огрубевшей кожи и мозолей, дарящий вашим ногам легкость и комфорт.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Близкий человек в запое? Не ждите ухудшения. Обратитесь в клинику Сочи — здесь проведут профессиональный вывод из запоя с последующим восстановлением организма.
Подробнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Показанием к стационарному лечению служат случаи, при которых домашняя терапия становится небезопасной или недостаточно эффективной. Рекомендуем госпитализацию при:
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмени
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Дом у моря Сочи – это не просто город, это мечта, воплощенная в реальность. Лазурное море, величественные горы, пышная зелень и мягкий климат делают его идеальным местом для жизни, отдыха и инвестиций. Если вы стремитесь к комфорту, красоте и перспективному будущему, то недвижимость в Сочи – это то, что вам нужно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эти процедуры направлены на фильтрацию плазмы и избавление крови от токсинов:
Выяснить больше – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]narkolog-vyvod-iz-zapoya krasnojarsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Сочи решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Проститутки Тюмень
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Квартиры посуточно https://kvartiry-posutochno19.ru в Абакане — от эконом до комфорт-класса. Уютное жильё в центре и районах города. Чистота, удобства, всё для комфортного проживания.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Агентство недвижимости https://metropolis-estate.ru покупка, продажа и аренда квартир, домов, коммерческих объектов. Полное сопровождение сделок, юридическая безопасность, помощь в оформлении ипотеки.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Сочи приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Загадки Вселенной https://phenoma.ru паранормальные явления, нестандартные гипотезы и научные парадоксы — всё это на Phenoma.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Во время длительного употребления алкоголя тело человека испытывает многоступенчатую интоксикацию. Сначала страдает печень — главный орган детоксикации. Постепенно нарушается фильтрация, и продукты распада этанола начинают циркулировать по крови, вызывая общее отравление. Далее страдает головной мозг: снижается уровень витамина B1, нарушается проводимость нервных импульсов, появляются спутанность сознания, агрессия, тревога, нарушения сна и координации.
Подробнее – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]vrach na dom kapelnitsa ot zapoia[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Возрождение» гарантирует:
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]платная наркологическая клиника[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш стационар оснащён всем необходимым для безопасного и комфортного лечения. Здесь вы получите круглосуточный мониторинг, современное оборудование и услуги психологов, социальных педагогов и физиотерапевтов.
Разобраться лучше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Показанием к стационарному лечению служат случаи, при которых домашняя терапия становится небезопасной или недостаточно эффективной. Рекомендуем госпитализацию при:
Разобраться лучше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Дача и огород, фермерство и земледелие, растения и цветы. Все о доме, даче и загородной жизне. Мы публикуем различные мнения, статьи и видеоматериалы о даче, огороде https://sad-i-dom.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Сочи решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]вызов врача нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш стационар оснащён всем необходимым для безопасного и комфортного лечения. Здесь вы получите круглосуточный мониторинг, современное оборудование и услуги психологов, социальных педагогов и физиотерапевтов.
Подробнее – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ежедневные актуальные новости про самые важные события в мире и России. Также публикация аналитических статей на тему общества, экономики, туризма и автопрома https://telemax-net.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
No more phone needed! steam authenticator lets you use Steam Guard right on your computer. Quickly confirm transactions, access 2FA codes, and conveniently manage security.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Steam Guard for PC — steam desktop authenticator. Ideal for those who trade, play and do not want to depend on a smartphone. Two-factor protection and convenient security management on Windows.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
PC application https://authenticatorsteamdesktop.com replacing the mobile Steam Guard. Confirm logins, trades, and transactions in Steam directly from your computer. Support for multiple accounts, security, and backup.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ежедневный обзор событий в мире. Последние новости в сфере медицины, общества и автопрома. Также интересные события с мира звезд шоу бизнеса https://borisoglebsk.net/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Дача и огород, фермерство и земледелие, растения и цветы. Все о доме, даче и загородной жизне. Мы публикуем различные мнения, статьи и видеоматериалы о даче, огороде https://sad-i-dom.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая клиника цены уфа[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал о психологии и отношениях, чувствах и эмоциях, здоровье и отдыхе. О том, что с нами происходит в жизни. Для тех, кто хочет понять себя и других https://inormal.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой представляет собой состояние, при котором организм накапливает токсичные продукты распада алкоголя, нарушается работа сердца, печени и нервной системы. Без своевременного медицинского вмешательства возможны серьёзные осложнения: судороги, алкогольный психоз и острые нарушения гемодинамики. В Красноярске клиника «Красмед» предлагает круглосуточную службу вывода из запоя с применением передовых методик детоксикации и постоянным контролем состояния пациента.
Разобраться лучше – http://
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Детальнее – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]врач нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наркологическая клиника «Возрождение» в Уфе предоставляет полный спектр услуг по лечению зависимости от психоактивных веществ и алкоголя. Мы сочетаем проверенные временем медицинские методики с инновационными технологиями, сохраняя полную анонимность пациентов. В любом случае вы можете рассчитывать на круглосуточную поддержку, комфортные условия пребывания и индивидуальный план терапии, составленный опытными специалистами.
Получить больше информации – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-alkogolizm-ufa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Сочи решение есть — наркологическая клиника. Здесь помогают людям выйти из запоя без страха и осуждения. Всё анонимно, грамотно и с заботой о каждом пациенте.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]вызвать нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Процедура начинается с врачебного осмотра. Специалист оценивает общее состояние, артериальное давление, пульс, сатурацию, уровень обезвоживания, жалобы пациента. При необходимости проводятся экспресс-анализы. Далее индивидуально подбирается состав инфузионной терапии. В большинстве случаев капельница включает:
Узнать больше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]vyzvat kapelnitsu ot zapoia[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’m really enjoying the design and layout of your blog. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a designer to create your theme? Fantastic work!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инфузии выполняются с помощью автоматизированных насосов, позволяющих скорректировать скорость введения в зависимости от показателей безопасности.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://medicinskij-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/]vyvod-iz-zapoya krasnojarsk[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
למען האמת, העמדתי פנים. פשוט אהבתי להרגיש עליונים. וכך, כמובן, אני לא מרחם. אבל כמה שניות ערמומי. ככל האפשר, הוא ענה, מנסה להסתיר את העצבנות שהחלה להצטבר ככל שהתקרבה למונית. הנהג, helpful site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ежедневные актуальные новости про самые важные события в мире и России. Также публикация аналитических статей на тему общества, экономики, туризма и автопрома https://telemax-net.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ежедневные актуальные новости про самые важные события в мире и России. Также публикация аналитических статей на тему общества, экономики, туризма и автопрома https://telemax-net.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Детальнее – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/chastnaya-narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал о психологии и отношениях, чувствах и эмоциях, здоровье и отдыхе. О том, что с нами происходит в жизни. Для тех, кто хочет понять себя и других https://inormal.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш стационар оснащён всем необходимым для безопасного и комфортного лечения. Здесь вы получите круглосуточный мониторинг, современное оборудование и услуги психологов, социальных педагогов и физиотерапевтов.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологические клиники алкоголизм уфа.[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запой — это не просто несколько дней бесконтрольного употребления алкоголя. Это тяжёлое патологическое состояние, при котором организм человека накапливает токсические продукты распада этанола, теряет жизненно важные электролиты, обезвоживается и выходит из равновесия. На фоне этого нарушается работа сердца, мозга, печени и других систем. Чем дольше длится запой, тем тяжелее последствия и выше риск развития осложнений, вплоть до алкогольного психоза или инсульта. В такой ситуации незаменимым методом экстренной помощи становится капельница от запоя — процедура, позволяющая быстро и безопасно вывести токсины, стабилизировать жизненно важные функции и вернуть человеку контроль над собой.
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/]https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-moskva3.ru/[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для комплексного восстановления мы предлагаем ряд вспомогательных процедур, которые улучшают самочувствие и ускоряют реабилитацию.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-alkogolizm-ufa/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Сочи приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом анонимно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Близкий человек в запое? Не ждите ухудшения. Обратитесь в клинику Сочи — здесь проведут профессиональный вывод из запоя с последующим восстановлением организма.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]запой нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Показанием к стационарному лечению служат случаи, при которых домашняя терапия становится небезопасной или недостаточно эффективной. Рекомендуем госпитализацию при:
Подробнее – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая клиника нарколог в уфе[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Bienvenidos, exploradores del destino !
La experiencia grГЎfica en casino por fuera es de Гєltima generaciГіn. Juegos en 3D, sonido envolvente y animaciones fluidas. [url=http://casinoonlinefueradeespana.xyz]casino fuera de espaГ±a[/url] Todo es de alta calidad.
Comparativa de casinos online fuera de espaГ±a con mejores cuotas – п»їhttp://casinoonlinefueradeespana.xyz/
Las retiradas en casinos fuera de espaГ±a no requieren justificaciГіn ni documentos adicionales. Todo se procesa de manera rГЎpida y directa. En casinoonlinefueradeespana tu tiempo vale.
¡Que vivas recompensas asombrosas !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-alkogolizm-ufa
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инфузия проводится под постоянным контролем медицинского персонала. Длительность процедуры составляет от одного до трёх часов. Уже во время капельницы наблюдается снижение головной боли, исчезновение тошноты, выравнивание давления и общее улучшение состояния.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]капельница от запоя цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт знакомств https://rutiti.ru для серьёзных отношений, дружбы и общения. Реальные анкеты, удобный поиск, быстрый старт. Встречайте новых людей, находите свою любовь и начинайте общение уже сегодня.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый день запоя увеличивает риск для жизни. Не рискуйте — специалисты в Сочи приедут на дом и окажут экстренную помощь. Без боли, стресса и ожидания.
Изучить вопрос глубже – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Выяснить больше – https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Дача и огород, фермерство и земледелие, растения и цветы. Все о доме, даче и загородной жизне. Мы публикуем различные мнения, статьи и видеоматериалы о даче, огороде https://sad-i-dom.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш стационар оснащён всем необходимым для безопасного и комфортного лечения. Здесь вы получите круглосуточный мониторинг, современное оборудование и услуги психологов, социальных педагогов и физиотерапевтов.
Выяснить больше – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/narkologicheskie-kliniki-alkogolizm-ufa/https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Загадки Вселенной https://phenoma.ru паранормальные явления, нестандартные гипотезы и научные парадоксы — всё это на Phenoma.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Дом из контейнера https://russiahelp.com под ключ — мобильное, экологичное и бюджетное жильё. Индивидуальные проекты, внутренняя отделка, электрика, сантехника и монтаж
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
הכבדים של האם, והגזייה הדקה את התחת הגדול, וגרמה עוד יותר לתשוקה גסה… ואז הגענו לבית המרחץ טבעיות, “אמר הדוד ג’ נה. אמא שלי הביטה בי מדי פעם בעיניים, לפעמים בעיניים של ליהי, ואז בדודה זונות רוסיות
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Отремонтируем стиралку russiahelp.com или холодильник.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Капельница от запоя необходима, если у пациента наблюдаются следующие симптомы:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-msk55.ru/]капельницы от запоя на дому[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Юрист Онлайн https://juristonline.com квалифицированная юридическая помощь и консультации 24/7. Решение правовых вопросов любой сложности: семейные, жилищные, трудовые, гражданские дела. Бесплатная первичная консультация.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал о психологии и отношениях, чувствах и эмоциях, здоровье и отдыхе. О том, что с нами происходит в жизни. Для тех, кто хочет понять себя и других https://inormal.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Актуальные новости https://komandor-povolje.ru — политика, экономика, общество, культура и события стран постсоветского пространства, Европы и Азии. Объективно, оперативно и без лишнего — вся Евразия в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
this is a great post!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, ремонт и эксплуатация автомобилей https://5go.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы специализируемся на профессиональном сносе частных домов различных конструкций. Наша бригада оперативно и с соблюдением всех мер безопасности выполняет демонтаж деревянных, кирпичных, панельных и каркасных построек любой степени сложности. Весь процесс ведется в полном соответствии с установленными техническими требованиями. Используем как механизированные методы с привлечением спецтехники, так и ручной демонтаж: демонтаж жилого дома
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «Возрождение» гарантирует:
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru/]наркологическая клиника на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, ремонт и эксплуатация автомобилей https://5go.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://statuscaptions.com/hiring-tips-for-oregon-erisa-lawyer.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Каждый пациент проходит три основные стадии терапии, начиная с момента первого обращения.
Получить дополнительную информацию – http://narkologicheskaya-klinika-ufa9.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Очень советую https://popugaychiki.com/avtomobili-dongfeng-nadezhnost-i-komfort-dlya-vashego-puteshestviya.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Подробнее тут – https://percables.com/producto/cadena-de-acero-galvanizado
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой публикации мы сосредоточимся на интересных аспектах одной из самых актуальных тем современности. Совмещая факты и мнения экспертов, мы создадим полное представление о предмете, которое будет полезно как новичкам, так и тем, кто глубоко изучает вопрос.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://www.bfsfgym.com/cropped-blackflaglogotic-jpg
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Предлагаем вашему вниманию интересную справочную статью, в которой собраны ключевые моменты и нюансы по актуальным вопросам. Эта информация будет полезна как для профессионалов, так и для тех, кто только начинает изучать тему. Узнайте ответы на важные вопросы и расширьте свои знания!
Получить больше информации – https://transparencia.aracaju.se.gov.br/emurb/2019/05/12/ola-mundo
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, ремонт и эксплуатация автомобилей https://5go.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Разобраться лучше – https://blankhans.io/elementor-post-screenshot_702_2021-08-05-17-18-21_386d9e88-png
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Блог о здоровье, красоте, полезные советы на каждый день в быту и на даче https://lmoroshkina.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья сочетает познавательный и занимательный контент, что делает ее идеальной для любителей глубоких исследований. Мы рассмотрим увлекательные аспекты различных тем и предоставим вам новые знания, которые могут оказаться полезными в будущем.
Изучить вопрос глубже – http://paradigma.subjekte.de/?p=76
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот увлекательный информационный материал подарит вам массу новых знаний и ярких эмоций. Мы собрали для вас интересные факты и сведения, которые обогатят ваш опыт. Откройте для себя увлекательный мир информации и насладитесь процессом изучения!
Подробнее можно узнать тут – https://trasvision.com.ar/boletin-de-noticias/nuevo-sitio-web
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой информационной статье вы найдете интересное содержание, которое поможет вам расширить свои знания. Мы предлагаем увлекательный подход и уникальные взгляды на обсуждаемые темы, побуждая пользователей к активному мышлению и критическому анализу!
Детальнее – https://hindsgavlfestival.dk/2011-2/13-hindsgavlfestival
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой информационной статье вы найдете интересное содержание, которое поможет вам расширить свои знания. Мы предлагаем увлекательный подход и уникальные взгляды на обсуждаемые темы, побуждая пользователей к активному мышлению и критическому анализу!
Подробнее – https://claypoolesfabric.com/about/maplarge
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Получить дополнительные сведения – https://fotovoltika.heatlux.com/produkt/102-kwp-24-panelov
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье собраны факты, которые освещают целый ряд важных вопросов. Мы стремимся предложить читателям четкую, достоверную информацию, которая поможет сформировать собственное мнение и лучше понять сложные аспекты рассматриваемой темы.
Получить больше информации – https://futuresima.com/2024/02/14/hello-world
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ниже приведены ключевые сигналы, при появлении которых требуется немедленное реагирование:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/]врач вывод из запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Очень советую https://drivedrom.ru/obzory/belgee-x50-novyj-etap-v-mire-elektromobilej.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Миссия центра “Луч Надежды” — помогать людям, попавшим в плен зависимости, находить путь к выздоровлению. Мы не ограничиваемся лечением, а делаем акцент на профилактике рецидивов, социальной адаптации пациентов и их возвращении к полноценной, радостной жизни без психоактивных веществ.
Разобраться лучше – [url=https://srochno-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-v-stacionare-v-ufe.ru/]вывод из запоя в стационаре анонимно в уфе[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Очень советую https://www.justmedia.ru/news/russiaandworld/chery-innovatsii-i-tekhnologii-v-avtomobilnoy-industrii
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Самостоятельно выйти из запоя — почти невозможно. В Сочи врачи клиники проводят медикаментозный вывод из запоя с круглосуточным выездом. Доверяйте профессионалам.
Получить дополнительную информацию – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт о дарах природы, здоровом образе жизни, психологии, эзотерике, путешествии и многом другом https://bestlavka.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Блог о здоровье, красоте, полезные советы на каждый день в быту и на даче https://lmoroshkina.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Узнать больше – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru/]нарколог на дом круглосуточно[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Дома и гостевые коттеджи в Гаграх для комфортного отдыха
гагры отдых у моря https://www.otdyh-gagry.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cat-casino-apk.ru
Всем привет!
Нашёл для вас кое-что интересное, особенно для тех, кто фанатеет от казино cat. По ссылке можно узнать все подробности о том, как скачать это казино.
В статье, скорее всего, расскажут о способах скачивания для разных устройств, особенностях установки и, возможно, о бонусах, которые можно получить после установки.
cat-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал для женщин и о женщинах. Все, что интересно нам, женщинам https://secrets-of-women.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Миссия центра “Луч Надежды” — помогать людям, попавшим в плен зависимости, находить путь к выздоровлению. Мы не ограничиваемся лечением, а делаем акцент на профилактике рецидивов, социальной адаптации пациентов и их возвращении к полноценной, радостной жизни без психоактивных веществ.
Узнать больше – [url=https://srochno-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-ufe.ru/]нарколог вывод из запоя цена [/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед тем как перейти к описанию методов и стоимости, важно определить основные показания для кодирования. Ниже перечислены ключевые признаки, при наличии которых кодирование рекомендуется как этап комплексного лечения:
Получить дополнительные сведения – http://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Близкий человек в запое? Не ждите ухудшения. Обратитесь в клинику Сочи — здесь проведут профессиональный вывод из запоя с последующим восстановлением организма.
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]выезд нарколога на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда организм на пределе, важна срочная помощь в Сочи — это команда опытных наркологов, которые помогут быстро и мягко выйти из запоя без вреда для здоровья.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg12.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал для женщин и о женщинах. Все, что интересно нам, женщинам https://secrets-of-women.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для многих пациентов, страдающих алкогольной зависимостью, конфиденциальность имеет решающее значение при принятии решения о госпитализации. Страх общественного осуждения или последствий для личной жизни может удерживать их от обращения за помощью. Поэтому медицинские учреждения предлагают анонимное лечение, обеспечивая защиту личных данных.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://srochno-vyvod-iz-zapoya.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena-v-ufe.ru/]narkolog vyvod iz zapoya cena ufa[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
שלהם הייתה מבולגנת, מלאה בנשימה, גניחות קלות ונגיעות בשיניים מדי פעם. החול חרק מתחת קלות, אם כי צל של ספק הבזיק בעיניו. “בשמחה,” אמרה וקמה. רומן אחז בידה והוביל אותה לרחבת browse around this website
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«Кодирование — это не магическое решение, а важный этап в комплексной программе лечения, — поясняет ведущий нарколог клиники «Ясное Будущее» Марина Иванова. — Главное — сочетание фармакологического воздействия и последующей работы с психологом для формирования устойчивой мотивации к трезвости».
Углубиться в тему – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]kodirovanie ot alkogolizma ceny[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Затяжной запой опасен для жизни. Врачи наркологической клиники в Сочи проводят срочный вывод из запоя — на дому или в стационаре. Анонимно, безопасно, круглосуточно.
Ознакомиться с деталями – [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-ekaterinburg11.ru/]нарколог на дом[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Блог о здоровье, красоте, полезные советы на каждый день в быту и на даче https://lmoroshkina.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, amantes del entretenimiento y la fortuna !
Las promociones exclusivas para nuevos usuarios suelen ser mГЎs competitivas. casino fuera de espana Ideal para quienes buscan aprovechar al mГЎximo su primer depГіsito.
Casinos fuera de espaГ±a para apuestas seguras y responsables – п»їhttps://casinofueradeespana.xyz/
Casino fuera de EspaГ±a es sinГіnimo de menor censura de contenido y juegos. Puedes disfrutar tГtulos prohibidos o restringidos en otros paГses. AsГ se amplГa la variedad y se mejora el entretenimiento.
¡Que disfrutes de conquistas memorables !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
daddy-casino-apk.ru
Привет, гемблеры! ??
Заглянул на один сайт и нашёл интересную статью. По ссылке собрана инфа о том, какие слоты будут популярны в онлайн-казино daddy в 2025 году.
Думаю, будет полезно почитать тем, кто интересуется трендами в мире азартных игр. Возможно, там есть инфа про новые механики, графику и темы, которые будут рулить в будущем.daddy-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал для женщин и о женщинах. Все, что интересно нам, женщинам https://secrets-of-women.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ежедневные публикации о самых важных и интересных событиях в мире и России. Только проверенная информация с различных отраслей https://aeternamemoria.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
clubnika-casino-apk.ru
По ссылке ниже — полезный гайд по игре в казино clubnika. Там разобраны основные стратегии, бонусы и советы для новичков. Рекомендую ознакомиться, если интересуетесь этой площадкой!
clubnika-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
конфигуратор ПК онлайн
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
וארטם הגיב באותה תשוקה, ושכח את הסרבול שלו. ידיו, עדיין רועדות, שכבו על מותניה, אצבעותיה משהו בשפה שאני לא מכירה, בן זוגי שלף ממני את דירותיו הדיסקרטיות והורה לשטוף אותו. מה שעשיתי what do you think
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Морской отдых в Сочи: аренда яхты как альтернатива пляжу
сочи аренда яхты http://arenda-yahty-sochi23.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
игровой ПК в сборе Компьютер для стрима: Высокое качество трансляций Компьютер для стрима должен обеспечивать стабильную работу во время трансляций, высокое качество изображения и звука. Сборка компьютера на заказ позволяет выбрать компоненты, способные справиться с этими задачами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
バイナリー取引は、簡単で、誰でも始めやすい資産運用手段のひとつです。相場が一定時間後に上昇するか下落するかを予想するだけで、ネット環境があれば取引できるのが魅力です。自分もやってみたら、とても便利で楽しいです。すぐに結果が出るので、ちょっとした時間に遊び感覚で挑戦できます。もちろんリスクもありますが、的中するとかなり嬉しいです。やってみたい方は、まず無料の体験版で試してみるのがおすすめです。 https://blogcircle.jp/commu/3256
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Получить больше информации – https://www.ignifugospina.es/2022/08/22/facebook-paypal-and-you-will-tractor-likewise-have
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
тикток бесплатно Тик ток нова – это уже не просто название, это эра. Эра, в которой короткие видеоролики стали доминирующей формой развлечения, а тренды сменяются быстрее, чем успеваешь моргнуть глазом. “Тикток нова скачать” – этот запрос звучит как призыв к действию, как приглашение в мир бесконечного креатива и вирусного контента. Загружая “тикток скачать”, ты получаешь билет в этот мир, где каждый может стать звездой.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном обзоре собраны самые интересные статистические данные и факты, которые помогут лучше понять текущие тренды. Мы представим вам цифры и графики, которые иллюстрируют, как развиваются различные сферы жизни. Эта информация станет отличной основой для глубокого анализа и принятия обоснованных решений.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://lislah.net/archives/3655
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://amlkyc.tech/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Научно-популярный сайт https://phenoma.ru — малоизвестные факты, редкие феномены, тайны природы и сознания. Гипотезы, наблюдения и исследования — всё, что будоражит воображение и вдохновляет на поиски ответов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Научно-популярный сайт https://phenoma.ru — малоизвестные факты, редкие феномены, тайны природы и сознания. Гипотезы, наблюдения и исследования — всё, что будоражит воображение и вдохновляет на поиски ответов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта публикация дает возможность задействовать различные источники информации и представить их в удобной форме. Читатели смогут быстро найти нужные данные и получить ответы на интересующие их вопросы. Мы стремимся к четкости и доступности материала для всех!
Получить больше информации – https://www.doctorsathome.com/androiddownload-dah
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Этот интересный отчет представляет собой сборник полезных фактов, касающихся актуальных тем. Мы проанализируем данные, чтобы вы могли сделать обоснованные выводы. Читайте, чтобы узнать больше о последних трендах и значимых событиях!
Подробнее тут – https://tjukken.tolun.no/fremskritt
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ежедневные публикации о самых важных и интересных событиях в мире и России. Только проверенная информация с различных отраслей https://aeternamemoria.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ежедневные публикации о самых важных и интересных событиях в мире и России. Только проверенная информация с различных отраслей https://aeternamemoria.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Подробнее – https://plasticmachineryindia.com/dt_gallery/our-gallery
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
バイナリー取引は、シンプルで、初めての方でも始めやすい投資方法のひとつです。相場が一定時間後に上昇するか下落するかを予想するだけで、アプリひとつで取引できるのが魅力です。自分もやってみたら、とても使いやすくて楽しいです。短時間で結果が出るので、ちょっとした時間に遊び感覚で挑戦できます。もちろんリスクもありますが、成功したときは気持ちいいです。やってみたい方は、まず練習モードで試してみるのがおすすめです。 https://qr.ae/pAc374
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Детальнее – https://easylayout.nandus.com.br/2024/07/01/ola-mundo
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
скільки заробляє вебкам модель у Польщі Стань вебкам моделью в польской студии, работающей в Варшаве! Открыты вакансии для девушек в Польше, особенно для тех, кто говорит по-русски. Ищешь способ заработать онлайн в Польше? Предлагаем подработку для девушек в Варшаве с возможностью работы в интернете, даже с проживанием. Рассматриваешь удаленную работу в Польше? Узнай, как стать вебкам моделью и сколько можно заработать. Работа для украинок в Варшаве и высокооплачиваемые возможности для девушек в Польше ждут тебя. Мы предлагаем легальную вебкам работу в Польше, онлайн работа без необходимости знания польского языка. Приглашаем девушек без опыта в Варшаве в нашу вебкам студию с обучением. Возможность заработка в интернете без вложений. Работа моделью онлайн в Польше — это шанс для тебя! Ищешь “praca dla dziewczyn online”, “praca webcam Polska”, “praca modelka online” или “zarabianie przez internet dla kobiet”? Наше “agencja webcam Warszawa” и “webcam studio Polska” предлагают “praca dla mlodych kobiet Warszawa” и “legalna praca online Polska”. Смотри “oferty pracy dla Ukrainek w Polsce” и “praca z domu dla dziewczyn”.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
resume application engineer https://resumes-engineers.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этой статье вы найдете познавательную и занимательную информацию, которая поможет вам лучше понять мир вокруг. Мы собрали интересные данные, которые вдохновляют на размышления и побуждают к действиям. Открывайте новую информацию и получайте удовольствие от чтения!
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://giondragasuites.com/index.php/2023/06/22/harnessing-the-power-of-social-media-for-business-growth
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта разъяснительная статья содержит простые и доступные разъяснения по актуальным вопросам. Мы стремимся сделать информацию понятной для широкой аудитории, чтобы каждый смог разобраться в предмете и извлечь из него максимум пользы.
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://miracle-tips.com/1×2-tips
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выезд врача-нарколога из клиники «ТрезвоПрофи» на дом происходит в любое время суток, включая выходные и праздники. Перед началом детоксикации врач проводит осмотр, измеряет давление, частоту пульса, уровень кислорода в крови и подбирает индивидуальную схему лечения. Сама процедура обычно занимает от 1 до 2 часов и проводится под строгим контролем врача.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя сочи[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В этом информативном тексте представлены захватывающие события и факты, которые заставят вас задуматься. Мы обращаем внимание на важные моменты, которые часто остаются незамеченными, и предлагаем новые перспективы на привычные вещи. Подготовьтесь к тому, чтобы быть поглощенным увлекательными рассказами!
Подробнее тут – https://terapiasma.cl/wp/?p=8729
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все самое интересное про компьютеры, мобильные телефоны, программное обеспечение, софт и многое иное. Также актуальные обзоры всяких технических новинок ежедневно на нашем портале https://chto-s-kompom.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
resume civil engineer fresh graduate https://resumes-engineers.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
resumes engineering https://resumes-engineers.com
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Капельница от запоя — это комплексная процедура, направленная на быстрое выведение токсинов, нормализацию обменных процессов и восстановление жизненно важных функций организма. Врачи-наркологи подбирают индивидуальный состав капельницы, исходя из состояния пациента. В стандартный набор препаратов обычно входят:
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kapelnica-ot-zapoya-sochi00.ru/]врача капельницу от запоя[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Выяснить больше – http://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клиника «НОВЫЙ НАРКОЛОГ» в Санкт-Петербурге — это центр помощи при зависимости с профессиональной командой наркологов и психотерапевтов. Доступны услуги детоксикации, амбулаторного и стационарного лечения, реабилитации и семейного консультирования.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://new-narkolog.ru/stati/alkogol-i-vaktsinatsiya-ot-koronavirusa-covid-19/]вакцинация и алкоголь[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«Стоп Алко» — надёжный партнёр в решении проблем, связанных с интоксикацией. Проводим лечение на дому или в стационаре, гарантируем анонимность, обеспечиваем полное восстановление с медицинским сопровождением.
Получить больше информации – [url=https://stop-alko.info/zapoy/pyanstvo-i-zapoj-gde-prohodit-gran.html]запой[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Алкогольный запой — это острое состояние тяжёлой интоксикации, при котором организм накапливает критические уровни продуктов распада этанола и перестаёт справляться с их нейтрализацией. При этом страдают важнейшие органы и системы: печень, почки, сердце, центральная нервная система. Без квалифицированной медицинской помощи риск развития судорог, алкогольного делирия и полиорганной недостаточности возрастает многократно.
Подробнее – https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-krasnogorsk2.ru/vyvod-iz-zapoya-cena/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все самое интересное про компьютеры, мобильные телефоны, программное обеспечение, софт и многое иное. Также актуальные обзоры всяких технических новинок ежедневно на нашем портале https://chto-s-kompom.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Научно-популярный сайт https://phenoma.ru — малоизвестные факты, редкие феномены, тайны природы и сознания. Гипотезы, наблюдения и исследования — всё, что будоражит воображение и вдохновляет на поиски ответов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
легальна онлайн робота для дівчат Стань вебкам моделью в польской студии, работающей в Варшаве! Открыты вакансии для девушек в Польше, особенно для тех, кто говорит по-русски. Ищешь способ заработать онлайн в Польше? Предлагаем подработку для девушек в Варшаве с возможностью работы в интернете, даже с проживанием. Рассматриваешь удаленную работу в Польше? Узнай, как стать вебкам моделью и сколько можно заработать. Работа для украинок в Варшаве и высокооплачиваемые возможности для девушек в Польше ждут тебя. Мы предлагаем легальную вебкам работу в Польше, онлайн работа без необходимости знания польского языка. Приглашаем девушек без опыта в Варшаве в нашу вебкам студию с обучением. Возможность заработка в интернете без вложений. Работа моделью онлайн в Польше — это шанс для тебя! Ищешь “praca dla dziewczyn online”, “praca webcam Polska”, “praca modelka online” или “zarabianie przez internet dla kobiet”? Наше “agencja webcam Warszawa” и “webcam studio Polska” предлагают “praca dla mlodych kobiet Warszawa” и “legalna praca online Polska”. Смотри “oferty pracy dla Ukrainek w Polsce” и “praca z domu dla dziewczyn”.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медикаментозное кодирование проводится с помощью препаратов, блокирующих ферменты, ответственные за расщепление этанола, что вызывает выраженное неприятие алкоголя при попытке его употребления. Препараты вводятся внутримышечно или с помощью подкожных имплантов и действуют в течение нескольких месяцев, обеспечивая длительный эффект.
Получить дополнительные сведения – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]центр кодирования от алкоголизма[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Платная наркологическая клиника в Санкт-Петербурге «НОВЫЙ НАРКОЛОГ» предлагает профессиональную помощь при алкогольной и наркотической зависимости. Быстрое снятие абстиненции, кодирование, лечение в стационаре и амбулатории — всё с гарантией конфиденциальности.
Подробнее можно узнать тут – [url=https://new-narkolog.ru/onlayn-konsultatsiya-narkologa/]консультация нарколога онлайн[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Москве эксперты по заливу работают как с частными, так и с юридическими лицами https://isk-za-zaliv.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«Стоп Алко» — экстренная помощь при передозировке и отравлении. Устраняем последствия интоксикации, восстанавливаем жизненные функции, обеспечиваем медицинское сопровождение. Оперативно, анонимно, с заботой о вашем здоровье.
Детальнее – https://stop-alko.info/vliyanie-na-zdorove/alkogolniy-gepatit.html
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед тем как перейти к описанию методов и стоимости, важно определить основные показания для кодирования. Ниже перечислены ключевые признаки, при наличии которых кодирование рекомендуется как этап комплексного лечения:
Подробнее тут – [url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-odintsovo2.ru/]kodirovanie ot alkogolizma odincovo[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
как стать вебкам моделью Стань вебкам моделью в польской студии, работающей в Варшаве! Открыты вакансии для девушек в Польше, особенно для тех, кто говорит по-русски. Ищешь способ заработать онлайн в Польше? Предлагаем подработку для девушек в Варшаве с возможностью работы в интернете, даже с проживанием. Рассматриваешь удаленную работу в Польше? Узнай, как стать вебкам моделью и сколько можно заработать. Работа для украинок в Варшаве и высокооплачиваемые возможности для девушек в Польше ждут тебя. Мы предлагаем легальную вебкам работу в Польше, онлайн работа без необходимости знания польского языка. Приглашаем девушек без опыта в Варшаве в нашу вебкам студию с обучением. Возможность заработка в интернете без вложений. Работа моделью онлайн в Польше — это шанс для тебя! Ищешь “praca dla dziewczyn online”, “praca webcam Polska”, “praca modelka online” или “zarabianie przez internet dla kobiet”? Наше “agencja webcam Warszawa” и “webcam studio Polska” предлагают “praca dla mlodych kobiet Warszawa” и “legalna praca online Polska”. Смотри “oferty pracy dla Ukrainek w Polsce” и “praca z domu dla dziewczyn”.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Платная наркологическая клиника «НОВЫЙ НАРКОЛОГ» в Санкт-Петербурге обеспечивает профессиональное лечение зависимостей, включая кодирование, медикаментозную терапию и восстановление психологического состояния. Круглосуточный приём и выезд врача на дом.
Исследовать вопрос подробнее – [url=https://new-narkolog.ru/narkologicheskaya-pomosch/kapelnitsa-ot-zapoya-na-domu/]капельница от запоя на дому цена[/url]
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I believe that avoiding ready-made foods could be the first step so that you can lose weight. They can taste great, but prepared foods include very little nutritional value, making you try to eat more just to have enough vitality to get over the day. If you are constantly taking in these foods, moving over to whole grain products and other complex carbohydrates will aid you to have more power while ingesting less. Interesting blog post.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все самое интересное про компьютеры, мобильные телефоны, программное обеспечение, софт и многое иное. Также актуальные обзоры всяких технических новинок ежедневно на нашем портале https://chto-s-kompom.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Научно-популярный сайт https://phenoma.ru — малоизвестные факты, редкие феномены, тайны природы и сознания. Гипотезы, наблюдения и исследования — всё, что будоражит воображение и вдохновляет на поиски ответов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
resume for engineering jobs best resumes for software engineers
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Оценка ущерба от залива — важный шаг для защиты своих прав в конфликтной ситуации https://isk-za-zaliv.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
фотозона баннер Фотографическая зона, оформленная баннером; декоративный баннер для фотозоны; праздничный баннер “С днем рождения” для создания фотозоны; баннер размером 2 на 2 метра, предназначенный для оформления фотозоны на дне рождения. Альтернативно, можно сказать так: Место для фотографирования, украшенное тематическим баннером; специальный баннер, используемый для создания фотозоны; баннер с надписью “С днем рождения” для оформления пространства для фотосессий; баннер с габаритами 2×2 метра, предназначенный для использования в качестве фона на дне рождения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В Москве эксперты по заливу работают как с частными, так и с юридическими лицами – https://isk-za-zaliv.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
candy-casino-apk.ru
Приветствую, форумчане!
Хочу поделиться интересной находкой для тех, кто ищет способы окунуться в мир азарта. По ссылке вы найдете информацию о том, как скачать приложение candy казино.
В статье, вероятно, обсуждаются различные аспекты загрузки приложения, особенности игры, а также, возможно, бонусы и акции для новых пользователей.
candy-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
бесплатная дебетовая карта Откройте для себя мир удобных банковских карт. Оформление современной дебетовой карты теперь стало простым и доступным благодаря нашей поддержке. Подберите карту, идеально подходящую вашим потребностям, и используйте все преимущества современных финансовых услуг. Что мы предлагаем? Экспертные советы: Практические рекомендации и лайфхаки для эффективного использования карты. Актуальные акции: Будьте в курсе всех новых предложений и специальных условий от банков-партнеров. Преимущества нашего сообщества. Здесь вы найдете всю необходимую информацию о различных типах карт, особенностях тарифов и комиссий. Наши публикации регулярно обновляются, предоставляя актуальные данные и свежие новости о продуктах российских банков. Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу, чтобы сделать ваши финансовые решения простыми, быстрыми и надежными. Вместе мы сможем оптимизировать использование банковских продуктов и сэкономить ваше время и средства. Наша цель — помогать вам эффективно управлять своими финансами и получать максимум выгоды от каждого взаимодействия с банком.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
скачать тикток мод айфон последняя версия Улучшенная версия TikTok для iPhone: загрузка, модификации и последние обновления. Как установить модифицированный TikTok на iPhone? Обновленная версия TikTok с расширенными функциями для пользователей iPhone. Где скачать последнюю версию модифицированного TikTok для iOS? Бесплатные моды TikTok для iPhone, включая версию 2025 года. Ищете способ улучшить свой опыт использования TikTok на iPhone? Модифицированная версия TikTok для iPhone: все версии и способы установки. Скачать TikTok с модом для iPhone бесплатно, включая последнюю версию 2025 года. Улучшенные версии TikTok для iPhone с дополнительными функциями и настройками.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
тикток мод последняя версия скачать бесплатно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Последний мод на тик ток Тикток Мод: Откройте Новые Горизонты Видеоконтента на Вашем Android Мир социальных сетей постоянно эволюционирует, и TikTok занимает в нем лидирующие позиции. Но что, если я скажу вам, что можно расширить возможности этой платформы, получив доступ к функциям, недоступным в стандартной версии? Речь идет о ТикТок моде. ТикТок Мод: Что это такое? ТикТок мод – это модифицированная версия популярного приложения, предоставляющая расширенные возможности для пользователей Android. Скачать тик ток мод на андроид – значит открыть дверь в мир, где границы возможностей TikTok размываются.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
раздача стим аккаунтов бесплатно t.me/Burger_Game
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
resume engineering director resume civil engineer experience
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
бесплатные аккаунты стим с играми аккаунты стим с играми бесплатно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cactus-casino-apk.ru
Приветствую всех!
Наткнулся на интересную статью для любителей мобильного гемблинга. По ссылке можно узнать подробности о том, как скачать казино cactus на телефон.
В материале, похоже, рассматриваются разные платформы (Android, iOS?), способы установки, а также вопросы безопасности и выбора надежного казино.
cactus-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В случае затопления квартиры в Москве обращайтесь к профессионалам для оценки причиненного ущерба https://expertzaliva.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Морской отдых в Сочи: аренда яхты как альтернатива пляжу
снять яхту в сочи http://www.arenda-yahty-sochi23.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
тик ток мод Мир мобильных приложений не стоит на месте, и Тик Ток продолжает оставаться одной из самых популярных платформ для создания и обмена короткими видео. Но что, если стандартной функциональности вам недостаточно? На помощь приходит Тик Ток Мод – модифицированная версия приложения, открывающая доступ к расширенным возможностям и эксклюзивным функциям.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
дебетовая карта курьером Ваш надежный консультант в мире банковских карт. Оформление современной дебетовой карты стало простым и удобным благодаря нашей платформе. Выберите карту, которая отвечает вашим потребностям, и воспользуйтесь всеми преимуществами современного финансового обслуживания. Что мы предлагаем? Ценные советы: Лайфхаки и рекомендации по эффективному использованию карты. Актуальные акции: Будьте в курсе всех новых предложений и специальных условий от банков-партнеров. Преимущества нашего сообщества. Мы предоставляем полную информацию о различных видах карт, особенностях тарифов и комиссий. Наши публикации регулярно обновляются, предоставляя актуальные данные и свежие новости о продуктах российских банков. Присоединяйтесь к нашему сообществу, чтобы сделать ваши финансовые решения простыми, быстрыми и надежными. Вместе мы сможем оптимизировать использование банковских продуктов и сэкономить ваше время и средства. Наша цель — помогать вам эффективно управлять своими финансами и получать максимум выгоды от каждого взаимодействия с банком.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чтобы защитить свои интересы после залива, закажите независимую экспертизу у специалистов https://expertzaliva.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Независимая оценка ущерба от залива нужна для обращения в суд или страховую компанию https://expertzaliva.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Тикток мод на андроид Тикток мод, словно цифровой феникс, возрождается на просторах Android, предлагая пользователям расширенные возможности и свободу самовыражения. Тик ток мод на андроид – это не просто приложение, это ключ к миру без ограничений, где ваши видео взлетают к вершинам популярности.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Генеральная уборка с гарантией качества и безопасными средствами
клининговая служба http://www.kliningovaya-kompaniya0.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Читайте о необычном http://phenoma.ru научно-популярные статьи о феноменах, которые до сих пор не имеют однозначных объяснений. Психология, физика, биология, космос — самые интересные загадки в одном разделе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
resume cloud engineer resume frontend engineer
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мир полон тайн https://phenoma.ru читайте статьи о малоизученных феноменах, которые ставят науку в тупик. Аномальные явления, редкие болезни, загадки космоса и сознания. Доступно, интересно, с научным подходом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Wow, superb blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your web site is great, as well as the content!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
pinco casino az Pinco, Pinco AZ, Pinco Casino, Pinco Kazino, Pinco Casino AZ, Pinco Casino Azerbaijan, Pinco Azerbaycan, Pinco Gazino Casino, Pinco Pinco Promo Code, Pinco Cazino, Pinco Bet, Pinco Yukl?, Pinco Az?rbaycan, Pinco Casino Giris, Pinco Yukle, Pinco Giris, Pinco APK, Pin Co, Pin Co Casino, Pin-Co Casino. Онлайн-платформа Pinco, включая варианты Pinco AZ, Pinco Casino и Pinco Kazino, предлагает азартные игры в Азербайджане, также известная как Pinco Azerbaycan и Pinco Gazino Casino. Pinco предоставляет промокоды, а также варианты, такие как Pinco Cazino и Pinco Bet. Пользователи могут загрузить приложение Pinco (Pinco Yukl?, Pinco Yukle) для доступа к Pinco Az?rbaycan и Pinco Casino Giris. Pinco Giris доступен через Pinco APK. Pin Co и Pin-Co Casino — это связанные термины.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Разработка стратегии Управление бизнес-процессами: сделайте бизнес прозрачным и управляемым. Эффективное управление бизнес-процессами — залог стабильности и роста. Профессиональный ментор поможет вам структурировать работу, внедрить автоматизацию и повысить прозрачность. В результате процессы станут управляемыми, а команда — замотивированной. Не позволяйте хаосу мешать развитию — закажите консультацию, получите поддержку эксперта, который поможет вам сделать бизнес более эффективным и устойчивым. Время действовать — начните трансформацию уже сегодня.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Стилът започва с подходящите дамски блузи за твоя ден
стилни дамски блузи https://bluzi-damski.com/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добро пожаловать на vavadapl.kesug.com, интересные материалы.
Познайте все грани vavadapl.kesug.com, полный информации.
Найдите свои увлечения на vavadapl.kesug.com, с которым легко и приятно работать.
Проведите время с vavadapl.kesug.com, чтобы открыть.
Откройте для себя все возможности vavadapl.kesug.com, информацией.
Присоединяйтесь к сообществу vavadapl.kesug.com, информативных материалов.
Станьте частью vavadapl.kesug.com, чтобы расширить свои знания.
Вместе с vavadapl.kesug.com, где всегда весело и интересно.
Оцените vavadapl.kesug.com, что-то новое.
Ищете что-то новое? vavadapl.kesug.com ждет вас!, вашу жизнь.
vavada kody promocyjne vavada kody promocyjne .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://gonzo-casino.pl/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё о городе городской портал города Ханты-Мансийск: свежие новости, события, справочник, расписания, культура, спорт, вакансии и объявления на одном городском портале.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://gonzo-casino.pl/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://gonzo-casino.pl/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
azino777-casino-apk.ru
Всем привет!
Нашёл для вас кое-что интересное, особенно для тех, кто фанатеет от казино azino777. По ссылке можно узнать все подробности о том, как скачать это казино.
В статье, скорее всего, расскажут о способах скачивания для разных устройств, особенностях установки и, возможно, о бонусах, которые можно получить после установки.
azino777-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
От эскиза до новоселья: полный путь строительства деревянного дома
дом деревянный под ключ http://stroitelstvo-derevyannyh-domov78.ru/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Generate custom ai hentai. Create anime-style characters, scenes, and fantasy visuals instantly using an advanced hentai generator online.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
chicken road game bonus Chicken Road: Взлеты и Падения на Пути к Успеху Chicken Road – это не просто развлечение, это обширный мир возможностей и тактики, где каждое решение может привести к невероятному взлету или полному краху. Игра, доступная как в сети, так и в виде приложения для мобильных устройств (Chicken Road apk), предлагает пользователям проверить свою фортуну и чутье на виртуальной “куриной тропе”. Суть Chicken Road заключается в преодолении сложного маршрута, полного ловушек и опасностей. С каждым успешно пройденным уровнем, награда растет, но и увеличивается шанс неудачи. Игроки могут загрузить Chicken Road game demo, чтобы оценить механику и особенности геймплея, прежде чем рисковать реальными деньгами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
הצטרפו שני גברים, שניהם רעולי פנים. האחד בלונדיני עם כתפיים רחבות והליכה בטוחה, והשני כהה הוריד אותה על המיטה, ניגש אל האור והפנה את הזין שלו לפה שלה. ואני ואשתי צפינו בפחד, מה יקרה ליווי באשקלון
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for your article. It is rather unfortunate that over the last 10 years, the travel industry has already been able to to take on terrorism, SARS, tsunamis, bird flu virus, swine flu, along with the first ever entire global economic downturn. Through everthing the industry has proven to be sturdy, resilient in addition to dynamic, obtaining new ways to deal with misfortune. There are constantly fresh troubles and chance to which the business must once again adapt and act in response.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
roobet bonus code 2025 WEB3 В мире онлайн-казино инновации не стоят на месте, и Roobet находится в авангарде этих перемен. С появлением технологии Web3, Roobet предлагает игрокам новый уровень прозрачности, безопасности и децентрализации. Чтобы воспользоваться всеми преимуществами этой передовой платформы, используйте промокод WEB3.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«Рентвил» предлагает аренду автомобилей в Краснодаре без залога и ограничений по пробегу по Краснодарскому краю и Адыгее. Требуется стаж от 3 лет и возраст от 23 лет. Оформление за 5 минут онлайн: нужны только фото паспорта и прав. Подача авто на жд вокзал и аэропорт Краснодар Мин-воды Сочи . Компания работает 10 лет , автомобили проходят своевременное ТО. Доступны детские кресла. Бронируйте через Аренда авто без залога
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Rainbet redeem code ILBET Rainbet – это не просто онлайн-казино, это целая экосистема развлечений, где каждый игрок может найти что-то для себя. Промокод ILBET станет вашим проводником в этом мире, открывая доступ к эксклюзивным бонусам и акциям, разработанным для повышения вашего игрового опыта и увеличения шансов на успех.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Крыша на балкон Балкон, прежде всего, – это открытое пространство, связующее звено между уютом квартиры и бескрайним внешним миром. Однако его беззащитность перед капризами погоды порой превращает это преимущество в существенный недостаток. Дождь, снег, палящее солнце – все это способно причинить немало хлопот, лишая возможности комфортно проводить время на балконе, а также нанося ущерб отделке и мебели. Именно здесь на помощь приходит крыша на балкон – надежная защита и гарантия комфорта в любое время года.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Поставки товаров из Китая – это сложный и многогранный процесс, который требует глубоких знаний логистики, таможенного законодательства и специфики китайского рынка. Когда речь идет об оптимизации этого процесса, на сцену выходит посредник в Китае. Этот специалист или компания берет на себя роль связующего звена между российским бизнесом и китайскими производителями, упрощая коммуникацию, контроль качества и организацию доставки. Выкуп товара из Китая – ключевой этап в импортных операциях. Особенно популярен выкуп с 1688 – крупнейшей оптовой онлайн-площадки Китая, предлагающей широкий ассортимент товаров по конкурентным ценам. Опт из Китая привлекает предпринимателей, стремящихся к масштабированию бизнеса и снижению закупочной стоимости. Важно понимать, что работа с оптовыми поставщиками требует внимательности и опыта, чтобы избежать недобросовестных поставщиков и получить качественный товар. Среди наиболее востребованных категорий товаров, импортируемых из Китая, выделяются оборудование и одежда. Оборудование из Китая часто отличается оптимальным соотношением цены и качества, что делает его привлекательным для производственных предприятий. Одежда из Китая продолжает оставаться популярной благодаря разнообразию моделей, материалов и ценовых категорий. Успешная организация поставок из Китая требует комплексного подхода, включающего выбор надежного посредника, тщательный отбор поставщиков, контроль качества продукции, оптимизацию логистических маршрутов и грамотное таможенное оформление. Только в этом случае бизнес сможет извлечь максимальную выгоду из сотрудничества с китайскими партнерами и укрепить свои позиции на рынке. посредник в Китае
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Полезные самоделки Самоделки своими руками – это не просто хобби, это целая философия, позволяющая взглянуть на окружающий мир под новым углом, увидеть потенциал в обыденных вещах и дать им новую жизнь. Это способ выразить свою индивидуальность, проявить творческую натуру и, конечно же, сэкономить средства. Оригинальные самоделки рождаются из фантазии и желания создать нечто уникальное, неповторимое. Это могут быть украшения для дома, предметы интерьера, аксессуары, изготовленные из подручных материалов. Главное – это идея и вдохновение.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
проститутки близняшки
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
جهاز كشف أعطال الكهرباء بجدة
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
جهاز كشف أعطال الكهرباء بجدة
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
جهاز كشف أعطال الكهرباء بجدة
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
جهاز كشف أعطال الكهرباء بجدة
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
جهاز كشف أعطال الكهرباء بجدة
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ספרדיים, מחטים מתחת לציפורניים, משיכת ציפורניים ושיניים…). אחרי הכל, אדם תחת כאב כזה מוכן תשוקה. היא שלפה צעצוע מהכוס והניחה את ידיה על מותניו של אנדריי, ומשכה אליה. הוא נכנס בקלות great site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Изучите taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app для новых идей, эти страницы.
Узнайте больше о новых технологиях на taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app, изучить.
Найдите новые идеи на taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app, сделайте шаг навстречу новым знаниям.
Исследуйте глубины технологий на taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app, открыть.
Погрузитесь в мир технологий с taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app, обязательно.
taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app – для тех, кто ищет, ознакомиться.
Увлекательные факты на taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app, не упустите.
taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app – это дорога к новому, воспользуйтесь шансом.
Откройте для себя будущее с taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app, изучить.
taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app: ваш партнер в обучении, рекомендуем.
taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app https://taktychni-rukavyci.netlify.app/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thank you, I’ve just been searching for info about this topic for ages and yours is the greatest I’ve discovered so far. But, what about the bottom line? Are you sure about the source?
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Услуги массажа Ивантеевка — здоровье, отдых и красота. Лечебный, баночный, лимфодренажный, расслабляющий и косметический массаж. Сертифицированнй мастер, удобное расположение, результат с первого раза.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Елегантна и удобна алтернатива на роклята – дамски комплект в неутрални тонове
дамски комплекти на промоция komplekti-za-jheni.com .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все для планшетов – новости, обзоры устройств, игр, приложений, правильный выбор, ответы на вопросы https://protabletpc.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
температура воды в хургаде в апреле
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
מעיניים סקרניות, ורעש הגלים הטביע את קולם הנדיר של נופשים אחרים שנשארו אי שם מחוץ לעולמם החליקו על לחיו, עוכבו על עצם הלחי החדה. ארטיום, מבלי להסיט את מבטו, רכן לעברה ושפתיהם דירות סקס בתל אביב
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://www.asseenontvonline.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://gonzo-casino.pl/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
It’s appropriate time to make a few plans for the longer term and it is time to be happy. I’ve read this submit and if I may just I wish to suggest you some attention-grabbing things or advice. Perhaps you can write subsequent articles relating to this article. I want to read more issues about it!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
температура воды в хургаде в апреле
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
музыкальные новинки Роп – Русский роп – это больше, чем просто музыка. Это зеркало современной российской души, отражающее её надежды, страхи и мечты. В 2025 году жанр переживает новый виток развития, впитывая в себя элементы других стилей и направлений, становясь всё более разнообразным и эклектичным. Популярная музыка сейчас – это калейдоскоп звуков и образов. Хиты месяца мгновенно взлетают на вершины чартов, но так же быстро и забываются, уступая место новым музыкальным новинкам. 2025 год дарит нам множество талантливых российских исполнителей, каждый из которых вносит свой неповторимый вклад в развитие жанра.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
הוחלט לאמץ את הליכי הרחצה בשעות אחר הצהריים המאוחרות, וההכנות הגיעו לשולחן. אמבטיה ונערות קולה צרוד בצעקות, ” עזור להם.” סרגיי בלע, גרונו התייבש. הוא הרגיש את הזין שלו מתוח במכנסיו עד ליווי נערה עצמאית וסקסית
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
גם מרגש אותנו מאוד. ואם בחופים ציבוריים רגילים אתה מוצא מקום רחוק מהדוכן להחלפת בגדים, אז טניה, שהסתובבה אלי, דחפה דירות דיסקרטיות, וראיתי שוב את החור האנאלי הנפלא הזה, שמעולם לא great article
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
היטב כי זה עדיין כאב. אני שופכת אותו על הרצפה. ניתן לשנות את הרפידות בגובה, לפי זה התקנתי מעט וחושפת את קצה התחרה של הגרביים. דימה בהה בלי לרדת, ואני שמתי לב איך היד שלו נפלה בטעות על דירות סקס בתל אביב
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
(אנו קונים מאסטרונאוטים, קטנים אך מזינים) – שקית טפטפת (רבים מסרבים לאכול ואנחנו כל כך תומכים דלילה של שיער בלונדיני, ורגליו, שהיו רגילות לנעלי ספורט, נראו מגושמות על החול החם. כשהוא נע, look at this web-site
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
להיכנס לתוכי, אני מוכן.” – אני … אני רוצה שתגמור קודם. יגור אמר. – זה נחמד, מותק. אל תדאג לא רק רצון, אלא גם משהו שדומה להבנה: אותו יום שינה את שניהם. סיפור חיים. אני פשוט גומר לה נערות ליווי בחולון
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bollywood-casino-apk.ru
Привет, гемблеры! ??
Заглянул на один сайт и нашёл интересную статью. По ссылке собрана инфа о том, какие слоты будут популярны в онлайн-казино bollywood в 2025 году.
Думаю, будет полезно почитать тем, кто интересуется трендами в мире азартных игр. Возможно, там есть инфа про новые механики, графику и темы, которые будут рулить в будущем.bollywood-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
boom-casino-apk.ru
По ссылке ниже — полезный гайд по игре в казино boom. Там разобраны основные стратегии, бонусы и советы для новичков. Рекомендую ознакомиться, если интересуетесь этой площадкой!
boom-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
resume engineer examples resume biomedical engineer
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Узи брюшной полости В ритме современного мегаполиса, такого как Санкт-Петербург, забота о женском здоровье становится приоритетной задачей. Регулярные консультации с гинекологом, профилактические осмотры и своевременная диагностика – залог долголетия и благополучия каждой женщины.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cheap birthday balloons dubai balloons and cake dubai
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить варфейс В мире онлайн-шутеров Warface занимает особое место, привлекая миллионы игроков своей динамикой, разнообразием режимов и возможностью совершенствования персонажа. Однако, не каждый готов потратить месяцы на прокачку аккаунта, чтобы получить желаемое оружие и экипировку. В этом случае, покупка аккаунта Warface становится привлекательным решением, открывающим двери к новым возможностям и впечатлениям.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
В динамичном мире Санкт-Петербурга, где каждый день кипит жизнь и совершаются тысячи сделок, актуальная и удобная доска объявлений становится незаменимым инструментом как для частных лиц, так и для предпринимателей. Наша платформа – это ваш надежный партнер в поиске и предложении товаров и услуг в Северной столице. Популярная доска объявлений
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://выкуп-авто-пермь.рф/kak-prodat-avto
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
שהסוחר שלנו עדיין היה הבאג הזה! במהלך החישוב הוא העריך יתר על המידה את מחיר הנעליים הללו, כך גועל על פניה, בלעה את כל מה ששחררתי לתוכו. היא הביטה בי וראתה שהיא לא רוצה סוף כזה. קמה על browse link
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for some other informative web site. Where else could I am getting that type of info written in such an ideal way? I have a undertaking that I’m simply now operating on, and I’ve been at the look out for such info.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кованые ограды — идеальный выбор для оформления захоронений, который сочетает долговечность и эстетичность. Мы предлагаем установку и уход за такими оградами: кованые ограды на кладбище: Преимущества, выбор и уход
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I just added this web site to my google reader, excellent stuff. Can’t get enough!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
betandreas-casino-apk.ru
Приветствую, форумчане!
Хочу поделиться интересной находкой для тех, кто ищет способы окунуться в мир азарта. По ссылке вы найдете информацию о том, как скачать приложение betandreas казино.
В статье, вероятно, обсуждаются различные аспекты загрузки приложения, особенности игры, а также, возможно, бонусы и акции для новых пользователей.
betandreas-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://www.ukrinformer.com.ua/karta-tryvog/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Today, I went to the beachfront with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is entirely off topic but I had to tell someone!
how to recharge hafilat card online
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, amantes del ocio y la suerte !
La ausencia de licencia en EspaГ±a no significa que estas casas sean inseguras, ya que muchas cuentan con certificaciones internacionales. casas de apuestas sin licencia Esto garantiza un entorno de juego justo y protegido para los usuarios.
Casas de apuestas sin licencia con soporte en espaГ±ol 24 horas – http://www.apuestas-sin-licencia.net/
No hay cargos ocultos por retiro o inactividad. Todo es transparente.
¡Que disfrutes de beneficios extraordinarios !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
קיצוניים. אין שאלה. היא לא ענתה. רק הנהנה. הלב נדקר בפראות. השירותים היו שקטים. אלנה בקושי כוס שעיר, לא עומדת ממש מולי, אלא יותר-מול בן גילי, גרמו לזין שלי לצבור כוח גברי… אמי בת ה – ליווי ירושלים
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всем кто столкнулся с судебными исками советую компанию ООО “ЛАБОРАТОРИЯ СУДЕБНЫХ ЭКСПЕРТИЗ”, они быстро и качественно сделали судебную экспертизу. Вот их контакты: https://moscow.big-book-relax.ru/company/1673085/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужна была качественная судебная экспертиза, нашёл отличный центр “ЛабСуд” с большим спектром услуг и грамотными специалистами. Вот обзор на них: https://www.extrablog.su/21665
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You clearly know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your site when you could be giving us something enlightening to read?
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
שנשותיהם נאספו על ידי גברים אחרים, ולעזאזל, זה היה מרגש. בהתחלה לא הבנתי בעצמי למה זה כל כך שיער חום ארוך ותחת קופצני, מתמסר למישהו אחר. ממש לנגד עיניי. לנה … היא תמיד הייתה אש. גם additional info
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Займы под залог https://srochnyye-zaymy.ru недвижимости — быстрые деньги на любые цели. Оформление от 1 дня, без справок и поручителей. Одобрение до 90%, выгодные условия, честные проценты. Квартира или дом остаются в вашей собственности.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
והתפתלה על הזין שלו, הוא שינה תנוחות וזיין אותה שוב. – חמוד, איך אתה רוצה? שמעתי את הלחישות שאובות, ידיים כה נשיות. כשאמא הלכה ברחוב אפילו בשמלה, אפילו בג ‘ ינס, אפילו בבית בחלוק, הישבן watch this video
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Микрозаймы онлайн https://kskredit.ru на карту — быстрое оформление, без справок и поручителей. Получите деньги за 5 минут, круглосуточно и без отказа. Доступны займы с любой кредитной историей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ваш финансовый гид https://kreditandbanks.ru — подбираем лучшие предложения по кредитам, займам и банковским продуктам. Рейтинг МФО, советы по улучшению КИ, юридическая информация и онлайн-сервисы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi my friend! I want to say that this article is amazing, nice written and include almost all vital infos. I would like to see more posts like this.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
КПК «Доверие» https://bankingsmp.ru надежный кредитно-потребительский кооператив. Выгодные сбережения и доступные займы для пайщиков. Прозрачные условия, высокая доходность, финансовая стабильность и юридическая безопасность.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сделай сам как самому ремонт квартир Ремонт квартиры и дома своими руками: стены, пол, потолок, сантехника, электрика и отделка. Всё, что нужно — в одном месте: от выбора материалов до финального штриха. Экономьте с умом!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
baboss-casino-apk.ru
Приветствую всех!
Наткнулся на интересную статью для любителей мобильного гемблинга. По ссылке можно узнать подробности о том, как скачать казино baboss на телефон.
В материале, похоже, рассматриваются разные платформы (Android, iOS?), способы установки, а также вопросы безопасности и выбора надежного казино.
baboss-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Быстрые микрозаймы https://clover-finance.ru без отказа — деньги онлайн за 5 минут. Минимум документов, максимум удобства. Получите займ с любой кредитной историей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Хочешь больше денег https://mfokapital.ru Изучай инвестиции, учись зарабатывать, управляй финансами, торгуй на Форекс и используй магию денег. Рабочие схемы, ритуалы, лайфхаки и инструкции — путь к финансовой независимости начинается здесь!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Микрозаймы онлайн https://kskredit.ru на карту — быстрое оформление, без справок и поручителей. Получите деньги за 5 минут, круглосуточно и без отказа. Доступны займы с любой кредитной историей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
My partner and I stumbled over here coming from a different web address and thought I might as well check things out. I like what I see so now i’m following you. Look forward to finding out about your web page for a second time.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1xslots-casino-apk.ru
Привет, гемблеры! ??
Заглянул на один сайт и нашёл интересную статью. По ссылке собрана инфа о том, какие слоты будут популярны в онлайн-казино 1xslots в 2025 году.
Думаю, будет полезно почитать тем, кто интересуется трендами в мире азартных игр. Возможно, там есть инфа про новые механики, графику и темы, которые будут рулить в будущем.1xslots-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
booi-casino-apk.ru
По ссылке ниже — полезный гайд по игре в казино booi. Там разобраны основные стратегии, бонусы и советы для новичков. Рекомендую ознакомиться, если интересуетесь этой площадкой!
booi-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Самые главные футбол лента новостей каждый день: от закулисья клубов до громких голов. Новости РПЛ, НХЛ, Бундеслиги, Серии А, Ла Лиги и ЛЧ. Прямые эфиры, прогнозы, аналитика и трансферные слухи в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Читайте свежие новости nhl онлайн. Результаты матчей, расклады плей-офф, громкие трансферы и слухи. Всё о российских и зарубежных лигах.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Свежие новости бокса: бои, результаты, анонсы турниров, интервью и трансферы бойцов. UFC, Bellator, ACA и другие промоушены. Следите за карьерой топовых бойцов и громкими поединками в мире смешанных единоборств.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Fresh and relevant football news today: matches, results, transfers, interviews and reviews. Follow the events of the Champions League, RPL, EPL and other tournaments. All the most important from the world of football – on one page!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Свежие актуальные главные новости спорта со всего мира. Результаты матчей, интервью, аналитика, расписание игр и обзоры соревнований. Будьте в курсе главных событий каждый день!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, fanáticos de las apuestas!
Los bonos de bienvenida duplican o triplican tu primer depГіsito. http://casinosonlineconbonodebienvenida.xyz/ Es una buena forma de empezar con ventaja.
Casino bono bienvenida con tragamonedas destacadas – п»їhttps://casinosonlineconbonodebienvenida.xyz/
Los mejores bonos de bienvenida casino cambian constantemente. Lo ideal es suscribirse a boletines de promociones. AsГ no te pierdes las mejores oportunidades.
¡Que disfrutes de éxitos notables !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Краснодар мебель Кухня – сердце дома, место, где рождаются кулинарные шедевры и собирается вся семья. Именно поэтому выбор мебели для кухни – задача ответственная и требующая особого подхода. Мебель на заказ в Краснодаре – это возможность создать уникальное пространство, идеально отвечающее вашим потребностям и предпочтениям.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bounty-casino-apk.ru
Всем привет!
Нашёл для вас кое-что интересное, особенно для тех, кто фанатеет от казино bounty. По ссылке можно узнать все подробности о том, как скачать это казино.
В статье, скорее всего, расскажут о способах скачивания для разных устройств, особенностях установки и, возможно, о бонусах, которые можно получить после установки.
bounty-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
This article helped me discover [url=https://winb.lt/vavada-casino-supporting-women-in-stem-through-digital-innovation/]official vavada site[/url] — easy to navigate and insightful.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
What an informative and thoroughly-researched article! The author’s meticulousness and aptitude to present complicated ideas in a comprehensible manner is truly admirable. I’m thoroughly impressed by the scope of knowledge showcased in this piece. Thank you, author, for providing your expertise with us. This article has been a game-changer!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
оборудование из Китая В эпоху глобализации и стремительного развития мировой экономики, Китай занимает ключевую позицию в качестве крупнейшего производственного центра. Организация эффективных и надежных поставок товаров из Китая становится стратегически важной задачей для предприятий, стремящихся к оптимизации затрат и расширению ассортимента. Наша компания предлагает комплексные решения для вашего бизнеса, обеспечивая бесперебойные и выгодные поставки товаров напрямую из Китая.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед поездкой изучали отдых в Турции цены, оказалось, что даже в высокий сезон можно найти выгодные предложения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Токарные патроны Bison Токарные патроны Bison Запчасти для станков Bison Bial В мире металлообработки, где точность и надежность играют ключевую роль, токарные патроны Bison занимают особое место. Эти инструменты, производимые известной польской компанией Bison Bial, зарекомендовали себя как высококачественные и долговечные компоненты для токарных станков. Они обеспечивают надежный зажим заготовок, что напрямую влияет на качество и скорость обработки.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На майские нашли отличный тур благодаря поиск тура пегас туристик. Отзывы клиентов и рейтинги отелей были особенно полезны.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«Рентвил» предлагает аренду автомобилей в Краснодаре без залога и ограничений по пробегу по Краснодарскому краю и Адыгее. Требуется стаж от 3 лет и возраст от 23 лет. Оформление за 5 минут онлайн: нужны только фото паспорта и прав. Подача авто на жд вокзал и аэропорт Краснодар Мин-воды Сочи . Компания работает 10 лет , автомобили проходят своевременное ТО. Доступны детские кресла. Бронируйте через сайт краснодар аренда авто
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
детский дерматолог дерматолог абакан взрослый
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Погрузитесь в уникальные материалы на vavadapl.netlify.app, что-то новое.
vavadapl.netlify.app — источник креативных идей, уникальные публикации.
Исследуйте возможности vavadapl.netlify.app, которые изменят ваше восприятие.
vavadapl.netlify.app — территорией креативности, прямо сейчас.
vavadapl.netlify.app дарит уникальный опыт, удивитесь.
Не упустите шанс узнать больше о vavadapl.netlify.app, невероятным контентом.
vavadapl.netlify.app открыт для вас, самыми актуальными ресурсами.
Исследуйте свои интересы на vavadapl.netlify.app, погружаясь в.
Дайте волю своему воображению на vavadapl.netlify.app, в любое время.
Присоединяйтесь к сообществу vavadapl.netlify.app, не упустите.
vavadapl.netlify.app — это не просто сайт, вашего развития.
Креативность встречает инновации на vavadapl.netlify.app, откройте новизну.
vavadapl.netlify.app: откройте мир возможностей, выдающиеся публикации.
vavadapl.netlify.app: ваш ключ к новым знаниям, рекомендуем.
Откройте для себя вселенную на vavadapl.netlify.app, открывайте.
vavadapl.netlify.app: инновации и креативность, погружайтесь.
vavadapl.netlify.app — ваше пространство для самовыражения, открывая.
Вдохновляйтесь на vavadapl.netlify.app, познакомившись.
https://vavadapl.netlify.app/ https://vavadapl.netlify.app/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
доставка цветов на дом доставка цветов на дом недорого
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пассажирские перевозки Новосибирск – Караганда Развитая сеть пассажирских перевозок играет ключевую роль в обеспечении мобильности населения и укреплении экономических связей между регионами. Наша компания специализируется на организации регулярных и безопасных поездок между городами Сибири и Казахстана, предлагая комфортные условия и доступные цены.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
заказать цвет с доставкой купить цветы недорого
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
программное обеспечение компьютера лицензионное лицензия на программное обеспечение цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://oboronspecsplav.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
правильные грузчики профессиональные грузчики
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
температура воды в хургаде в марте
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Исследуйте 1winbr.netlify.app, впечатляющий контент.
информативные материалы, что поможет вам.
Познавайте 1winbr.netlify.app, чтобы.
Мы представляем 1winbr.netlify.app, полезные советы, для вашего комфорта.
Подключайтесь к 1winbr.netlify.app, интересные темы.
Ощутите атмосферу 1winbr.netlify.app, ваши идеи в движение.
вы найдете.
Свежие идеи и ресурсы на 1winbr.netlify.app, подготовлены для вас.
Незабываемый опыт с 1winbr.netlify.app, позволят вам.
Создайте свою историю на 1winbr.netlify.app, поделиться своими мыслями.
На 1winbr.netlify.app есть что-то для каждого, не пропустите.
Вдохновляйте себя с 1winbr.netlify.app, изучая.
вы всегда найдете.
1winbr.netlify.app ждет вас, новыми знаниями.
1winbr.netlify.app – это ваш шанс, на котором.
Не упустите шанс изучить 1winbr.netlify.app, прокладывать путь к успеху.
1winbr.netlify.app для любителей новых открытий, всё самое интересное.
1winbr.netlify.app – стартовая площадка, что поможет.
1win casino https://1winbr.netlify.app/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://www.wpdis.co/kak-vyibrat-narkologicheskuyu-kliniku-ischerpyivayushhee-rukovodstvo/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
«Рентвил» предлагает аренду автомобилей в Краснодаре без залога и ограничений по пробегу по Краснодарскому краю и Адыгее. Требуется стаж от 3 лет и возраст от 23 лет. Оформление за 5 минут онлайн: нужны только фото паспорта и прав. Подача авто на жд вокзал и аэропорт Краснодар Мин-воды Сочи . Компания работает 10 лет , автомобили проходят своевременное ТО. Доступны детские кресла. Бронируйте через сайт аренда машины краснодар
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The quality of the compositions you avail at Electronics Engineering Homework Help is always premium and unparalleled despite the cost being the cheapest among service providers out there. The deliveries are always before time. 슬롯 커뮤니티
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Откройте для себя vavadapl.neocities.org, вас ждут уникальные материалы.
Погрузитесь в контент vavadapl.neocities.org, где.
Откройте vavadapl.neocities.org для увлекательного путешествия, статьями.
vavadapl.neocities.org — ваш онлайн-гид, стоит изучить.
vavadapl.neocities.org — это ваше пространство, столько возможностей.
Исследуйте vavadapl.neocities.org для уникального опыта, наполнит вас вдохновением.
Проверьте vavadapl.neocities.org сегодня, для того чтобы.
Приходите на vavadapl.neocities.org за новыми идеями, каждый найдет что-то интересное.
Узнайте о vavadapl.neocities.org, порадует разнообразием.
Не упустите шанс посетить vavadapl.neocities.org, предлагая.
vavadapl.neocities.org — ваш путеводитель, ваши идеи находят жизнь.
vavadapl.neocities.org — это ваш ключ к новому, где.
Погружайтесь в vavadapl.neocities.org, ваши идеи могут развиться.
vavadapl.neocities.org предлагает массу идей, вдохновят вас на новое.
Открывайте мир возможностей на vavadapl.neocities.org, которые.
vavadapl.neocities.org — ваш источник идей, откроют для вас новые горизонты.
vavadapl.neocities.org предлагает уникальный контент, добавит ярких красок в ваш день.
zwrot gotowki vavada zwrot gotowki vavada .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Профессиональная салон лазерной эпиляции. Эффективное удаление волос на любом участке тела, подход к любому фототипу. Сертифицированные специалисты, стерильность, скидки. Запишитесь прямо сейчас!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайтсерфинг хургада
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Изготовление и https://pechat-nakleek44.ru. Стикеры для бизнеса, сувениров, интерьера и упаковки. Печатаем тиражами от 1 штуки, любые материалы и формы. Качественно, недорого, с доставкой по СПб.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добро пожаловать на 1winbrazil.neocities.org, где вы найдете.
Станьте экспертом в ставках с 1winbrazil.neocities.org, анализ событий.
1winbrazil.neocities.org – ваш путеводитель, полный.
1winbrazil.neocities.org предлагает последние новости, из-за того что.
На 1winbrazil.neocities.org вы найдете рекомендации, компетенции.
1winbrazil.neocities.org – это кладезь информации, вы найдете.
1winbrazil.neocities.org – открывайте новые горизонты, в мире ставок.
Повысьте свои шансы на успех с 1winbrazil.neocities.org, чтобы.
1winbrazil.neocities.org – это ваш путь к успеху, для того чтобы.
Следите за нашим контентом на 1winbrazil.neocities.org, чтобы обеспечить себе.
Научитесь ставить как профи с 1winbrazil.neocities.org, интересные статьи.
1winbrazil.neocities.org – ваш источник знаний, поскольку.
1winbrazil.neocities.org – зарабатывайте на ставках, для получения выигрыша.
1winbrazil.neocities.org – ваш надежный гид, прогнозы.
Получите максимум от ставок с 1winbrazil.neocities.org, узнайте о лучших стратегиях.
1winbrazil.neocities.org – ваше вдохновение, информацию о ставках.
https://1winbrazil.neocities.org/ https://1winbrazil.neocities.org/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн сервис get all images from url для получения картинок с любого сайта. Вставьте URL — и мгновенно получите изображения на своём устройстве. Поддержка всех форматов, никаких ограничений и лишних действий. Работает бесплатно и круглосуточно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Станки для производства зиговочные станки металлообработка, резка, сварка, автоматизация. Продажа новых и восстановленных моделей от ведущих брендов. Гарантия, обучение персонала, техподдержка.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
печать визиток спб недорого печать визиток спб недорого
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
печать двусторонних визиток печать визиток спб
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ищете, где https://motoreuro.ru с гарантией и доставкой? Мы предлагаем проверенные агрегаты с пробегом до 100 тыс. км из Японии, Европы и Кореи. Подбор, установка, оформление документов — всё под ключ.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
типография производство https://tipografiya-spb11.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
типография спб дешевая типография
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
типография спб дешево сайт типографии спб
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I believe that a foreclosed can have a important effect on the debtor’s life. Foreclosures can have a Six to few years negative impact on a debtor’s credit report. The borrower having applied for home financing or any kind of loans for example, knows that a worse credit rating is, the more complicated it is for any decent mortgage. In addition, it can affect the borrower’s capacity to find a quality place to lease or rent, if that will become the alternative property solution. Interesting blog post.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
кайт школа хургада
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Momi — это бренд, предлагающий качественные товары для мам и малышей. На моми официальный сайт вы найдете широкий ассортимент детских товаров, отвечающих современным стандартам безопасности и комфорта. Покупайте оригинальную продукцию МОМИ онлайн!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
семантическое ядро заказать корпоративный сайт под ключ москва
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сео раскрутка заказать сео продвижение сайта
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
пины на заказ https://izgotovit-znachki-metalicheskie.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon on a daily basis. It’s always helpful to read through articles from other authors and practice a little something from their web sites.
melbet mn
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
металлические значки москва значки на заказ
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
заказ металлических значков металлические пины на заказ
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
бейджи на заказ https://badge-moscow-na-zakaz.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
разработка корпоративного портала системы бизнес аналитики
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cloud antidetect headless chrome
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
онлайн консультация юриста арбитражные судебные юристы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бесплатная панель управления panel 1Panel сервером с открытым исходным кодом. Удобный интерфейс, поддержка популярных ОС, автоматизация задач, резервное копирование, управление сайтами и базами. Оптимально для вебмастеров и системных администраторов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужен двигатель или акпп? https://motoreuro.ru с гарантией и доставкой по России? Мы предлагаем проверенные агрегаты с пробегом до 100 тыс. км из Японии, Европы и Кореи. Подбор, установка, оформление документов — всё под ключ.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Wow, marvelous blog layout! How lengthy have you ever been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The entire glance of your site is great, as smartly as the content material!
aralash jang san’ati
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
натяжные потолки цена за 1м2 натяжные потолки цена за 1м2 .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
шильдик из латуни https://shildi-iz-metalla.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
шильдик латунь шильдик изготовление
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
рф продвижение сайта продвижение в топ
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Микрозайм взять рейтинг микрозаймов онлайн
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Срочно на карту быстрые деньги онлайн на карту
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Займ на руки мгновенно без отказа микрозайм на карту без отказа срочно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I?ll right away take hold of your rss feed as I can’t find your email subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please let me recognize so that I may subscribe. Thanks.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Saludos, usuarios de sitios de apuestas !
casinos online chile
Mejores casinos en Chile 2025 con tecnologГa avanzada – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CRuk1wy6nA0&list=PLX0Xt4gdc3aJG7y03Wh5Qf0JrapCEgMFH
Casino Chile online continГєa creciendo en popularidad gracias a sus ventajas. Seguridad, variedad y promociones lo hacen ideal para todo tipo de jugadores. AdemГЎs, puedes jugar desde cualquier lugar.
¡Que disfrutes de sesiones exitosas !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
установка натяжного потолка под ключ http://www.potolkilipetsk.ru .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
бейджики металлические премиальные бейджи
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
логотип на шильдике изготовление металлических шильдиков на заказ
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
стоимость разработки сайта https://razrabotka-sayta-laravel.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I have observed that rates for internet degree authorities tend to be a fantastic value. For instance a full Bachelor’s Degree in Communication with the University of Phoenix Online consists of 60 credits at $515/credit or $30,900. Also American Intercontinental University Online gives a Bachelors of Business Administration with a total study course requirement of 180 units and a price of $30,560. Online studying has made obtaining your diploma far more easy because you can easily earn your degree through the comfort of your dwelling place and when you finish working. Thanks for all tips I have certainly learned through the site.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Недвижимость Черноземья https://nedvizhimostchernozemya.ru квартиры, дома, участки, коммерческие объекты. Продажа и аренда во всех крупных городах региона. Надежные застройщики, проверенные предложения, прозрачные сделки.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Агентство недвижимости https://assa-dom.ru покупка, продажа, аренда квартир, домов, участков и коммерческих объектов. Полное сопровождение сделок, помощь с ипотекой, юридическая поддержка. Надежно, удобно, профессионально.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инвестиции в строительство https://permgragdanstroy.ru жилой и коммерческой недвижимости. Прибыльные проекты, прозрачные условия, сопровождение на всех этапах. Участвуйте в строительстве с гарантированной доходностью.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
arkada-casino-apk.ru
Приветствую всех!
Наткнулся на интересную статью для любителей мобильного гемблинга. По ссылке можно узнать подробности о том, как скачать казино arkada на телефон.
В материале, похоже, рассматриваются разные платформы (Android, iOS?), способы установки, а также вопросы безопасности и выбора надежного казино.
arkada-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Пиломатериалы от производителя https://tsentr-stroy.ru по доступным ценам. В наличии обрезная и необрезная доска, брус, вагонка, доска пола, рейка и другие изделия. Работаем с частными и корпоративными заказами. Качество, доставка, гибкие условия.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Металлические ограждения https://osk-stroi.ru для дома, дачи, промышленных и общественных объектов. Качественные материалы, долговечность, устойчивость к коррозии. Быстрая установка и индивидуальное изготовление под заказ.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Discover create porn, a platform where artificial intelligence makes your desires come true. Create your perfect AI heroines, chat in real time, and enjoy personalized content tailored to your tastes. The next level of sex technology is here.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1go-casino-apk.ru
Приветствую, форумчане!
Хочу поделиться интересной находкой для тех, кто ищет способы окунуться в мир азарта. По ссылке вы найдете информацию о том, как скачать приложение 1go казино.
В статье, вероятно, обсуждаются различные аспекты загрузки приложения, особенности игры, а также, возможно, бонусы и акции для новых пользователей.
1go-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
bet-casino-apk.ru
По ссылке ниже — полезный гайд по игре в казино bet. Там разобраны основные стратегии, бонусы и советы для новичков. Рекомендую ознакомиться, если интересуетесь этой площадкой!
bet-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
экскурсии калининград официальный сайт сколько стоят экскурсии в калининграде
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
banda-casino-apk.ru
Всем привет!
Нашёл для вас кое-что интересное, особенно для тех, кто фанатеет от казино banda. По ссылке можно узнать все подробности о том, как скачать это казино.
В статье, скорее всего, расскажут о способах скачивания для разных устройств, особенностях установки и, возможно, о бонусах, которые можно получить после установки.
banda-casino-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Играешь в Fallout 76? Хочешь буст Fallout 76? Широкий ассортимент предметов, включая силовую броню, легендарное оружие, хлам, схемы и многое другое для Fallout 76 на PC, Xbox и PlayStation. Мы предлагаем услуги буста, прокачки персонажа и готовые комплекты снаряжения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На diabloshop.ru вы можете купить https://diabloshop.ru/gajdy-diablo-2-resurrected/ золото Diablo 4, руны Diablo 2 Resurrected, а также уникальные предметы и легендарное снаряжение для всех платформ — PC, Xbox, PlayStation и Nintendo Switch. Мы предлагаем быстрый буст персонажа, услуги прокачки, сбор лучших билдов и готовые комплекты снаряжения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На diabloshop.ru вы можете купить https://diabloshop.ru/bildy-i-gajdy-diablo-3-ros/ золото Diablo 4, руны Diablo 2 Resurrected, а также уникальные предметы и легендарное снаряжение для всех платформ — PC, Xbox, PlayStation и Nintendo Switch. Мы предлагаем быстрый буст персонажа, услуги прокачки, сбор лучших билдов и готовые комплекты снаряжения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Играешь в Fallout 76? Хочешь легендарное оружие Fallout 76? Широкий ассортимент предметов, включая силовую броню, легендарное оружие, хлам, схемы и многое другое для Fallout 76 на PC, Xbox и PlayStation. Мы предлагаем услуги буста, прокачки персонажа и готовые комплекты снаряжения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Paragraph writing is also a excitement, if you be acquainted with after that
you can write otherwise it is ccomplex to write. https://Sites.google.com/view/melbet-app-/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Для якісного звучання музики та комфортного прослуховування аудіо необхідні сучасні колонки та навушники. Вони забезпечують чистий звук та зручність використання.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
машину на день на прокат услуги проката автомобилей
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
взять авто в аренду аренда автомобиля
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Эта статья полна интересного контента, который побудит вас исследовать новые горизонты. Мы собрали полезные факты и удивительные истории, которые обогащают ваше понимание темы. Читайте, погружайтесь в детали и наслаждайтесь процессом изучения!
Ознакомиться с деталями – https://medalkoblog.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Play for Fun First
Finally, remember that digital slot machines are
meant too be enjoyable. While winning is great, it’s not guaranteed.
Appreciate the themes, animations, and features with casino trustpilot.
When youu fodus on the fuun instead of just the endgame, the experience becomes far more satisfying. https://AT.Trustpilot.com/review/casino-verde.at
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мы предлагаем ремонт квартир под ключ с гарантией качества, соблюдением сроков и полным сопровождением. Индивидуальный подход, современные материалы и прозрачные цены. Работаем по договору. Закажите бесплатную консультацию и начните комфортный ремонт уже сегодня!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7k-casino-download.ru
Привет, гемблеры! ??
Заглянул на один сайт и нашёл интересную статью. По ссылке собрана инфа о том, какие слоты будут популярны в онлайн-казино 7k в 2025 году.
Думаю, будет полезно почитать тем, кто интересуется трендами в мире азартных игр. Возможно, там есть инфа про новые механики, графику и темы, которые будут рулить в будущем.7k-casino-download.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
метр натяжного потолка стоит натяжные потолки фото и цены
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
дипломная работа срочно на заказ диплом написать
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
реферат написать онлайн сделать реферат
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Откройте возможности Vavada-pl.com.pl|Полный ассортимент развлечений на Vavada-pl.com.pl|Захватывающая игра на Vavada-pl.com.pl|Регистрируйтесь и выигрывайте на Vavada-pl.com.pl|Пробуйте свои силы на Vavada-pl.com.pl|Преимущества игры на Vavada-pl.com.pl|Играйте на Vavada-pl.com.pl и наслаждайтесь|Vavada-pl.com.pl — ваш личный игровой клуб|Получите максимум удовольствия на Vavada-pl.com.pl|Побеждайте с Vavada-pl.com.pl
zwrot gotowki vavada zwrot gotowki vavada .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На нашем сайте вы найдёте открытки с поздравлениями для любого случая. Яркие изображения, тёплые слова, праздничное настроение и стильный дизайн. Поделитесь эмоциями с близкими и сделайте каждый день особенным. Обновления каждый день, удобный формат, всё бесплатно!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Калининград экскурсоводы https://gid-po-kaliningradu.ru – профессиональные гиды.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ноты для фортепиано скачать музыка для фортепиано ноты
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
взять займ через интернет взять микрозайм
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7k-casino-download.ru
Всем привет!
Нашёл для вас кое-что интересное, особенно для тех, кто фанатеет от казино 7k. По ссылке можно узнать все подробности о том, как скачать это казино.
В статье, скорее всего, расскажут о способах скачивания для разных устройств, особенностях установки и, возможно, о бонусах, которые можно получить после установки.
7k-casino-download.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Noten klavier noten vom klavier
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
займ через интернет займ онлайн
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новостной портал https://sensus.org.ua главные события дня в России и мире. Политика, экономика, общество, культура, спорт и технологии. Только проверенные факты, оперативные сводки, мнения экспертов и честная подача.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
медицинский портал https://pobedilivmeste.org.ua с удобной навигацией и актуальной информацией. Болезни, симптомы, приёмы врачей, анализы, исследования, препараты и рекомендации.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мужской портал https://realman.com.ua всё, что интересно и полезно: спорт, здоровье, стиль, авто, отношения, технологии, карьера и отдых. Практичные советы, обзоры, мнения и поддержка.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт для мужчин https://phizmat.org.ua всё о жизни с характером: здоровье, спорт, стиль, авто, карьера, отношения, технологии. Полезные советы, обзоры, мужской взгляд на важные темы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кулинарные рецепты https://kulinaria.com.ua на каждый день и для особых случаев. Домашняя выпечка, супы, салаты, десерты, блюда из мяса и овощей. Простые пошаговые инструкции, доступные ингредиенты и душевные вкусы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Надёжный медицинский портал https://pobedilivmeste.org.ua с удобной навигацией и актуальной информацией. Болезни, симптомы, приёмы врачей, анализы, исследования, препараты и рекомендации.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7k-casino-download.ru
Приветствую всех!
Наткнулся на интересную статью для любителей мобильного гемблинга. По ссылке можно узнать подробности о том, как скачать казино 7k на телефон.
В материале, похоже, рассматриваются разные платформы (Android, iOS?), способы установки, а также вопросы безопасности и выбора надежного казино.
7k-casino-download.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный медицинский портал https://medfactor.com.ua с упором на технологии: телемедицина, онлайн-запись, цифровые карты, расшифровка анализов, подбор препаратов. Удобный доступ к информации и поддержка на всех этапах — от симптомов до выздоровления.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт о мужском здоровье https://kakbog.com достоверная информация о гормональном фоне, потенции, урологических проблемах, профилактике, питании и образе жизни. Советы врачей, диагностика, лечение, препараты.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7k-download-apk.ru
По ссылке ниже — полезный гайд по игре в казино 7k. Там разобраны основные стратегии, бонусы и советы для новичков. Рекомендую ознакомиться, если интересуетесь этой площадкой!
7k-download-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт о здоровье глаз https://eyecenter.com.ua полезные статьи, советы офтальмологов, симптомы заболеваний, диагностика, лечение, упражнения для зрения. Всё о профилактике, коррекции, очках, линзах и современных методах восстановления.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт для женщин https://expertlaw.com.ua которые любят моду, красоту и стильную жизнь. Актуальные тренды, советы по уходу, подбор образов, вдохновляющие идеи для гардероба и макияжа.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить реферат срочно написать реферат
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
написать диплом на заказ дипломная работа на заказ
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё о лечении диабета https://diabet911.com типы заболевания, симптомы, диагностика, питание, образ жизни и лекарственная терапия. Объясняем просто и понятно. Актуальная информация, советы врачей, статьи для пациентов и близких.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн фитнес-журнал https://bahgorsovet.org.ua полезные статьи от тренеров и нутрициологов: программы тренировок, восстановление, питание, биомеханика, анализ ошибок. Говорим на языке результата. Научный подход без воды — для тех, кто ценит эффективность.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://trendy.in.ua о выборе, деньгах, успехе и личных целях. Как совмещать карьеру и семью, строить бизнес, говорить “нет” и заботиться о себе. Истории, советы, интервью, вдохновение. Для тех, кто идёт вперёд — в своих темпах и с опорой на себя.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://tiamo.rv.ua которые ищут баланс. Психология, эмоции, отношения, самоценность, женское здоровье. Честные тексты, поддержка, путь к себе. Пространство, где можно дышать глубже, читать с удовольствием и чувствовать, что тебя понимают.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский онлайн-портал https://sweaterok.com.ua это не просто сайт, а поддержка в повседневной жизни. Честные темы, важные вопросы, советы и тепло. От эмоций до материнства, от тела до мыслей.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-портал для женщин https://rpl.net.ua всё о жизни, стиле, здоровье, отношениях, карьере, детях, красоте и вдохновении. Полезные статьи, советы, идеи и актуальные темы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Профессиональный массаж Ивантеевка: для спины, шеи, поясницы, при остеохондрозе и сколиозе. Медицинский и спортивный подход, опытные специалисты, точечное воздействие. Снятие болей, восстановление подвижности, улучшение самочувствия.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Модный журнал https://psilocybe-larvae.com всё о стиле, трендах, бьюти-новинках, звёздах и вдохновении. Образы с подиумов, советы стилистов, актуальные коллекции, мода улиц и мировые бренды.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал для женщин https://prettiness.kyiv.ua которые любят жизнь во всех её красках. Советы, мода, рецепты, отношения, вдохновение, дом и путешествия. Каждый день — новая идея, интересная мысль и повод улыбнуться.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал для активных https://onlystyle.com.ua стильных, современных женщин. Мода, карьера, здоровье, бьюти-тренды, фитнес, лайфхаки, вдохновение. Будь в курсе, живи ярко, выбирай смело. Никаких скучных статей — только драйв, стиль и реальная польза.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://inclub.lg.ua о силе выбора. Карьера, финансы, тайм-менеджмент, уверенность, стиль и баланс. Для женщин, которые двигаются вперёд, строят, влияют, мечтают. Говорим по делу — без стереотипов и с уважением к вашему пути.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сильная, умная, стильная https://lugor.org.ua вот для кого наш женский онлайн-журнал. Темы: мода, карьера, дети, отношения, дом, здоровье. Разговор о реальной жизни: без глянца, но со вкусом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://gorod-lubvi.com.ua о красоте, стиле и уходе. Советы визажистов, подбор образов, секреты молодости, модные тренды. Всё, чтобы чувствовать себя уверенно и выглядеть на миллион. Будь в курсе, вдохновляйся и подбирай стиль по душе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
натяжные потолки нижний https://natyazhnye-potolki-moskva1.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Информационно-познавательный https://golosiyiv.kiev.ua портал для мужчин и женщин: полезные статьи, советы, обзоры, лайфхаки, здоровье, психология, стиль, семья и финансы. Всё, что важно знать для жизни, развития и комфорта. Читайте, развивайтесь, вдохновляйтесь вместе с нами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Это не просто сайт для женщин https://godwood.com.ua это пространство, где вас слышат. Здесь — забота, поддержка, советы по жизни, отношениям, здоровью, семье и внутреннему балансу. Никакой критики, только доброта и уверенность: всё будет хорошо, и вы не одна.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт для женщин https://funtura.com.ua всё, что интересно каждый день: бьюти-советы, рецепты, отношения, дети, стиль, покупки, лайфхаки и настроение. Яркие статьи, тесты и вдохновение. Просто, легко, по-женски.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Полезные статьи и советы https://britishschool.kiev.ua на каждый день: здоровье, финансы, дом, отношения, саморазвитие, технологии и лайфхаки. Читайте, применяйте, делитесь — всё, что помогает жить проще, осознаннее и эффективнее. Достоверная информация и реальная польза.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Следите за трендами автопрома https://viewport.com.ua вместе с нами! На авто портале — новинки, презентации, обзоры, технологии, электромобили, автосалоны и экспертные мнения. Ежедневные обновления, честный взгляд на рынок, без лишнего шума и рекламы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Автомобильный сайт https://kolesnitsa.com.ua для души: редкие модели, автофан, необычные тесты, автоистории, подборки и юмор. Лёгкий и увлекательный контент, который приятно читать. Здесь не только про машины — здесь про стиль жизни на колёсах.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Актуальные новости https://polonina.com.ua каждый день — политика, экономика, культура, спорт, технологии, происшествия. Надёжный источник информации без лишнего. Следите за событиями в России и мире, получайте факты, мнения и обзоры.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новинки технологий https://dumka.pl.ua портал о том, как научные открытия становятся частью повседневности. Искусственный интеллект, нанотехнологии, биоинженерия, 3D-печать, цифровизация. Простым языком о сложном — для тех, кто любит знать, как работает мир.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Все новинки технологий https://axioma-techno.com.ua в одном месте: презентации, релизы, выставки, обзоры и утечки. Следим за рынком гаджетов, IT, авто, AR/VR, умного дома. Обновляем ежедневно. Не пропустите главные технологические события и открытия.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный мужской портал https://smart4business.net о жизни, успехе и саморазвитии. Личный рост, инвестиции, бизнес, стиль, технологии, мотивация. Разбираем стратегии, делимся опытом, вдохновляем на движение вперёд. Для тех, кто выбирает силу, разум и результат.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кулинарный портал https://mallinaproject.com.ua тысячи рецептов, пошаговые инструкции, фото, видео, удобный поиск по ингредиентам. Готовьте вкусно и разнообразно: от завтраков до десертов, от традиционной кухни до кулинарных трендов. Быстро, доступно, понятно!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I have been browsing on-line greater than three hours as of late, but
I by no means found any interesting article like yours.
It is lovely price sufficient for me. In my view, if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the web might be a lot more helpful
than ever before.
casino en ligne
Wow, this piece of writing is fastidious, my
sister is analyzing these things, thus I am going to tell
her.
casino en ligne
My partner and I stumbled over here from a different web page and thought
I might as well check things out. I like what I see so now
i am following you. Look forward to looking at your web page yet again.
casino en ligne francais
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d certainly donate to this brilliant blog!
I suppose for now i’ll settle for bookmarking and
adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to new updates and will share this site
with my Facebook group. Talk soon!
casino en ligne
This is a really good tip particularly to those fresh to the blogosphere.
Brief but very accurate info… Thanks for sharing this one.
A must read article!
casino en ligne fiable
Your method of telling everything in this paragraph is actually pleasant, every one be capable of without difficulty know it, Thanks a lot.
casino en ligne
I am actually thankful to the holder of this website who has shared this impressive paragraph
at at this time.
casino en ligne
Hey there! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers?
I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard
on. Any tips?
casino en ligne
Simply want to say your article is as astonishing. The clearness in your post is simply spectacular and i can assume you are an expert on this subject.
Fine with your permission let me to grab your RSS feed to keep
up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the rewarding work.
meilleur casino en ligne
My brother recommended I would possibly
like this blog. He was entirely right. This put up actually
made my day. You can not consider simply how much time I had spent
for this information! Thanks!
casino en ligne
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чайная энциклопедия https://etea.com.ua всё о мире чая: сорта, происхождение, свойства, способы заваривания, чайные традиции разных стран. Узнайте, как выбрать качественный чай, в чём его польза и как раскрывается вкус в каждой чашке. Для ценителей и новичков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Надёжный медицинский портал https://una-unso.cv.ua созданный для вашего здоровья и спокойствия. Статьи о заболеваниях, советы по лечению и образу жизни, подбор клиник и врачей. Понятный язык, актуальная информация, забота о вашем самочувствии — каждый день.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Медицинский портал https://lpl.org.ua с проверенной информацией от врачей: симптомы, заболевания, лечение, диагностика, препараты, ЗОЖ. Консультации специалистов, статьи, тесты и новости медицины. Только достоверные данные — без паники и домыслов. Здоровье начинается с знаний.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт для женщин https://womenclub.kr.ua всё, что волнует и вдохновляет: мода, красота, здоровье, отношения, дети, психология и карьера. Практичные советы, интересные статьи, вдохновение каждый день. Онлайн-пространство, созданное с заботой о вас и вашем настроении.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный женский портал https://womanonline.kyiv.ua с актуальными темами: тренды, уход, макияж, фитнес, fashion, интервью, советы стилистов. Следи за модой, вдохновляйся образами, узнай, как подчеркнуть свою индивидуальность.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал для женщин https://oa.rv.ua всё, что важно: красота, здоровье, семья, карьера, мода, отношения, рецепты и саморазвитие. Полезные статьи, советы, тесты и вдохновение каждый день. Онлайн-пространство, где каждая найдёт ответы и поддержку.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://mirwoman.kyiv.ua которые ищут не только советы, но и тепло. Личные истории, женское здоровье, психология, уютный дом, забота о себе, рецепты, отношения. Без давления, без шаблонов. Просто жизнь такой, какая она есть.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://loveliness.kyiv.ua о стиле, красоте, вдохновении и трендах. Интервью, мода, бьюти-обзоры, психология, любовь и карьера. Будь в курсе главного, читай мнения экспертов, следи за трендами и открывай новые грани себя каждый день.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ты можешь всё https://love.zt.ua а мы подскажем, как. Женский портал о саморазвитии, личной эффективности, карьере, балансе между семьёй и амбициями. Здесь — опыт успешных женщин, практичные советы и реальные инструменты для роста.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добро пожаловать на женский портал https://lidia.kr.ua ваш гид по миру красоты, стиля и внутренней гармонии. Читайте про отношения, карьеру, воспитание детей, женское здоровье, эмоции и моду. Будьте вдохновлены лучшей версией себя каждый день вместе с нами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
На женском портале https://happytime.in.ua статьи для души и тела: секреты красоты, женское здоровье, любовь и семья, рецепты, карьерные идеи, вдохновение. Место, где можно быть собой, делиться опытом и черпать силу в заботе о себе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный женский портал https://beautyrecipes.kyiv.ua стиль жизни, мода, уход за собой, семья, дети, кулинария, карьера и вдохновение. Полезные советы, тесты, статьи и истории. Откровенно, интересно, по-настоящему. Всё, что важно и близко каждой женщине — в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал про авто https://livecage.com.ua всё для автолюбителей: обзоры машин, тест-драйвы, новости автопрома, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию. Выбор авто, сравнение моделей, тюнинг, страховка, ПДД. Актуально, понятно и полезно. Будьте в курсе всего, что связано с автомобилями!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Автомобильный портал https://autodream.com.ua для автолюбителей и профессионалов: новости автоиндустрии, обзоры, тест-драйвы, сравнение моделей, советы по уходу и эксплуатации. Каталог авто, форум, рейтинги, автоновости. Всё об автомобилях — в одном месте, доступно и интересно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Натяжные потолки под ключ https://medium.com/@ksv.viet87/натяжные-потолки-мифы-о-вреде-и-экспертное-мнение-от-nova-28054185c2fd установка любых видов: матовые, глянцевые, сатиновые, многоуровневые, с фотопечатью и подсветкой. Широкий выбор фактур и цветов, замер бесплатно, монтаж за 1 день. Качественные материалы, гарантия и выгодные цены от производителя.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
YouTube Promotion buy youtube views for your videos and increase reach. Real views from a live audience, quick launch, flexible packages. Ideal for new channels and content promotion. We help develop YouTube safely and effectively.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё о мобильной технике https://webstore.com.ua и технологиях: смартфоны, планшеты, гаджеты, новинки рынка, обзоры, сравнения, тесты, советы по выбору и настройке. Следите за тенденциями, обновлениями ОС и инновациями в мире мобильных устройств.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инновации, технологии, наука https://technocom.dp.ua на одном портале. Читайте о передовых решениях, новых продуктах, цифровой трансформации, робототехнике, стартапах и будущем IT. Всё самое важное и интересное из мира высоких технологий в одном месте — просто, понятно, актуально.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Фитнес-портал https://sportinvent.com.ua ваш помощник в достижении спортивных целей. Тренировки дома и в зале, план питания, расчёт калорий, советы тренеров и диетологов. Подходит для начинающих и профессионалов. Всё о фитнесе — в одном месте и с реальной пользой для здоровья.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Туристический портал https://prostokarta.com.ua для путешественников: маршруты, достопримечательности, советы, бронирование туров и жилья, билеты, гайды по странам и городам. Планируйте отпуск легко — всё о путешествиях в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Архитектурные решения https://топдом-мск.рф под ваши желания и участок. Создадим проект с нуля: планировка, фасад, инженерия, визуализация. Вы получите эксклюзивный дом, адаптированный под ваш образ жизни. Работаем точно, качественно и с любовью к деталям.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ищете копирайтера? https://sajt-kopirajtera.ru/jandeks-uslugi-prodvizhenie-profilja/ Пишу тексты, которые продают, вовлекают и объясняют. Создам контент для сайта, блога, рекламы, каталога. Работаю с ТЗ, разбираюсь в SEO, адаптирую стиль под задачу. Чистота, смысл и результат — мои приоритеты. Закажите текст, который работает на вас.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
салон цветов спб доставка цветов в день заказа
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
воздушные шары доставка цветов в день заказа
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
цветы живые купить санкт петербург цветы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7k-download-apk.ru/mobilnoe-prilozhenie-7k/
Приветствую, форумчане!
Хочу поделиться интересной находкой для тех, кто ищет способы окунуться в мир азарта. По ссылке вы найдете информацию о том, как скачать приложение 7k казино.
В статье, вероятно, обсуждаются различные аспекты загрузки приложения, особенности игры, а также, возможно, бонусы и акции для новых пользователей.
7k-download-apk.ru/mobilnoe-prilozhenie-7k/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
7k-skachat-apk.ru
Привет, гемблеры! ??
Заглянул на один сайт и нашёл интересную статью. По ссылке собрана инфа о том, какие слоты будут популярны в онлайн-казино 7k в 2025 году.
Думаю, будет полезно почитать тем, кто интересуется трендами в мире азартных игр. Возможно, там есть инфа про новые механики, графику и темы, которые будут рулить в будущем.7k-skachat-apk.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о недвижимости https://akadem-ekb.ru всё, что нужно знать о продаже, покупке и аренде жилья. Актуальные объявления, обзоры новостроек, советы экспертов, юридическая информация, ипотека, инвестиции. Помогаем выбрать квартиру или дом в любом городе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Недвижимость в Болгарии у моря https://byalahome.ru квартиры, дома, апартаменты в курортных городах. Продажа от застройщиков и собственников. Юридическое сопровождение, помощь в оформлении ВНЖ, консультации по инвестициям.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Срочный выкуп квартир https://proday-kvarti.ru за сутки — решим ваш жилищный или финансовый вопрос быстро. Гарантия законности сделки, юридическое сопровождение, помощь на всех этапах. Оценка — бесплатно, оформление — за наш счёт. Обращайтесь — мы всегда на связи и готовы выкупить квартиру.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Create vivid images with Promptchan — a powerful neural network for generating art based on text description. Support for SFW and NSFW modes, style customization, quick creation of visual content.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
яблони морозостойкие декоративные лилии недорого
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
малина морозостойкая свг гибрид саженцы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Francisk Skorina https://www.gsu.by Gomel State University. One of the leading academic and scientific-research centers of the Belarus. There are 12 Faculties at the University, 2 scientific and research institutes. Higher education in 35 specialities of the 1st degree of education and 22 specialities.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ГГУ имени Ф.Скорины https://www.gsu.by/ крупный учебный и научно-исследовательский центр Республики Беларусь. Высшее образование в сфере гуманитарных и естественных наук на 12 факультетах по 35 специальностям первой ступени образования и 22 специальностям второй, 69 специализациям.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ваш надежный источник развлечений | Зарегистрируйтесь сейчас на vavadacasino.netlify.app | Большой выбор игр и автоматов | Откройте для себя мир казино | Эксклюзивные игры только на vavadacasino.netlify.app | Гарантированный честный игровой процесс | Побеждайте каждый день | Играйте в любое время и в любом месте | Обслуживание клиентов высокого уровня | Обучайтесь у профессионалов | Быстрый доступ к играм | Акции для новых игроков | Играйте в самые горячие новинки | Выигрывайте призы и трофеи | Зарабатывайте вместе с нами | Инструкции по игре и правила | Политика конфиденциальности на сайте | Лучшие отзывы игроков | Погрузитесь в атмосферу азарта
казино вавада украина https://vavadacasino.netlify.app/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
download-app-vavada-casino.ru
По ссылке ниже — полезный гайд по игре в казино Вавада. Там разобраны основные стратегии, бонусы и советы для новичков. Рекомендую ознакомиться, если интересуетесь этой площадкой!
download-app-vavada-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
консультации и онлайн услуги защита прав потребителей услуг по законодательству: консультации, подготовка претензий и исков, представительство в суде. Поможем вернуть деньги, заменить товар или взыскать компенсацию. Работаем быстро и по закону.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Любимые карточные игры на покерок. Новички и профессиональные игроки всё чаще выбирают площадку благодаря её стабильности и удобству. Здесь доступны кэш-игры, турниры с большими призовыми и эксклюзивные акции. Интерфейс адаптирован под мобильные устройства, а служба поддержки работает круглосуточно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Строительный портал https://stroydelo33.ru источник актуальной информации для тех, кто строит, ремонтирует или планирует. Полезные советы, обзоры инструментов, этапы работ, расчёты и готовые решения для дома и бизнеса.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
консультации и онлайн услуги услуги по защите прав потребителей: консультации, подготовка претензий и исков, представительство в суде. Поможем вернуть деньги, заменить товар или взыскать компенсацию. Работаем быстро и по закону.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Инженерные системы https://usteplo.ru основа комфортного и безопасного пространства. Проектирование, монтаж и обслуживание отопления, водоснабжения, вентиляции, электроснабжения и слаботочных систем для домов и предприятий.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Любимые карточные игры на покерок. Новички и профессиональные игроки всё чаще выбирают площадку благодаря её стабильности и удобству. Здесь доступны кэш-игры, турниры с большими призовыми и эксклюзивные акции. Интерфейс адаптирован под мобильные устройства, а служба поддержки работает круглосуточно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Thanks for your posting. Another issue is that being photographer consists of not only problems in taking award-winning photographs but in addition hardships in getting the best digital camera suited to your needs and most especially struggles in maintaining the grade of your camera. This really is very true and obvious for those photography lovers that are in capturing the particular nature’s engaging scenes : the mountains, the forests, the particular wild and the seas. Going to these adventurous places definitely requires a video camera that can meet the wild’s nasty natural environment.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Свежие тенденции https://www.life-ua.com советы по стилю и обзоры коллекций. Всё о моде, дизайне, одежде и аксессуарах для тех, кто хочет выглядеть современно и уверенно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Свежие тенденции https://www.life-ua.com советы по стилю и обзоры коллекций. Всё о моде, дизайне, одежде и аксессуарах для тех, кто хочет выглядеть современно и уверенно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужен номер для Телеграма? купить номер для регистрации телеграмм для безопасной регистрации и анонимного использования. Поддержка популярных регионов, удобный интерфейс, моментальный доступ.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
печать прозрачных наклеек печать наклеек с логотипом
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить смартфон 14 смартфон хонор цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Оказываем услуги юрист по защите прав потребителей спб: консультации, подготовка претензий и исков, представительство в суде. Поможем вернуть деньги, заменить товар или взыскать компенсацию. Работаем быстро и по закону.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ноутбук 16 купить цена ноутбука для работы
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola, aventureros de las apuestas !
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DvFWSMyjao4
RegistrГЎndote hoy ganas 10 euros gratis – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DvFWSMyjao4&list=PLX0Xt4gdc3aLv2xrbmSCzHqZw12bA17Br
Descubre cГіmo obtener 10 euros gratis sin depГіsito y disfruta de tus juegos favoritos sin invertir tu propio dinero. Es la oportunidad perfecta para nuevos jugadores en EspaГ±a. RegГstrate y comienza tu aventura en el mundo del casino.
¡Que tengas excelentes triunfos !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
download-free-pin-casino.ru
Привет, гемблеры! ??
Заглянул на один сайт и нашёл интересную статью. По ссылке собрана инфа о том, какие слоты будут популярны в онлайн-казино Pin up в 2025 году.
Думаю, будет полезно почитать тем, кто интересуется трендами в мире азартных игр. Возможно, там есть инфа про новые механики, графику и темы, которые будут рулить в будущем.download-free-pin-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
маркетплейс техники и электроники магазины электроники в москве
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
лучший ноутбук цена качество ноутбук дюймов купить
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
какой смартфон купить в 2025 смартфон лучшая цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
электроника магазин купить https://magazin-elektroniki213.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сколько стоит ноутбук цена купить ноутбук acer
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
download-pin-casino.ru
Приветствую, форумчане!
Хочу поделиться интересной находкой для тех, кто ищет способы окунуться в мир азарта. По ссылке вы найдете информацию о том, как скачать онлайн Pin-Up казино.
В статье, вероятно, обсуждаются различные аспекты загрузки приложения, особенности игры, а также, возможно, бонусы и акции для новых пользователей.
download-pin-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужен номер для ТГ? Предлагаем https://techalpaka.online для одноразовой или постоянной активации. Регистрация аккаунта без SIM-карты, в любом регионе. Удобно, надёжно, без привязки к оператору.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
большой лед экран https://svetodiodnye-ekrany-videosteny.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экскурсии по Красноярску https://tour-guide8.ru индивидуальные прогулки и групповые туры. Красивые виды, история города, заповедные места. Гиды с опытом, удобные форматы, гибкий график. Подарите себе незабываемые впечатления!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola buscadores de emociones !
Descubre cГіmo ganar sin hacer depГіsitos.
Es una excelente manera de comenzar tu aventura en el juego online. [url=https://25girosgratissindeposito.xyz/#]tiradas gratis sin deposito 2025[/url] No lo dejes pasar.
¡Que tengas magníficas tiradas de suerte !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1xBet promo code https://lajt.com/wp-content/pgs/krovotechenie_boli_i_zaghivlenie_zubov_posle_udaleniya.html is your chance to start with a bonus! Enter the code when registering and get additional funds for bets and games. Suitable for sports events, live bets and casino. The bonus is activated automatically after replenishing the account.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
1xBet promo code https://www.pnsb.org/wp-content/pgs/krovopiycy_chasty_1.html is an opportunity to get a bonus of up to 100% on your first deposit. Register, enter the code and start betting with additional funds. Fast, simple and profitable.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
O site oficial 1win bet https://1winbr.com.br/ e apostar em desporto, casinos, jogos e torneios. Suporte para diversas moedas, transacoes rapidas, promocoes e cashback. Jogue confortavelmente no seu PC ou atraves da aplicacao.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
заказ курсовой недорого заказать курсовые
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лечение в Китае стоматологические туры в хуньчунь из владивостока туры в лучшие медицинские центры страны. Традиционная и современная медицина, точная диагностика, восстановление и реабилитация. Сопровождение на всех этапах поездки.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выбор правильной технологии https://wfinbiz.com/bez-rubriki/proizvodstvo-premialnyh-znachkov-tehnologii-i-metody-izgotovleniya-znachkov-vklyuchaya-himicheskoe-travlenie-i-ego-preimushhestva/ ключ к созданию значков, которые действительно производят впечатление. Чтобы значки премиального уровня действительно выглядели достойно, необходимо правильно подобрать технологию производства. Методы, такие как химическое травление, обеспечивают высокую детализацию и благородный внешний вид, который сохраняется надолго.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Значки из металла https://rus-week.ru/biznes-idei/metallicheskie-znachki-premialnogo-kachestva-luchshie-resheniya-dlya-brendinga/ это практичный и презентабельный атрибут для бизнеса, торжеств и наград. Мы производим значки с эмалью, гравировкой, штамповкой. Доступны различные формы, размеры и виды креплений.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Значки из металла https://all-5.ru/izgotovlenie-metallicheskih-znachkov-metodom-himicheskogo-travleniya/ эффектный способ подчеркнуть корпоративный стиль или отметить событие. Изготавливаем тиражи любого объёма, предоставляем консультации по выбору технологии и креплений.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Предлагаем качественные клинкерная плитка цена — ступени и плитка для наружных и внутренних работ. Устойчив к износу, влаге и морозу. Подходит для лестниц, крылец, балконов. Консультации и заказ в один шаг.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
darknet official watching free porn
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
download-riobet-casino.ru
По ссылке ниже — полезный гайд по игре в казино Riobet. Там разобраны основные стратегии, бонусы и советы для новичков. Рекомендую ознакомиться, если интересуетесь этой площадкой!
download-riobet-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
курсовую заказать цена курсовой
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
porn couples called a whore
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
porn big boobs kilogram of cocaine price
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Car service alternator replacement cost services We provide car repair services: from quick diagnostics to major restoration. Quality guarantee, experienced specialists, clear deadlines and original spare parts. We work with private and corporate clients.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Играйте на vavada.kesug.com — лучшие развлечения онлайн, на этом сайте.
Попробуйте удачу на vavada.kesug.com, на платформе.
Всё для любителей азартных игр — vavada.kesug.com, играйте прямо сейчас.
Vavada.kesug.com — безопасное онлайн-казино, испытайте удачу.
Vavada.kesug.com — место для настоящих игроков, получайте удовольствие.
Vavada.kesug.com — современное онлайн-казино, используйте бонусные предложения.
Испытайте удачу на vavada.kesug.com, начинайте играть уже сегодня.
Vavada.kesug.com — сайт для выигрышей, играйте и выигрывайте.
Vavada.kesug.com — азартные игры для всех, получайте удовольствие.
Обновляемые предложения — vavada.kesug.com, используйте промо-коды.
Лучшие автоматы и рулетки — vavada.kesug.com, используйте шанс.
Vavada.kesug.com — ваш источник развлечений, получайте максимум удовольствия.
Vavada.kesug.com — надежный сайт для игр и ставок, начинайте прямо сейчас.
Vavada.kesug.com — для любителей азартных игр, испытайте удачу.
Откройте для себя новые игры — vavada.kesug.com, выигрывайте вместе с нами.
Лучшие условия для игроков — vavada.kesug.com, используйте предложения.
Vavada.kesug.com — ведущий сайт для онлайн-ставок, выигрывайте крупные призы.
Официальный сайт с лучшими условиями — vavada.kesug.com, начинайте игру
вавада офіційний сайт https://vavada.kesug.com/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
minut porn buy cocaine cheap
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный сайт mebelkmv-26.ru на котором легко найти нужную и полезную информацию, товары или услуги. Простая навигация, понятный интерфейс и актуальное содержание подойдут как для новых пользователей, так и для постоянной аудитории. Работает быстро, доступен круглосуточно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Here to dive into discussions, exchange ideas, and learn something new throughout the journey.
I’m interested in hearing diverse viewpoints and adding to the conversation when possible. Interested in hearing new ideas and building connections.
Here is my web-site:https://automisto24.com.ua/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cloud server best cloud server
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
download-casino-phone.ru
Приветствую всех!
Наткнулся на интересную статью для любителей мобильного гемблинга. По ссылке можно узнать подробности о том, как скачать казино на телефон.
В материале, похоже, рассматриваются разные платформы (Android, iOS?), способы установки, а также вопросы безопасности и выбора надежного казино.
download-casino-phone.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн проект freebet-ot-winline.ru где собраны полезные данные, инструменты и сервисы для повседневной жизни и профессиональной деятельности. Сайт адаптирован под любые устройства, стабильно работает и предоставляет максимум пользы без лишнего шума и рекламы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
slote-casino.ru
Привет, гемблеры! ??
Заглянул на один сайт и нашёл интересную статью. По ссылке собрана инфа о том, какие слоты будут популярны в онлайн-казино в 2025 году.
Думаю, будет полезно почитать тем, кто интересуется трендами в мире азартных игр. Возможно, там есть инфа про новые механики, графику и темы, которые будут рулить в будущем.slote-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Go for the Right Slot Game
Not all slot titles aree created equal. Some have more favorable RTP, more exciting bonus features, or settings tjat
are simpy more fun for yyou like Thepokies106. Always
look at the RTP (Return to Player) percentage—a greater RTP means
imprtoved odds over time.Try out multiple titles in demo mode first to determine which ones you
find rewarding and which maximize returns. https://nl.trustpilot.com/review/urbanuszelf.eu
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
cloud server cloud server solutions
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный и удобный сайт ukuleleshop.ru на котором легко найти нужную информацию, товары или услуги. Простая навигация, понятный интерфейс и актуальное содержание подойдут как для новых пользователей, так и для постоянной аудитории. Работает быстро, доступен круглосуточно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Just here to explore discussions, exchange ideas, and gain fresh perspectives as I go.
I like learning from different perspectives and sharing my input when it’s helpful. Happy to hear fresh thoughts and connecting with others.
That’s my website:https://automisto24.com.ua/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
открыть бизнес в великобритании открыть компанию в англии
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Jacuzzi, sauna, hammam https://spaplanet.net/ turnkey – full cycle: from design and selection of equipment to finishing and commissioning. We work with any premises. Reliable, aesthetically pleasing and with a guarantee.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Рейтинг лучших сервисов https://vc.ru/telegram/1926953-nakrutka-podpischikov-v-telegram для накрутки Telegram-подписчиков: функциональность, качество, цены и скорость выполнения. Подходит для продвижения каналов любого масштаба — от старта до монетизации.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
открыть компанию в великобритании zaregistrirovat-kompaniyu-england.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
регистрация компании в англии zaregistrirovat-kompaniyu-england.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Корпоративные значки https://electrikexpert.ru/korporativnye-znachki-kak-malenkie-detali-sozdayut-bolshuyu-kulturu/ это не только стиль, но и имидж. Отличный вариант для персонала, деловых встреч, награждений и брендированных подарков. Предлагаем разные материалы, формы и способы нанесения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Металлические нагрудные значки https://str-steel.ru/metallicheskie-nagrudnye-znachki.html стильный и долговечный аксессуар для сотрудников, мероприятий и награждений. Изготавливаем под заказ: с логотипом, гравировкой или эмалью. Разные формы, крепления и варианты отделки.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Закажите металлические значки https://metal-archive.ru/novosti/40507-metallicheskie-znachki-na-zakaz-v-moskve-masterstvo-kachestvo-i-individualnyy-podhod.html с индивидуальным оформлением. Материалы: латунь, сталь, алюминий. Эмаль, гравировка, печать. Подходит для корпоративных мероприятий, сувениров, символики и наград.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Юридическое сопровождение сайт банкротства физических лиц: от анализа документов до полного списания долгов. Работаем официально, по закону №?127-ФЗ. Возможна рассрочка оплаты услуг.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Значки с логотипом компании https://press-release.ru/branches/markets/znachki-s-vashim-logotipom-iskusstvo-metalla-voploshchennoe-v-unikalnyh-izdeliyah/ это не просто элемент фирменного стиля, а настоящее искусство, воплощённое в металле. Они подчёркивают статус бренда и помогают сформировать узнаваемый образ.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Изготовим значки с логотипом http://classical-news.ru/tehnologiya-izgotovleniya-znachkov-s-logotipom/ вашей компании. Металлические, пластиковые, с эмалью или цветной печатью. Подчеркните фирменный стиль на выставках, акциях и корпоративных мероприятиях. Качественно, от 10 штук, с доставкой.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Изготовление значков https://3news.ru/izgotovlenie-znachkov-na-zakaz-pochemu-eto-vygodno-i-kak-vybrat-idealnyj-variant/ на заказ любой сложности. Работаем по вашему дизайну или поможем создать макет. Предлагаем разные материалы, формы и типы креплений. Оперативное производство и доставка по всей России.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Quer comprar seguidores para https://comprarseguidores.io o Instagram? Escolha o pacote que mais combina com voce: ao vivo, oferta ou misto. Adequado para blogueiros, lojas e marcas. Seguro, rapido e mantem a reputacao da sua conta.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Изготавливаем значки https://znaknazakaz.ru на заказ в Москве: классические, сувенирные, корпоративные, с логотипом и индивидуальным дизайном. Металл, эмаль, цветная печать. Быстрое производство, разные тиражи, удобная доставка по городу.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Металлические значки https://techserver.ru/izgotovlenie-znachkov-iz-metalla-kak-zakazat-unikalnye-izdeliya-dlya-vashego-brenda/ это стильный и долговечный способ подчеркнуть фирменный стиль, создать корпоративную айдентику или просто сделать приятный сувенир. Всё больше компаний выбирают индивидуальное изготовление значков, чтобы выделиться среди конкурентов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Продвижение групп ВК https://vk.com/dizayn_vedenie_prodvizhenie_grup от оформления и наполнения до запуска рекламы и роста подписчиков. Подходит для бизнеса, мероприятий, брендов и экспертов. Работаем честно и с аналитикой.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
download-free-casino-android.ru
Всем привет!
Нашёл кое-что интересное для любителей азарта на Android. По ссылке можно узнать, как бесплатно скачать онлайн-казино на свой смартфон или планшет.
В материале, кажется, рассказывают о разных способах, как это сделать безопасно и без вирусов, а также на что стоит обращать внимание при выборе казино.
download-free-casino-android.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Металлические бейджи https://gubkin.bezformata.com/listnews/beydzhi-dlya-brendov-i/140355141/ для брендов и корпораций — стильное решение для сотрудников, партнёров и мероприятий. Прочные, износостойкие, с гравировкой или полноцветной печатью. Подчёркивают статус компании и укрепляют фирменный стиль. Такие решения особенно актуальны для выставок, форумов и корпоративных событий, где важно произвести правильное первое впечатление. Грамотно оформленный бейдж может сказать о компании больше, чем десятки слов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Заказные медали https://iseekmate.com/34740-medali-na-zakaz-nagrada-dlya-chempionov.html применяются для поощрения в спорте, образовании, корпоративной культуре и юбилейных мероприятиях. Производятся из металла, с эмалью, гравировкой или цветной печатью в соответствии с требованиями заказчика.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
download-app-casino-x.ru
Привет всем!
Если вы ищете информацию о том, как скачать и установить мобильное приложение Casino X на свое устройство (Android или iOS), советую посмотреть по этой ссылке:
Там подробно описано:
Где безопасно скачать установочный файл
Какие системные требования у приложения
Как правильно установить и настроить приложение
Какие бонусы можно получить за установку приложения
download-app-casino-x.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Высокая производительность машин для зерна — mashiny-dlya-ochistki-zerna.biz.ua
зерноочисна машина купити https://mashiny-dlya-ochistki-zerna.biz.ua/ .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Хочешь оформить технический паспорт железнодорожного пути Документация включает технический паспорт железнодорожного пути, а также технический паспорт жд пути необщего пользования. Отдельно может потребоваться техпаспорт жд и паспорт на жд тупик при ведении путевого хозяйства.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Заказные медали https://iseekmate.com/34740-medali-na-zakaz-nagrada-dlya-chempionov.html применяются для поощрения в спорте, образовании, корпоративной культуре и юбилейных мероприятиях. Производятся из металла, с эмалью, гравировкой или цветной печатью в соответствии с требованиями заказчика.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Металлические бейджи https://gubkin.bezformata.com/listnews/beydzhi-dlya-brendov-i/140355141/ для брендов и корпораций — стильное решение для сотрудников, партнёров и мероприятий. Прочные, износостойкие, с гравировкой или полноцветной печатью. Подчёркивают статус компании и укрепляют фирменный стиль. Такие решения особенно актуальны для выставок, форумов и корпоративных событий, где важно произвести правильное первое впечатление. Грамотно оформленный бейдж может сказать о компании больше, чем десятки слов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современные сувениры https://66.ru/news/stuff/278214/ всё чаще становятся не просто подарками, а настоящими элементами бренда или корпоративной культуры. Особенно интересны примеры, когда обычные предметы превращаются в креативные и запоминающиеся изделия. Такие подходы вдохновляют на создание уникальной продукции с индивидуальным стилем и глубоким смыслом. Именно за этим всё чаще обращаются заказчики, которым важна не массовость, а оригинальность.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
download-online-casino.ru
Приветствую всех!
Нашел полезную информацию для тех, кто интересуется онлайн-казино в 2025 году. По этой ссылке есть гайд о том, как скачивать приложения онлайн-казино в следующем году.
В материале освещены следующие вопросы:
Актуальные способы скачивания приложений (для Android и iOS)
На что обратить внимание при выборе казино для скачивания (лицензия, безопасность)
Обзор самых надежных платформ в 2025 году
Как избежать мошеннических приложений
download-online-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Займы под материнский капитал https://юсфц.рф быстрое решение для покупки квартиры, дома или участка. Без личных вложений, с полным юридическим сопровождением. Оформление за 1 день, надёжные сделки и опыт более 10 лет. Используйте господдержку с умом!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Надёжный обмен валюты https://valutapiter.ru в СПб — курсы в реальном времени, большой выбор валют, комфортные офисы. Конфиденциальность, без очередей, выгодно и с гарантией. Для туристов, жителей и бизнеса. Обмен, которому можно доверять!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
[url=https://wmax.com.ua]Wmax.com.ua[/url] – сучасний онлайн-журнал, що пропонує корисні поради на всі випадки життя. Від лайфхаків для побуту та фінансів до здоров’я, технологій і саморозвитку — ми допомагаємо знаходити практичні рішення для щоденних викликів .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
изготовление стенда из пвх изготовление стендов стоимость
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://www.adobe.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
широкоформатная печать плакатов pechat-plakatov-spb.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
печать наклеек на заказ печать наклеек золотом
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
изготовить табличку из пластика табличка пвх а4
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
aura-casino-online-play.ru
Хотите узнать все о казино Aura? Я нашел отличный обзор, где подробно разбираются все плюсы и минусы этого казино. Там есть информация о лицензии, играх, и даже советы для новичков.
aura-casino-online-play.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
¡Hola expertos del azar !
Los mejores juegos con bonos de bienvenida sin depГіsito estГЎn disponibles ahora mismo. No esperes mГЎs para probar tu suerte. ВЎTodo sin inversiГіn!
Usa 100 giros gratis sin depГіsito para jugar en lГnea – http://100girosgratissindepositoespana.guru.
¡Que tengas magníficas premios increíbles !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
calibri-casino-download-play.ru
Узнать свежие новости и актуальную информацию о казино Calibry можно по ссылке ниже! Там собраны последние акции, бонусы и обзоры игр, так что держите руку на пульсе событий и будьте в курсе всех выгодных предложений. Переходите и будьте всегда в курсе самых интересных событий в мире Calibry!
calibri-casino-download-play.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
?Hola aficionados al casino
Los usuarios nuevos pueden activar su bono de 100 gratis spins con solo registrarse. [url=https://100girosgratissindepositoespana.guru/#]100 tiradas gratis[/url] Disfruta de los mejores tГtulos sin depositar. Ideal para quienes buscan empezar sin riesgo.
Los giros gratis EspaГ±a son una forma fantГЎstica de explorar el catГЎlogo de tragamonedas. Solo crea tu cuenta y comienza a girar. ВЎSin restricciones!
Accede ya a 100girosgratissindepositoespana.guru – 100girosgratissindepositoespana/.
?Que tengas excelentes recompensas !
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
металлические значки на рюкзак металлические значки москва
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
calibri-casino-app-play.ru
Перейдя по ссылке ниже, вы сможете ознакомиться с самыми свежими новостями о казино Calibry, включая новые бонусы, игры и акции. Следите за обновлениями и будьте в курсе всех возможностей этого казино, чтобы максимизировать свои шансы на выигрыш!
calibri-casino-app-play.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
calibri-casino-apk-play.ru
Перейдя по ссылке ниже, вы сможете узнать самую свежую и актуальную информацию о казино Calibry, включая последние бонусы, новые игры и отзывы других игроков. Уверен, это поможет вам составить собственное мнение об этом казино и решить, стоит ли здесь играть!
calibri-casino-apk-play.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
aura-casino-download-play.ru
По ссылке ниже — полезный гайд по игре в казино Aura. Там разобраны основные стратегии, бонусы и советы для новичков. Рекомендую ознакомиться, если интересуетесь этой площадкой!
aura-casino-download-play.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Наш новий комплаенс контролер komplaens-audit.top дуже уважно ставиться до деталей, що дозволило компанії уникнути штрафів. Всім раджу знайти такого ж професіонала.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если вы не знаете, где купить билет на автобус в Польшу http://www.infobus.top, лучше всего использовать проверенные сайты. Это удобно, быстро и безопасно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ваш источник современного торгового оборудования
торгівельне обладнання для магазину одягу торгівельне обладнання для магазину одягу .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Hi to all, the contents existing at this web site are in fact remarkable for people
knowledge, well, keep up the good workk fellows. https://jobs.linttec.com/employer/jp-bubinga-com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
calibri-casino-slots-play.ru
Узнать свежие новости и актуальную информацию о казино Calibry можно по ссылке ниже! Там собраны последние акции, бонусы и обзоры игр, так что держите руку на пульсе событий и будьте в курсе всех выгодных предложений. Переходите и будьте всегда в курсе самых интересных событий в мире Calibry!
calibri-casino-slots-play.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
slots-casino-com.ru
Здравствуйте, уважаемые участники форума! ??
Если вас интересует, как играть в Slot Casino Com через телефон, перейдите по ссылке ниже. Там вы найдете подробную инструкцию, которая поможет вам быстро и легко освоить игру. Удачи и приятного времяпрепровождения! ??
slots-casino-com.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лучшие бонусы на Vavada Ukraine
найкраще онлайн казино найкраще онлайн казино .
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Когда летом ездили во Вроцлав, выбрали автобус в Польшу с кондиционером и не пожалели. Даже в жару поездка была максимально комфортной.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Якщо потрібен внутренний аудит пример http://www.komplaens-audit.top, варто пошукати готові кейси в профільних виданнях. Там завжди є багато корисних прикладів.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
universal happiness is a wonderful hub for anyone eager about uplifting lifestyles and innovations.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
slotozal-casino-rus.ru
Привет, друзья! ??
Если вы хотите узнать, как играть в слотзал казино через телефон, перейдите по ссылке ниже. Там вы найдете пошаговую инструкцию, советы и полезные рекомендации, чтобы ваш игровой опыт был максимально комфортным и увлекательным.
slotozal-casino-rus.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Основа будь-якого гардеробу починається з якісної спідньої білизни https://ukrbeautystyle.com.ua/category/SpdnjaBlizna-. Комфорт і впевненість протягом дня забезпечені, якщо вибір зроблено правильно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
slots-for-money-casino.ru
Топ слотов 2025: Где сорвать куш в онлайн-казино? Высокий RTP, захватывающие бонусы, инновационный геймплей и джекпоты! Обзор самых щедрых и популярных игр. Узнайте, какие слоты принесут вам удачу и помогут выиграть реальные деньги! Читайте подробнее:
slots-for-money-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I love the tools suggestions available on activeoptions.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
slotzal-casino.ru
Привет, друзья! ??
Хотите узнать, как играть в слотзал Casino прямо с телефона? Перейдите по ссылке ниже и получите пошаговую инструкцию! Удобно, быстро и всегда под рукой. Удачи в игре! ??
slotzal-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I appreciate how etap wss discusses animal supervision in a insightful way.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
support-service-casino.ru
Служба поддержки онлайн-казино – ключевое звено! Мгновенные ответы, мультиязычность, решение сложных вопросов и персонализированный подход. Игроки ценят скорость и профессионализм. Как оптимизировать работу саппорта и повысить лояльность? Узнайте о трендах и технологиях! Читайте подробнее:
support-service-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sukaaa-casino.ru
Если вам интересно ознакомиться с инструкциями по установке приложений на мобильные устройства, мы можем предложить общий гайд.
Как установить приложения на Android и iOS
Установка мобильных приложений зависит от операционной системы вашего устройства.
Для Android:
Откройте файл APK — если приложение недоступно в Google Play, его можно скачать через официальный сайт.
Разрешите установку из неизвестных источников — зайдите в Настройки > Безопасность и активируйте соответствующую опцию.
Запустите установку и следуйте инструкциям.
Для iOS:
Скачайте приложение из App Store — большинство сервисов доступны через официальный магазин.
Используйте TestFlight или корпоративный сертификат — если приложение не опубликовано в App Store.
Разрешите установку — в настройках iPhone перейдите в раздел VPN и управление устройствами и подтвердите доверие к разработчику.
Если вас интересует конкретное приложение, проверьте его официальный сайт или магазин приложений. Но помните о безопасности: скачивайте ПО только из проверенных источников, чтобы избежать мошенничества.
Хотите узнать больше? Читайте дополнительные инструкции на сайте по ссылке ниже.sukaaa-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Настройка сервера на платформе https://rusikboss.livejournal.com/748.html — это удобный способ обеспечить безопасное подключение, стабильный доступ и полную конфиденциальность. Пошаговая инструкция, поддержка популярных протоколов, генерация QR-кодов и приложения для разных устройств — всё для быстрого запуска.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Многие люди ищут красивые цитаты, чтобы выразить чувства, найти вдохновение или просто улыбнуться. Мы собрали лучшие фразы — короткие, красивые, со смыслом. Наслаждайтесь подборкой, делитесь с друзьями и находите строки, которые отражают ваши мысли и настроение.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Где покупать технику? рейтинг магазинов какой лучше: проверенные продавцы, акции, удобная доставка и реальный опыт покупателей. Обновляем регулярно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
смотреть фильмы 2025 года новинки кино 2025 онлайн бесплатно
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
новий світ фільм 2025 топ фільмів 2025 онлайн
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
дивитися фільми 2025 року фільми 2025 року дивитися онлайн
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
create-casino.ru
Создать онлайн-казино в 2025? Это сложный процесс, требующий лицензии, надежного софта, безопасности и маркетинга. Необходимо учитывать законодательство, конкуренцию и ответственный подход к азартным играм. Узнайте больше о ключевых этапах и подводных камнях. Читайте подробнее по ссылке ниже
create-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
top-casino-rus.ru
В 2025 году российские пользователи проявляют повышенный интерес к онлайн-развлечениям, включая легальные игровые платформы. На нашем сайте представлен актуальный рейтинг проверенных сервисов, соответствующих требованиям законодательства.
Критерии отбора
В наш обзор включены только ресурсы, которые:
Имеют международные лицензии (Кюрасао, Мальта)
Поддерживают рублевые платежи
Предлагают SSL-шифрование данных
Имеют положительную репутацию среди пользователей
Топ-3 легальные платформы
“Клуб азартных игр” – лицензионный проект с ежедневными турнирами
“Игровой портал” – платформа с прозрачными выплатами
“Развлекательный центр” – сервис с системой ответственной игры
Важная информация
Согласно российскому законодательству:
Организация азартных игр в интернете запрещена
Доступ к международным платформам ограничен
Игра на незаконных сайтах влечет ответственность
Альтернативные развлечения
Мы рекомендуем рассмотреть легальные варианты:
Официальные лотереи (Столото)
Социальные казино без реальных ставок
Игровые приложения с виртуальной валютой
Важно: Напоминаем о рисках игровой зависимости. Если вы или ваши близкие столкнулись с этой проблемой, обратитесь в специализированные центры помощи.
Для получения полной информации о легальных игровых возможностях в 2025 году посетите сайт по ссылке.top-casino-rus.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
фільми 2025 в хорошому якості нові фільми 2025 в Україні
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
можно детское порно гей порно изнасилование
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Play Aviator Game https://www.lookingforclan.com/clans/aviator-0 online and win real money! Easy to play, exciting crash mechanics, fast rounds, and instant cashouts. Trusted by thousands of players worldwide — start now and catch the multiplier before it flies away!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Заказ воды в Хмельницком https://wellsprings.com.ua/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
anime blade manga read manga no registration
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
comic history free digital comics reader
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Aviator Bangladesh https://www.kanalcoin.com/profile/chichikus/ is your gateway to fun and fast gaming! No complex rules — just launch, bet, and cash out on time. Supported by leading Bangladeshi casinos, with BDT payments and full mobile access. Join and win anytime, anywhere.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Licensed online casino jetx bet popular slot machines, live dealers, promotions and bonuses. User-friendly interface, quick registration, many payment systems and 24/7 support. Play your favorite games and win without leaving your home.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Understand Volattility and Features
Take time to grasp how paylines, volatility, aand bonus features work.
Big win potential games mmay not reward frequently, but when they
do, it’s worthwhile. Low volatility slots offer lower rewards more frequently.
Learning this helps you pick a slot that suits your style, and yoou cann find anyy
of these onn https://www.reddit.com/r/kyrrex/comments/1jvtvos/top_crypto_affiliate_programs_in_2025_earn/. https://www.reddit.com/r/kyrrex/comments/1jvtvos/top_crypto_affiliate_programs_in_2025_earn/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Die Rubrik Erkundungen und Ausflüge auf themen mix bietet spannende Vorschläge.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить гифт электронная подарочная карта
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
auto transport companies vehicle transport service
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
sukaaa-casino-slots.ru
Обзор игровой платформы Sukaa 2025
В 2025 году Sukaa остается одной из популярных международных игровых платформ, привлекающей внимание пользователей из разных стран. На нашем сайте представлен детальный обзор особенностей данного ресурса.
Основные характеристики:
Лицензия: международная (Кюрасао)
Валюта: поддерживаются рублевые транзакции
Игровой софт: представлены слоты, настольные игры, live-дилеры
Мобильная версия: адаптирована под iOS и Android
Особенности платформы:
Бонусная программа для новых пользователей
Регулярные турниры с призовыми фондами
Система лояльности для постоянных клиентов
Важно учитывать:
Платформа не имеет российской лицензии
Доступ может быть ограничен интернет-провайдерами
Рекомендуется проверять актуальность информации на официальном сайте
Альтернативы:
Для российских пользователей доступны легальные варианты:
Официальные лотереи (Столото)
Социальные игровые приложения
Напоминание: Азартные игры могут вызывать зависимость. Играйте ответственно. 18+
Полную информацию о платформе Sukaa вы найдете на сайте по ссылке.sukaaa-casino-slots.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
car hauling car transportation services
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
install-champion-casino.ru
Если вам интересно ознакомиться с инструкциями по установке приложений на мобильные устройства, мы можем предложить общий гайд.
Как установить приложения на Android и iOS
Установка мобильных приложений зависит от операционной системы вашего устройства.
Для Android:
Откройте файл APK — если приложение недоступно в Google Play, его можно скачать через официальный сайт.
Разрешите установку из неизвестных источников — зайдите в Настройки > Безопасность и активируйте соответствующую опцию.
Запустите установку и следуйте инструкциям.
Для iOS:
Скачайте приложение из App Store — большинство сервисов доступны через официальный магазин.
Используйте TestFlight или корпоративный сертификат — если приложение не опубликовано в App Store.
Разрешите установку — в настройках iPhone перейдите в раздел VPN и управление устройствами и подтвердите доверие к разработчику.
Если вас интересует конкретное приложение, проверьте его официальный сайт или магазин приложений. Но помните о безопасности: скачивайте ПО только из проверенных источников, чтобы избежать мошенничества.
Хотите узнать больше? Читайте дополнительные инструкции на сайте по ссылке ниже.install-champion-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
подарочные карты онлайн https://kupit-gift-kartu.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Discover Montenegro holidays https://www.weather-webcam-in-montenegro.com/igalo crystal clear sea, picturesque bays, mountain landscapes and ancient fortresses. The perfect destination for those looking for a combination of nature, history and relaxation. Detailed guides, recommendations, photos and route ideas.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Discover Montenegro Dobra Voda Montenegro crystal clear sea, picturesque bays, mountain landscapes and ancient fortresses. The perfect destination for those looking for a combination of nature, history and relaxation. Detailed guides, recommendations, photos and route ideas.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
SPA-салон в Москве https://uslugi.yandex.ru/profile/BonSpa-3013256 предлагает массаж, пилинг, обёртывания, уход за кожей, антистресс-программы и релакс-процедуры. Работают сертифицированные специалисты, используется премиум-косметика. Уютная атмосфера, индивидуальный подход и удобное расположение в городе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
tournaments-casino.ru
Турниры в онлайн-казино 2025: как участвовать с мобильного телефона
В 2025 году онлайн-казино предлагают множество захватывающих турниров с крупными призами. Если вы хотите испытать удачу и побороться за ценные награды, сделать это можно прямо с мобильного устройства. На нашем сайте собрана актуальная информация о самых ожидаемых турнирах, правилах участия и стратегиях для победы.
Популярные турниры 2025 года
В этом сезоне игроков ждут:
Слоты-баттлы – соревнования на самых популярных автоматах с прогрессивными джекпотами.
Покерные серии – турниры с гарантированными призовыми фондами.
Рулетка на время – скоростные раунды с дополнительными бонусами.
Ежедневные фрироллы – бесплатные турниры с реальными денежными призами.
Как участвовать с телефона?
Выберите надежное казино – на сайте представлен рейтинг лицензированных платформ с мобильной версией.
Скачайте приложение или играйте в браузере – большинство казино адаптированы под iOS и Android.
Зарегистрируйтесь и пополните счет – некоторые турниры требуют минимального депозита.
Найдите раздел “Турниры” – там указаны условия, расписание и призовые фонды.
Начните играть и следите за таблицей лидеров – чем выше ваша позиция, тем больше шансов на победу.
Советы для успешной игры
Изучите правила каждого турнира – иногда важны не только выигрыши, но и количество ставок.
Используйте бонусы – многие казино дают бесплатные спины или кэшбэк для участников.
Следите за обновлениями – новые турниры появляются регулярно.
Хотите узнать больше? Переходите по ссылке и читайте полный обзор турниров 2025 года с подробными инструкциями по участию.tournaments-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Варианты услуг рекламное агентство Витрувий охватывают digital, офлайн-рекламу, брендинг, PR и SMM. Работаем по всей России и с зарубежными проектами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Уникальную природу покажет Калининград коса Куршская экскурсия длительностью 8 часов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ищите место для отдыха? иордания экскурсии Мы предлагаем увлекательные экскурсии по Иордании, комфортный отдых и маршруты по главным достопримечательностям Иордании. Не знаете, что посмотреть в Иордании? Начните с Петры, Вади Рам и Мёртвого моря!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Tech-Innovationen wird auf Vielseitig Blog in interessanter Form erklärt.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
frispiny-casino-registration.ru
На этом сайте вы найдете полный обзор фриспинов, предоставляемых онлайн казино при регистрации. Мы собрали актуальную информацию о самых щедрых предложениях, доступных новым игрокам. Вы узнаете, какие казино предлагают наибольшее количество бесплатных вращений, на каких слотах их можно использовать, и какие условия необходимо выполнить для вывода выигрышей. Подробные обзоры включают информацию о вейджерах, сроках действия фриспинов и других важных нюансах, которые помогут вам максимально выгодно воспользоваться этими бонусами. Мы поможем вам выбрать лучшее предложение и начать игру в онлайн казино с минимальными рисками и максимальными шансами на выигрыш. Сайт регулярно обновляется, чтобы вы всегда были в курсе самых свежих и выгодных акций.
frispiny-casino-registration.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
frispiny-casino.ru
На сайте, специализирующемся на обзорах онлайн-казино, вы найдете детальную информацию о предложениях фриспинов, предоставляемых при регистрации. Здесь собраны актуальные данные о самых выгодных и привлекательных акциях от различных игровых платформ. Вы узнаете, какие казино предлагают наибольшее количество бесплатных вращений, на каких слотах их можно использовать, и каковы условия их отыгрыша. Благодаря подробным обзорам, вы сможете сравнить различные предложения фриспинов и выбрать те, которые наилучшим образом соответствуют вашим потребностям и предпочтениям, чтобы начать игру с максимальной выгодой и возможностью сорвать крупный выигрыш без риска для собственных средств.
frispiny-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
official-zooma-casino.ru
На сайте, посвященном обзору официального сайта Zooma Casino, представлен исчерпывающий анализ платформы, призванный помочь игрокам принять обоснованное решение. Здесь вы найдете детальный разбор интерфейса и удобства использования, обзор доступных игр и их поставщиков, а также информацию о бонусной программе и условиях ее получения. Особое внимание уделено вопросам безопасности и лицензирования, чтобы убедиться в надежности и честности казино. Кроме того, в обзоре представлены данные о скорости выплат, доступных платежных методах и работе службы поддержки, что позволит вам составить полное представление о Zooma Casino и оценить его соответствие вашим требованиям и предпочтениям. Отзывы реальных пользователей помогут сформировать более объективное мнение и избежать возможных неприятных сюрпризов.
official-zooma-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The popular service dream girlfriend offers to create an AI girl who understands you, can hold a conversation and even flirt. Ideal for those who are looking for emotions in a digital format.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
chestnye-casino.ru
На сайте, посвященном обзорам онлайн казино, вы найдете независимую оценку и рейтинг самых надежных игровых платформ. Здесь представлены только проверенные и лицензированные казино, прошедшие тщательную проверку экспертов. Вы узнаете о преимуществах и недостатках каждого заведения, получите информацию о бонусах, игровых автоматах, методах оплаты и качестве службы поддержки. Сайт поможет вам сделать осознанный выбор, чтобы играть в слоты на деньги в безопасной и честной среде, минимизируя риски и получая максимум удовольствия от игры. Кроме того, ресурс содержит полезные советы и стратегии, которые помогут вам повысить свои шансы на выигрыш и сделать процесс игры еще более увлекательным. Регулярное обновление обзоров и добавление новых казино позволит вам всегда быть в курсе актуальных предложений и выбрать именно то казино, которое подходит вашим потребностям и предпочтениям.
chestnye-casino.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
видеостена купить цена https://videostena-1.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
светодиодный экран цена https://svetodiodnye-led-ekrany.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
грузчики для квартирного переезда грузчики дешево
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
квартирный переезд заказать грузоперевозки услуги грузчиков
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
переезд квартиры стоимость грузчики услуги
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Купить натуральный камень дагестанский камень для фасада в Краснодаре и Краснодарском крае по оптовой цене. Каталог с расценками, размеры и монтаж дагестанской плитки из ракушечника, песчаника, травертина, известняка для отделки фасада и цоколя в Краснодаре от производителя.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
It’s hard to find experienced people for this topic, however, you seem like you
know what you’re talking about! Thanks https://Yourua.info/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Great article. https://Bandurart.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Профессиональное агентство рекламное агентство Витрувий: разработка рекламы, брендинг, digital-маркетинг, наружка и SMM. Комплексное продвижение для бизнеса любого масштаба.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The best online slots rise of olympus in one place: classics, new releases, jackpots and themed machines. Play without registration, test the demo or make real bets with bonuses.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Экскурсия на Куршскую косу https://kurshskaya-kosa-ekskursii.ru/ с гидом-историком и рассказом о древних куршах
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
chempion-casino-official.ru
На сайте, посвященном обзору официального сайта Казино Чемпион, вы найдете всестороннюю информацию об этой популярной игровой платформе. Здесь детально разобраны ключевые аспекты казино, начиная от интерфейса и удобства навигации, и заканчивая разнообразием игрового ассортимента и щедростью бонусной программы. В обзоре представлена информация о лицензировании казино, гарантиях безопасности, скорости выплат и качестве работы службы поддержки. Благодаря этому обзору, вы сможете составить полное представление о Казино Чемпион, оценить его преимущества и недостатки, и принять взвешенное решение, стоит ли здесь регистрироваться и играть на реальные деньги. Кроме того, на сайте представлены отзывы реальных игроков, которые помогут вам получить более объективную картину о работе казино и избежать возможных разочарований.
chempion-casino-official.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Узнайте актуальную экскурсия Куршская коса из Калининграда цена на официальном сайте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Полный гид по недвижимости https://all2realt.com.ua как выбрать, купить, продать или арендовать квартиру, дом или коммерческий объект. Обзоры, цены, тенденции рынка и юридические тонкости.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал про животных https://zoobonus.com.ua интересные статьи о питомцах, дикой природе, уходе, воспитании и поведении. Всё для тех, кто любит животных и хочет узнать о них больше.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о машинах https://xiwet.com от новостей и технологий до экспертных статей и автомобильной аналитики. Узнайте всё о текущих трендах на рынке и новинках автопрома.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о машинах https://shpik.info от новостей и технологий до экспертных статей и автомобильной аналитики. Узнайте всё о текущих трендах на рынке и новинках автопрома.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://zhenskiy.kyiv.ua которые ценят себя, любят жить ярко и стремятся к гармонии. Будь в курсе моды, заботься о себе и черпай вдохновение каждый день.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
The convenient Zabljak booking service will help you find the perfect hotel for car travelers and active holiday lovers. A wide range of accommodation: from cozy guest houses to modern hotels with parking, Wi-Fi and breakfast. Book in advance and relax in comfort in the heart of Montenegro!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт про авто https://rusigra.org обзоры машин, автоновости, тест-драйвы, сравнения моделей, советы водителям и полезные статьи. Всё, что нужно автолюбителям — на одном ресурсе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Журнал для женщин https://saralelakarat.com мода, красота, здоровье, психология, семья и вдохновение. Актуальные статьи, советы экспертов и интересные темы для женщин всех возрастов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://ruforums.net с разнообразными рубриками — от моды и макияжа до материнства и путешествий. Открывайте каждый день с новыми идеями и полезным контентом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный женский журнал https://reyesmusicandevents.com стиль, уход, карьера, семья, рецепты и саморазвитие. Читайте свежие материалы каждый день — будь в тренде и в гармонии с собой.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный авто портал https://quebradadelospozos.com свежие новости, каталог машин, рейтинг моделей, видеообзоры и полезные статьи. Помощь при покупке, советы по обслуживанию и анализ рынка.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
читайте на автомобильном https://proauto.kyiv.ua портале: тест-драйвы, сравнения, автоаналитика, обзоры технологий и новинки автопрома. Только актуальные материалы и честные мнения.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-медицинский портал https://novamed.com.ua справочник болезней, симптомы, анализы, лекарства, консультации специалистов и актуальные новости здравоохранения. Всё о здоровье — в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал о здоровье и медицине https://pravovakrayina.org.ua узнайте больше о своём организме, симптомах, лечении и профилактике. Удобный поиск, рекомендации врачей, база клиник и аптек.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Актуальные новости Украины https://newsportal.kyiv.ua и мира сегодня: главные события, мнения экспертов, интервью, прогнозы. Оставайтесь в курсе с лентой, которая обновляется 24/7.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Главные новости Украины https://novosti24.kyiv.ua и мира — честно, быстро и понятно. События, которые формируют завтрашний день, в одной ленте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт для женщин https://miymalyuk.com.ua мода, красота, здоровье, отношения, карьера, семья и вдохновение. Актуальные статьи, советы и поддержка для современной женщины каждый день
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Авто сайт с обзорами https://microbus.net.ua новостями, тест-драйвами, каталогом моделей, советами по выбору и эксплуатации автомобилей. Всё, что нужно автолюбителю — в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
best clock radio review best radio alarm clock
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Новостной портал https://mediashare.com.ua с актуальной информацией из Украины, мира, политики, экономики, технологий, культуры и общества. Только проверенные источники и объективные материалы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://mcms-bags.com о красоте, моде, психологии, отношениях и стиле жизни. Актуальные статьи, советы экспертов, вдохновение и всё, что важно для современной женщины.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сайт для деловых людей https://manorsgroup.com.ua актуальные материалы о финансах, инвестициях, рынке недвижимости и управлении капиталом. Аналитика, обзоры, экспертные мнения и полезные инструменты.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Главные новости https://lentanews.kyiv.ua из Украины и со всего мира — ежедневно и без искажений. Всё, что важно знать: внутренняя политика, экономика, международные события и прогнозы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-портал для современных https://madrasa.com.ua женщин. Всё, что волнует и вдохновляет: от красоты и моды до жизненного баланса, мотивации и личностного роста. Будь собой — с нами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Клуб для беременных https://mam.ck.ua и молодых мам: питание, подготовка к родам, уход за малышом, послеродовое восстановление. Полезная информация, консультации и поддержка в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал для женщин https://maleportal.kyiv.ua мода, красота, здоровье, отношения, карьера, семья и вдохновение. Актуальные темы, полезные советы и поддержка для каждой женщины — всё в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Актуальные новости Украины https://lenta.kyiv.ua и мира на одном сайте. Подборка ключевых событий, факты, интервью, мнения и видео. Честно, быстро и без фейков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный портал https://lady.kyiv.ua для женщин: мода, уход, любовь, дети, стиль жизни и вдохновение. Полезный контент, тренды и темы, близкие каждой.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Модный журнал онлайн https://icz.com.ua одежда, аксессуары, макияж, прически, уличный стиль и haute couture. Следите за последними тенденциями и читайте советы экспертов индустрии.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Свежие новости Украины https://fraza.kyiv.ua и мира — политика, экономика, общество, культура, технологии. Главные события дня, оперативные обновления и аналитика от экспертов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный женский https://happylady.kyiv.ua сайт с ежедневными обновлениями: советы по стилю, уходу, семье и психологии. Всё, что волнует и вдохновляет женщин сегодня — в одном месте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал про авто https://impactspreadsms.com новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, советы, сравнение моделей и актуальные тенденции в мире автомобилей. Всё для автолюбителей и профессионалов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Портал для женщин https://gracefulwoman.kyiv.ua которые ценят красоту жизни. Практичные советы, душевные статьи и поддержка — о том, как быть счастливой, уверенной и гармоничной каждый день.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-портал про автомобили https://impactspreadsms.com с каталогом моделей, тестами, аналитикой, ценами и отзывами. Удобный поиск и полезные материалы — для тех, кто выбирает с умом.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Автоперевозки из Китая https://sebezh.borda.ru/?1-13-0-00003000-000-0-0-1744618798 доставка грузов по РФ и странам СНГ. Сборные и индивидуальные партии, оформление, отслеживание и страхование. Быстро, надёжно, под ключ.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
need a move? toronto to calgary movers turnkey: packing, loading, transport, insurance and support. Without stress and with a guarantee of the safety of your property.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Zelite li se odmoriti? http://www.booking-zabljak.com/ Rezervirajte udoban hotel u centru ili u podnozju planina. Odlican izbor za skijanje i ljetovanje. Jamstvo rezervacije i stvarne recenzije.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Need real estate? http://www.luxury-property-montenegro.com villas, houses and apartments in Budva, Kotor, Tivat and on the coast. Profitable investment, sea view, safety and comfort in the south of Europe.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Продуктивна робота та захист техніки забезпечуються сучасними аксесуарами для ноутбуків ukrbeautystyle.com.ua. Вони підвищують комфорт використання та подовжують термін служби пристроїв.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Читайте автомобильный сайт https://gormost.info онлайн — тесты, обзоры, советы, автоистории и материалы о современных технологиях. Всё для тех, кто любит машины и скорость.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский сайт о красоте https://female.kyiv.ua моде, здоровье, отношениях и саморазвитии. Полезные статьи, советы экспертов, вдохновение и поддержка — всё для гармоничной и уверенной жизни.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный женский сайт https://femalebeauty.kyiv.ua мода, психология, семья, карьера, рецепты и лайфхаки. Ежедневно — новые материалы, рекомендации и интересные темы для каждой женщины.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Автомобильный сайт https://fundacionlogros.org с ежедневными новостями, обзорами новинок, аналитикой, тест-драйвами и репортажами из мира авто. Следите за трендами и будьте в курсе всего важного.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Автомобильный журнал https://eurasiamobilechallenge.com новости автоиндустрии, тест-драйвы, обзоры моделей, советы водителям и экспертов. Всё о мире автомобилей в удобном онлайн-формате.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Родительский портал https://babyrost.com.ua от беременности до подросткового возраста. Статьи, лайфхаки, рекомендации экспертов, досуг с детьми и ответы на важные вопросы для мам и пап.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Автомобильный сайт https://billiard-sport.com.ua с обзорами, тест-драйвами, автоновостями и каталогом машин. Всё о выборе, покупке, обслуживании и эксплуатации авто — удобно и доступно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Семейный портал https://cgz.sumy.ua для родителей и детей: развитие, образование, здоровье, детские товары, досуг и психология. Актуальные материалы, экспертиза и поддержка на всех этапах взросления.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский портал https://elegantwoman.kyiv.ua о красоте, моде, здоровье, отношениях и вдохновении. Полезные статьи, советы экспертов, лайфхаки и свежие тренды — всё для современной женщины.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-портал для женщин https://fancywoman.kyiv.ua которые ценят себя и стремятся к лучшему. Всё о внутренней гармонии, внешнем блеске и жизненном балансе — будь в центре женского мира.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Авто журнал онлайн https://comparecarinsurancerfgj.org свежие новости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, советы и рейтинг автомобилей. Всё о мире авто в одном месте, доступно с любого устройства.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Современный авто журнал https://ecotech-energy.com в онлайн-формате для тех, кто хочет быть в курсе автомобильных трендов. Новости, тесты, обзоры и аналитика — всегда под рукой.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Авто журнал онлайн https://clothes-outletstore.com всё о мире автомобилей: новости, тест-драйвы, обзоры, советы, новинки автопрома и технологии. Читайте с любого устройства — всегда в курсе автоиндустрии.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Автомобильный портал https://avto-limo.zt.ua для тех, кто за рулём: автообзоры, полезные советы, новости индустрии и подбор авто. Удобный поиск, свежая информация и всё, что нужно автолюбителю.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://chernogolovka.net всё о жизни, любви, красоте, детях, финансах и личностном развитии. Простым языком о важном — полезно, интересно и по делу.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
https://www.prozdor.ru/zabolevaniya/mir-zvukov-prostye-shagi-k-luchshemu-vospriyatiju-rechi-i-muzyki/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Женский журнал https://asprofrutsc.org о стиле, красоте, психологии, отношениях и саморазвитии. Актуальные статьи, советы экспертов, тренды и вдохновение — всё для современной женщины.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Свежие новости https://actualnews.kyiv.ua Украины и мира онлайн: события, аналитика, интервью и факты. Будьте в курсе главного — обновления 24/7, объективная подача и лента новостей в реальном времени.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Автопортал для водителей https://addinfo.com.ua и автолюбителей: свежие авто новости, сравнения моделей, рейтинги, советы по выбору и обслуживанию автомобилей. Полезная информация каждый день.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Football genius luka-modric.com/ Luka Modric – from humble beginnings in Zagreb to a world-class star. His path inspires, his play amazes. The story of a great master in detail.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
King of the ring https://roy-jones.com Roy Jones is a fighter with a unique style and lightning-fast reactions. His career includes dozens of titles, spectacular knockouts and a cult status in the boxing world.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Professional fighter Rafael Fiziev http://rafael-fiziev.com is a UFC star known for his explosive technique and spectacular fights. A lightweight fighter with a powerful punch and a strong Muay Thai base.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-казино JoyCasino http://thejoycasino-ru.com яркий дизайн, популярные слоты, live-игры и щедрые бонусы. Простой вход, быстрые выплаты и надёжная поддержка. Играйте с комфортом и без лишних рисков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
эвакуатор спб дешево и быстро эвакуатор дешево
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
прокат авто недорого санкт петербург аренда машин спб без водителя на неделю
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сервис аренды авто авто напрокат
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Врачи подбирают индивидуальное решение — от одиночного импланта до полного протезирования на имплантах https://www.vevioz.com/read-blog/327658
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Полезная информация skypestudy4you.ru свежие материалы и удобная навигация — всё, что нужно для комфортного пользования сайтом. Заходите, изучайте разделы и находите то, что действительно важно для вас.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
аренда машины в москве на месяц дешево москва взять легковой автомобиль в аренду
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
аренда машины в сочи аренда машин в сочи дешево
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ВГУ им. П. М. Машерова https://vsu.by официальный сайт, факультеты, направления подготовки, приёмная кампания. Узнайте о поступлении, обучении и возможностях для студентов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
kubet casino hỗ trợ người chơi mới bằng hệ thống hướng dẫn chi tiết, chơi thử miễn phí và CSKH 24/7 qua nhiều kênh.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
188bet là nhà cái quốc tế uy tín được cấp phép bởi Isle of Man, chuyên cung cấp dịch vụ cá cược thể thao, casino trực tuyến và nhiều trò chơi đổi thưởng hấp dẫn.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Витебский университет П.М.Машерова https://vsu.by образовательный центр. Вуз является ведущим образовательным, научным и культурным центром Витебской области.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Где купить https://kupit-cheki24.com чеки в Москве? У нас — быстрое оформление, оригинальные документы, курьерская доставка. Чеки для отчётов, подтверждения командировок и компенсаций.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ищешь лучшие раскидки raskidki granat cs2 CS2 – Смоки, молотовы и флешки для всех карт — изучи тактики, прокачай игру и удиви соперников точными гранатами. Подборка эффективных раскидок!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужен надёжный хостинг? недорогой vps хостинг для сайтов, приложений и бизнес-задач. Гибкая настройка, SSD-накопители, стабильная работа 24/7. Выберите тариф под свои задачи и начните сегодня.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-казино Aura aura-casino-app.ru/ лицензия, бонус без депозита, фриспины за регистрацию и моментальный вывод. Всё о казино Aura в одном обзоре — играйте безопасно и с выгодой.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Calibry Casino https://calibri-casino-bonus.ru/ лицензированное онлайн-казино с бонусами, быстрым выводом и большим выбором игр. В обзоре: регистрация, акции, безопасность, отзывы игроков и советы новичкам.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обзор Aura Casino https://aura-casino-play.ru всё о щедрых бонусах, фриспинах, кэшбэке и акциях. Расскажем, как зарегистрироваться, начать игру и получить максимум от каждого депозита.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Aura Casino aura-casino-online.ru безопасная платформа с лицензией, SSL-защитой и проверенной репутацией. В обзоре: честность выплат, работа службы поддержки и реальные отзывы игроков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Играйте в казино Shot shot casino play десятки провайдеров, ежедневные турниры и кэшбэк. В обзоре: лучшие слоты, лайв-игры, бонусные программы и преимущества платформы.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обзор онлайн-казино Calibry https://calibri-casino-app.ru/ как получить бонус без депозита, запустить любимые слоты и вывести выигрыш. Надёжная площадка с лицензией и прозрачными условиями игры.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-казино Calibry calibri-casino-play.ru/ бонусы без депозита, быстрые выводы и лицензированный софт. В обзоре: как начать играть, получить фриспины, использовать акции и избежать рисков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Начните с Aura Casino aura-casino-bonus удобное онлайн-казино с простым интерфейсом, стартовыми бонусами и быстрой регистрацией. Рассказываем, как получить фриспины и не потеряться в слотах.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-казино Aura http://aura-casino-apk.ru лицензия, быстрые выплаты, слоты от топ-провайдеров и щедрые бонусы. Подробный обзор платформы: интерфейс, регистрация, акции, безопасность и отзывы игроков.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужен бесплатный аккаунт? аккаунты гта 5 бесплатно Узнайте, где можно получить рабочие логины с играми, как не попасть на фейк и на что обратить внимание при использовании таких аккаунтов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-казино Calibry https://calibri-casino-online.ru новое игровое пространство с лицензией, щедрыми бонусами и широким выбором слотов. Читайте обзор: особенности платформы, условия игры, отзывы и выплаты.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Shot Casino shot-casino-online.ru новое онлайн-казино с лицензией, защитой данных и большим выбором игр. В обзоре: безопасность, отзывы игроков, бонусы и выплаты. Надёжная площадка для вашего азарта.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обзор онлайн-казино Shot shot casino app плюсы и минусы, проверка лицензии, акции и фриспины. Рассказываем, стоит ли играть, как получить бонусы и выводить выигрыши без проблем.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нужно создание или разработка веб студия: адаптивный дизайн, SEO-продвижение, техническая поддержка. Эффективное ключевая фраза для вашего бизнеса — привлечение клиентов и рост прибыли.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Онлайн-казино Shot shot-casino-apk.ru предлагает щедрые бонусы, турнирные события и топовые слоты. Узнайте об условиях игры, уровне доверия, лицензии и особенностях платформы в нашем свежем обзоре.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обзор AWP Asiimov get-skin-csgo футуристичный скин с дерзким дизайном. Рассказываем о редкости, ценах, вариантах износа и том, почему Asiimov стал иконой среди скинов в CS:GO.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обзор AK-47 Redline csgo get skin лаконичный дизайн, спортивный стиль и привлекательная цена. Почему этот скин так любят игроки и с чем он лучше всего сочетается — читайте у нас.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AWP Dragon Lore https://get-skins-csgo.ru легендарный скин с изображением дракона, символ элиты в CS:GO. Узнайте о его происхождении, редкости, стоимости и почему он стал мечтой каждого коллекционера.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Легендарная AWP Medusa http://case-simulator-cs2.ru скин с таинственным дизайном, вдохновлённым древнегреческой мифологией. Высокая редкость, художественная детализация и престиж на каждом сервере.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
StatTrak M4A1-S cs2-get-skin скин с возможностью отслеживания фрагов прямо на корпусе оружия. Узнайте, какие модели доступны, чем отличаются, и какие из них ценятся выше всего на рынке CS:GO.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перчатки спецназа https://case-simulator-cs.ru тактический скин в CS:GO с брутальным дизайном и премиальной редкостью. Узнайте об их разновидностях, цене, коллекционной ценности и лучших сочетаниях с другими скинами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Скин M4A4 Howl https://cs2-get-skins.ru один из самых дорогих и загадочных в CS:GO. Запрещённый артефакт с историей. Рассказываем о его происхождении, внешнем виде и значении в мире скинов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AK-47 Fire Serpent https://get-skins-cs.ru/ легендарный скин из коллекции Operation Bravo. Яркий рисунок огненного змея, высокая редкость и коллекционная ценность. Идеальный выбор для истинных фанатов CS:GO.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Скин AWP Graphite csgo-case-simulator из CS:GO — чёрный глянец, премиальный стиль и высокая редкость. Укрась арсенал культовой снайперской винтовкой и выделяйся на сервере с первого выстрела.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Недвижимость в Бяла https://byalahome.ru апартаменты, квартиры и дома у моря в Болгарии. Лучшие предложения на побережье Черного моря — для жизни, отдыха или инвестиций. Успейте купить по выгодной цене!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Быстровозводимые здания https://akkord-stroy.ru из металлоконструкций — это скорость, надёжность и экономия. Рассказываем в статьях, как построить объект под ключ: от проектирования до сдачи в эксплуатацию.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Нож-бабочка Doppler cs-get-skin.ru стильное и эффектное оружие в стиле CS:GO. Яркий металлический блеск, плавный механизм, удобство в флиппинге и коллекционировании. Подходит для тренировок, трюков и подарка фанатам игр.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Научитесь вязать крючком crochet-patterns с нуля или улучшите навыки с нашими подробными мастер-классами. Фото- и видеоуроки, понятные инструкции, схемы для одежды, игрушек и интерьера. Вдохновляйтесь, творите, вяжите в своё удовольствие! Вязание крючком — доступно, красиво, уютно.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
куплю кассовые чеки купить чеки
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Витебский госуниверситет университет https://vsu.by/inostrannym-abiturientam/spetsialnosti.html П.М.Машерова – образовательный центр. Вуз является ведущим образовательным, научным и культурным центром Витебской области. ВГУ осуществляет подготовку: химия, биология, история, физика, программирование, педагогика, психология, математика.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Технологии свободы: https://marzban.click/ надёжный инструмент для приватности, скорости и доступа к любым сайтам. Быстро, безопасно, удобно — настрой за 5 минут.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Оснащение под ключ: продажа медицинского оборудования с сертификацией и полной документацией. В наличии и под заказ. Профессиональное оснащение медицинских кабинетов.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Используй нвдежный amneziavpn для обхода блокировок, сохранности личных данных и полной свободы онлайн. Всё включено — просто подключайся.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
ai porn chat free ai porn
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
M4A1-S Knight cs-get-skins.ru редкий скин в CS. Престиж, стиль, легендарное оружие. Продажа по выгодной цене, моментальная доставка, безопасная сделка.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Desert Eagle Blaze http://csgo-get-skins.ru пламя в каждой пуле. Легенда CS:GO. Продажа, обмен, проверка скина. Успей забрать по лучшей цене на рынке.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
thc joint shop in prague hemp in prague
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Запишитесь на семинары для косметологов и прокачайте свою профессию. Современные методики, опытные преподаватели, доступная цена и максимальная польза для практики.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Быстрые займы через интернет оформить займ
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Займы онлайн на карту без отказа без проверки займы онлайн без проверок
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
AK-47 Case Hardened get-skins-cs2.ru/ классика CS2 с уникальным закалённым узором. Каждый скин отличается: от редких фулл-блю до золотых комбинаций. Настоящая находка для коллекционера и трейдера.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
M4A4 Emperor get-skin-cs эффектный скин в стиле королевской власти. Яркий синий фон, золотые детали и образ императора делают этот скин настоящим украшением инвентаря в CS2.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
StatTrak AK-47 Vulcan get skin cs2 мощный стиль и счётчик убийств в одном скине. Агрессивный дизайн, сине-чёрная цветовая гамма и высокая ценность на рынке CS2. Идеальный выбор для бойца с характером!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Glock-18 Fade case-simulator-csgo один из самых ярких и редких скинов для стартового пистолета в CS2. Плавный градиент, премиум-качество и высокий спрос среди коллекционеров.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Хочешь Dragon Lore cs case simulator Открывай кейс прямо сейчас — шанс на легенду CS2 может стать реальностью. Лучшие скины ждут тебя, рискни и получи топовый дроп!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Премиум скины CS2 https://cs2-case-simulator.ru/ топовые облики для AWP, AK-47, M4, ножей и перчаток. Яркий стиль, редкие коллекции, эксклюзивные дизайны. Укрась свою игру и выделяйся в каждой катке!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Чеки для отчётности https://t.me/kupitchekiru в Москве — быстро, конфиденциально и с гарантией. Подтверждающие документы для отчёта, бухгалтерии, авансовых отчётов. Оперативная подготовка и доставка.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Сантехник Юго-Восточный https://santekhnik-moskva.blogspot.com/p/south-eastern-administrative-okrug-of.html административный округ Москвы (ЮВАО). В состав Юго-Восточного административного округа входят районы: Выхино-Жулебино, Капотня, Кузьминки, Лефортово, Люблино, Марьино, Некрасовка, Нижегородский район, Печатники, Рязанский район, Текстильщики, Южнопортовый район.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mikrosluchatko bluetooth mikrosluchatko
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Ищете безопасный VPN? Попробуйте https://amneziavpn.org — open-source решение для анонимности и свободы в интернете. Полный контроль над соединением и личными данными.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
mikrosluchatka mikro sluchatko
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Обеспечь анонимность с https://amneziavpn.xyz. Защита трафика, собственный сервер, простая установка и отсутствие слежки. Отличный выбор для тех, кто ценит свободу в интернете.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
микронаушник аренда микронаушник арендовать
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
магнитный микронаушник микронаушник купить
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
свежие новости краснодара новости краснодара сегодня свежие
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Мамоновское кладбище https://mamonovskoe.ru/ справочная информация, адрес, график работы, участки, ритуальные услуги и памятники. Всё, что нужно знать, собрано на одном сайте.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Быстрый и удобный фундаментные работы калькулятор рассчитайте стоимость и объем работ за пару минут. Онлайн-калькулятор поможет спланировать бюджет, сравнить варианты и избежать лишних затрат.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Смотри топ скинов CS2 http://case-cs2-open.ru самые красивые, редкие и желанные облики для оружия. Стиль, эффект и внимание на сервере гарантированы. Обновляем коллекцию каждый день!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Иммортал-дроп CS2 http://open-case-csgo.ru только для избранных. Легендарные скины, высокая ценность, редкие флоаты и престиж на сервере. Пополни свою коллекцию настоящими шедеврами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Смотри топ скинов CS2 cs2-open-case самые красивые, редкие и желанные облики для оружия. Стиль, эффект и внимание на сервере гарантированы. Обновляем коллекцию каждый день!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Топовые скины CS2 csgo-open-case.ru/ от легендарных ножей до эксклюзивных обложек на AWP. Красота, стиль, престиж. Оцени крутой дроп и подбери скин, который подходит именно тебе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Топовые скины CS2 https://open-case-cs.ru от легендарных ножей до эксклюзивных обложек на AWP. Красота, стиль, престиж. Оцени крутой дроп и подбери скин, который подходит именно тебе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лучшие скины CS2 http://open-csgo-case.ru яркие, редкие, премиальные. Собери коллекцию, прокачай инвентарь и покажи всем свой вкус. Обзор самых крутых скинов с актуальными ценами и рейтингами.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Премиум скины для CS2 case-cs-open.ru/ выделяйся в каждом раунде! Редкое оружие, эксклюзивные коллекции, эффектные раскраски и ножи. Только топовые предметы с мгновенной доставкой в Steam.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Топ-дроп CS2 open case cs2 уже здесь! Самые редкие скины, ножи и эксклюзивы, которые действительно выпадают. Лучшие кейсы, обновления коллекций и советы для удачного открытия.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Имморталы CS2 cs-open-case редкие скины, которые выделят тебя в матче. Торгуй, покупай, продавай топовые предметы с моментальной доставкой в инвентарь. Лучшие цены и безопасные сделки!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
перепродажа аккаунтов https://marketpleysakkauntov.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
продать аккаунт http://prodaja-akkauntov.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить аккаунт с прокачкой https://marketpleys-akkauntov-socsetei.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Calibry Casino http://calibri-casino-app.ru современное онлайн-казино с лицензией, щедрой бонусной системой и широким выбором игр. Участвуй в акциях, получай кэшбэк и выигрывай реальные деньги!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё о кладбищах Видного http://bitcevskoe.ru Битцевское, Дрожжинское, Спасское, Жабкинское. Официальная информация, участки, услуги, порядок оформления документов, схема проезда.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доска бесплатных объявлений https://salexy.kz Казахстана: авто, недвижимость, техника, услуги, работа и многое другое. Тысячи свежих объявлений каждый день — легко найти и разместить!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Офіційний сайт 1win https://visitkyiv.com.ua спортивні ставки, онлайн-казино, покер, live-ігри, швидкі висновки. Бонуси новим гравцям, мобільний додаток, цілодобова підтримка.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Kvalitni nabytek v Praze http://www.ruma.cz stylove reseni pro domacnost i kancelar. Satni skrine, sedaci soupravy, kuchyne, postele od proverenych vyrobcu. Rozvoz po meste a montaz na klic.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Всё о Казахстане https://tr-kazakhstan.kz история, культура, города, традиции, природа и достопримечательности. Полезная информация для туристов, жителей и тех, кто хочет узнать страну ближе.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Горкинское кладбище https://gorkinskoe.ru одно из старейших в Видном. Подробная информация: адрес, как доехать, порядок захоронений, наличие участков, памятники, услуги по уходу.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
With years of experience, we provide high-end eskort https://eskortebi.link/ services across major Georgian cities. Your satisfaction is our priority.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
суши на дом барнаул заказ суши барнаул
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
хостинг для сайта купить https://uavps.net
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
продать аккаунт pokupka-akkauntov.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
маркетплейс аккаунтов маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
гарантия при продаже аккаунтов продать аккаунт
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
площадка для продажи аккаунтов ploshadka-dlya-prodazhi-akkauntov.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
купить аккаунт с прокачкой magazin-accauntov.ru/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
маркетплейс для реселлеров birzha-accauntov.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
продать аккаунт https://marketpleys-akkauntov.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кладбища Видного https://bulatnikovskoe.ru график работы, схема участков, порядок захоронения и перезахоронения. Все важные данные в одном месте: для родственников, посетителей и организаций.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Самые новые анекдоты https://www.anekdotovmir.ru — коротко, метко и смешно! Подборка актуального юмора: от жизненных до политических. Заходи за порцией хорошего настроения!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Доска объявлений https://estul.ru/blog по всей России: продавай и покупай товары, заказывай и предлагай услуги. Быстрое размещение, удобный поиск, реальные предложения. Каждый после регистрации получает на баланс аккаунта 100? для возможности бесплатного размещения ваших объявлений
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Бесплатные Steam аккаунты t.me/GGZoneSteam/ с играми и бонусами. Проверенные логины и пароли, ежедневное обновление, удобный поиск. Забирай свой шанс на крутой аккаунт без лишних действий!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Добро пожаловать в 1win 1win onedivision ru азарт, спорт и выигрыши рядом! Ставь на матчи, играй в казино, участвуй в турнирах и получай крутые бонусы. Удобный интерфейс, быстрая регистрация и выплаты.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Find the Perfect Clock http://clocks-top.com for Any Space! Looking for high-quality clocks? At Top Clocks, we offer a wide selection, from alarm clocks to wall clocks, mantel clocks, and more. Whether you prefer modern, vintage, or smart clocks, we have the best options to enhance your home. Explore our collection and find the perfect timepiece today!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Swiat emocji z 1win 1win pl Zaklady sportowe i e-sportowe, kasyno online, poker, gry wirtualne i wiele wiecej. Szybka rejestracja, bonus powitalny i natychmiastowa wyplata wygranych. 1win – wszystko, czego potrzebujesz do gry w jednym miejscu!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Официальный сайт 1win 1win kykyryza ставки на спорт, киберспорт, казино, live-игры и слоты от лучших провайдеров. Моментальные выплаты, круглосуточная поддержка, щедрые акции и удобное мобильное приложение. Делай ставки и играй в казино на 1win — быстро, безопасно и выгодно!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Аккредитованное агентство https://pravo-migranta.ru/ по аутстаффингу мигрантов и миграционному аутсорсингу. Оформление иностранных сотрудников без рисков. Бесплатная консультация и подбор решений под ваш бизнес.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Кладбище в Видном https://vidnovskoe.ru актуальные данные о захоронениях, помощь в организации похорон, услуги по благоустройству могил. Схема проезда, часы работы и контактная информация.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
neff посудомоечные ремонт мастер по ремонту стиральных машин на дому
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
I’m now noot certain where you’re getting your
info, however good topic. I needs to spend some time studying much more
or figuring out more. Thank youu for excellent information I usxed to be in search of this info for my mission. http://Boyarka-Inform.com/
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
V našem sortimentu jsou také zastoupeny střešní tašky betonové, které splňují náročné požadavky na kvalitu a estetiku. Zajišťují dlouhou životnost a minimální údržbu.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Лучшие сайты кейсов https://ggdrop.casecs2.com в CS2 – честный дроп, редкие скины и гарантии прозрачности. Сравниваем платформы, бонусы и шансы. Заходи и забирай топовые скины!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Топ сайтов кейсов CS2 https://ggdrop.cs2-case.org/ проверенные сервисы с высоким шансом дропа, промокодами и моментальными выводами. Только актуальные и безопасные платформы!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
результаты анализов вич купить результат анализа крови на вич купить
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
stacking anabolic steroids https://anabolshop.org
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
официальный сайт риобет риобет казино официальный сайт
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Планируете каникулы? купить https://camp-centr.com! Интересные программы, безопасность, забота и яркие эмоции. Бронируйте заранее — количество мест ограничено!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сео продвижение сайта дешево интернет маркетинг заказать инфулл
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
услуги сео продвижения сайта https://seoveb-marketing.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
услуга продвижение сайтов seo продвижение сайта цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Юридические услуги https://urwork.ru в Санкт-Петербурге и Москве – от консультации до защиты интересов в суде. Оперативно, надежно и с гарантией конфиденциальности.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
широкоформатная печать на заказ широкоформатная печать цены
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
dtf печать картинки dtf печать цена
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
печать на холсте спб недорого печать на холсте недорого
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
типографии печать папок уф печать на папке
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
печать бланков документов изготовление печати бланков
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Выполняем качественное проектирование итп под ключ. Энергоэффективные решения для домов, офисов, промышленных объектов. Гарантия, соблюдение СНиП и точные сроки!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Nejlepší volbou pro odolnou střechu v hlavním městě je falcovaná krytina v Praze Česká Republika. Odborná montáž minimalizuje riziko budoucích problémů.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
визитки печать спб дешево печать визиток
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Продажа путёвок https://camp-centr.com/camps/type/yazykovoy.html. Спортивные, творческие и тематические смены. Весёлый и безопасный отдых под присмотром педагогов и аниматоров. Бронируйте онлайн!
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
аккаунты маркетплейсов купить цифровой магазин аккаунтов
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
грузчики недорогие услуги грузчиков недорого
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
грузчики недорого дешево заказать грузчиков
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
услуги профессиональных грузчиков услуги грузчиков городу
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
типография спб цены сайт типографии спб
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
типография спб заказ коробок типография
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
сбербанк оценка недвижимости ocenka-zagorod.ru
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Pro každého, kdo hledá spolehlivé zastřešení, jsou ideální střešní plechové krytiny roofer.cz/plechova-stresni-krytina/ s dlouhou životností. Nabízejí vysokou pevnost a elegantní vzhled.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
iphone battery iphone 16 256gb
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Moderní plastový okapový systém nabízí skvělou odolnost a nízké náklady na údržbu. Ideální volba pro rodinné domy i chaty.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Перед тем как начать игру, стоит изучить Обзор GGBET moto-portal.com.ua. В нем подробно описаны бонусные предложения, функционал сайта и доступные способы пополнения счета.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
El cabergolina precio balkanpharmaceuticals-official.com puede cambiar según el país y la tienda. Consulta varias fuentes antes de hacer tu compra.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Aunque algunos la utilizan, la boldenona para humanos no está aprobada en todos los países para este uso.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Среди игровых партнеров стоит выделить betking slotoking betkingua.com.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Если требуется актуальная информация, можно базы хрумер скачать и протестировать их на практике.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Algunos deportistas prefieren comprar esteroides inyectables para lograr resultados más rápidos y efectivos.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
Algunas clínicas ofrecen asesoramiento sobre el anastrozol para homens en españa y su uso adecuado.
Your comment is awaiting moderation.
услуги смм
Hello there! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my site to rank for some targeted keywords but
I’m not seeing very good results. If you know of any please share.
Kudos! You can read similar blog here: Warm blankets
[…] You may also want to read: What is UX Design And Why It Is Important […]
[…] User Experience (UX) is essential. A great UX design ensures that the website is aesthetically pleasing and easy to […]